Abstract
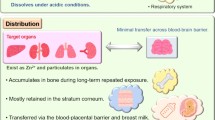
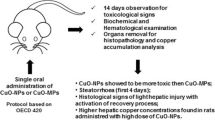
Nanometer zinc oxide (nano-ZnO) is widely used in diverse industrial and agricultural fields. Due to the extensive contact humans have with these particles, it is crucial to understand the potential effects that nano-ZnO have on human health. Currently, information related to the toxicity and mechanisms of nano-ZnO is limited. The aim of the present study was to investigate acute and cumulative toxic effects of 50-nm unmodified ZnO in mice. This investigation will seek to establish median lethal dose (LD50), a cumulative coefficient, and target organs. The acute and cumulative toxicity was investigated by Karber’s method and via a dose-increasing method, respectively. During the experiment, clinical signs, mortality, body weights, hematology, serum biochemistry, gross pathology, organ weight, and histopathology were examined. The LD50 was 5177-mg/kg·bw; the 95% confidence limits for the LD50 were 5116–5238-mg/kg·bw. It could be concluded that the liver, kidney, lung, and gastrointestinal tract were target organs for the 50-nm nano-ZnO acute oral treatment. The cumulative coefficient (K) was 1.9 which indicated that the cumulative toxicity was apparent. The results also indicated that the liver, kidney, lung, and pancrea were target organs for 50-nm nano-ZnO cumulative oral exposure and might be target organs for subchronic and chronic toxicity of oral administered 50-nm ZnO.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasalipourkabir R, Moradi H, Zarei S, Asadi S, Salehzadeh A, Ghafourikhosroshahi A, Mortazavi M, Ziamajidi N (2015) Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles on adult male Wistar rats. Food Chem Toxicol 84:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.08.019
Adamcakova-Dodd A, Stebounova LV, Kim JS, Vorrink SU, Ault AP, O’Shaughnessy PT (2014) Toxicity assessment of zinc oxide nanoparticles using sub-acute and sub-chronic murine inhalation models. Part Fibre Toxicol 11(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-11-15
Ben-Slama I, Mrad I, Rihane N, Mir LEL, Sakly M, Amara S et al (2015) Sub-acute oral toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles in male rats. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 6(3):284
Cho WS, Kang BC, Lee JK, Jeong J, Che JH, Hyeok SS et al (2013) Comparative absorption, distribution, and excretion of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles after repeated oral administration. Part Fibre Toxicol. 10(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-10-9
Colvin VL (2003) The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol 21(10):1166–1170. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt875
Du XL, Shi Z, Peng ZC, Zhao CX, Zhang YM, Wang Z et al (2017) Acetoacetate induces hepatocytes apoptosis by the ROS-mediated MAPKs pathway in ketotic cows. J Cell Physiol 232(12):3296–3308. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25773
Esmaeillou M, Moharamnejad M, Hsankhani R, Tehrani AA, Maadi H (2013) Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in healthy adult mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35(1):67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2012.11.003
Feng XL, Wu JR, Lai X, Zhang YL, Wei LM, Liu J et al (2017) Prenatal exposure to nanosized zinc oxide in rats: neurotoxicity and postnatal impaired learning and memory ability. Nanomedicine (Lond) 12(7):777–795
Ghosh M, Sinha S, Jothiramajayam M, Jana A, Nag A, Mukherjee A (2016) Cytogenoto- xicity and oxidative stress induced by zinc oxide nanoparticle in human lymphocyte cells in vitro and Swiss albino male mice in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol 97:286–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.09.025
Heim J, Felder E, Tahir MN, Kaltbeitzel A, Heinrich UR, Brochhausen C et al (2015) Genotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nano 7(19):8931–8938
Hong TK, Tripathy N, Son HJ, Ha KT, Jeong HS, Hahn YB (2013) A comprehensive in vitro and in vivo study of ZnO nanoparticles toxicity. J Mater Chem B 1(23):2985–2992. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20251h
Hou W, Westerhoff P, Posner JD (2013) Biological accumulation of engineered nanomaterials: a review of current knowledge. Environ Sci: Processes Impacts 15(1):103–122
Hussain N, Jaitley V, Florence AT (2001) Recent advances in the understanding of uptake of microparticulates across the gastrointestinal lymphatics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 50(1-2):107–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00152-1
Jacobsen NR, Stoeger T, Van Den Brule S, Saber AT, Beyerle A, Vietti G et al (2015) Acute and subacute pulmonary toxicity and mortality in mice after intratracheal instillation of ZnO nanoparticles in three laboratories. Food Chem Toxicol 85:84–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.08.008
Kaya H, Aydın F, Gürkan M, Yılmaz S, Ates M, Demir V, Arslan Z (2016) A comparative toxicity study between small and large size zinc oxide nanoparticles in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): organ pathologies, osmoregulatory responses and immunological parameters. Chemosphere 144:571–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.024
Kermanizadeh A, Jantzen K, Ward MB, Durhuus JA, Juel Rasmussen L, Loft S, Møller P (2017) Nanomaterial induced cell death in pulmonary and hepatic cells following exposure to three different metallic materials: the role of autophagy and apoptosis. Nanotoxicology 11(2):184–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2017.1279359
Ko JW, Hong ET, Lee IC, Park SH, Park J, Seong NW et al (2015) Evaluation of 2-week repeated oral dose toxicity of 100 nm zinc oxide nanoparticles in rats. Lab Anim Res 31(3):139–147. https://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2015.31.3.139
Lee CM, Jeong HJ, Yun KN, Kim DW, Sohn MH, Lee JK, Jeong J, Lim ST (2012) Optical imaging to trace near infrared fluorescent zinc oxide nanoparticles following oral exposure. Int J Nanomedicine 7:3203–3209. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S32828
Li MZ, Huang JT, Tsai YH, Mao SY, Fu CM, Lien TF (2016) Nanosize of zinc oxide and the effects on zinc digestibility, growth performances, immune response and serum parameters of weanling piglets. Anim Sci J 87(11):1379–1385. https://doi.org/10.1111/asj.12579
Mantecca P, Moschini E, Bonfanti P, Fascio U, Perelshtein I, Lipovsky A, Chirico G, Bacchetta R, del Giacco L, Colombo A, Gedanken A (2015) Toxicity evaluation of a new Zn-doped CuO nanocomposite with highly effective antibacterial properties. Toxicol Sci 146(1):16–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfv067
Mao SY, Lien TF (2017) Effects of nanosized zinc oxide and γ-polyglutamic acid on eggshell quality and serum parameters of aged laying hens. Arch Anim Nutr 71(5):373–383. https://doi.org/10.1080/1745039X.2017.1355600
Oberdorster G, Oberdorster E, Oberdorster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113(7):823–839. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7339
Osman IF, Baumgartner A, Cemeli E, Fletcher JN, Anderson D (2010) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide in HEp-2 cells. Nanomedicine (Lond) 5(8):1193–1203. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.10.52
Park HS, Shin SS, Meang EH, Hong JS, Park J, Kim SH et al (2014) A 90-day study of subchronic oral toxicity of 20 nm, negatively charged zinc oxide nanoparticles in Sprague Dawley rats. Int J Nanomedicine 9(Suppl 2):79–92
Seok SH, Cho WS, Park JS, Na Y, Jang A, Kim H, Cho Y, Kim T, You JR, Ko S, Kang BC, Lee JK, Jeong J, Che JH (2013) Rat pancreatitis produced by 13-week administration of zinc oxide nanoparticles: biopersistence of nanoparticles and possible solutions. J Appl Toxicol 33(10):1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2862
Setyawati MI, Tay CY, Leong DT (2015) Mechanistic investigation of the biological effects of SiO2, TiO2, and ZnO nanoparticles on intestinal cells. Small 11(28):3458–3468. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201403232
Shalini D, Senthilkumar S, Rajaguru P (2017) Effect of size and shape on toxicity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanomaterials in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Toxicol Mech Methods 13:1–28
Sharma V, Singh SK, Anderson D, Tobin DJ, Dhawan A (2011) Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced genotoxicity in primary human epidermal keratinocytes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11(5):3782–3788. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2011.4250
Sharma V, Singh P, Pandey AK, Dhawan A (2012) Induction of oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in mouse liver after sub-acute oral exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mutat Res/Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 745(1-2):84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.12.009
Sharma AK, Singh V, Gera R, Purohit MP, Ghosh D (2016) Zinc oxide nanoparticle induces microglial death by NADPH-oxidase-independent reactive oxygen species as well as energy depletion. Mol Neurobiol:1–14
Song Y, Li N, Gu J, Fu S, Peng Z, Zhao C, Zhang Y, Li X, Wang Z, Li X, Liu G (2016) β-Hydroxybutyrate induces bovine hepatocyte apoptosis via an ROS-p38 signaling pathway. J Dairy Sci 99(11):9184–9198. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-11219
Theodorou IG, Ruenraroengsak P, Gow A, Schwander S, Zhang JJ, Chung KF, Tetley TD, Ryan MP, Porter AE (2016) Effect of pulmonary surfactant on the dissolution, stability and uptake of zinc oxide nanowires by human respiratory epithelial cells. Nanotoxicology 10(9):1351–1362. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2016.1214762
Uski O, Torvela T, Sippula O, Karhunen T, Koponen H, Peräniemi S, Jalava P, Happo M, Jokiniemi J, Hirvonen MR, Lähde A (2017) In vitro toxicological effects of zinc containing nanoparticles with different physico-chemical properties. Toxicol in Vitro 42:105–113
Wang, B., Feng, W.Y., Wang, M., Wang, T.C., Gu,Y.Q., Zhu, M.T., 2008. Acute toxicological impact of nano- and submicro-scaled zinc oxide powder on healthy adult mice. J Nanopart Res 10, 263–276, 2, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-007-9245-3
Wu C, Wen LX, Yuan H, Peng T (2008) Toxicity of nano zinc oxide in mice. Cereal Feed Industry (China) 5:38–39
Yan G, Huang Y, Bu Q, Lv L, Deng P, Zhou J, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu Q, Cen X, Zhao Y (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles cause nephrotoxicity and kidney metabolism alterations in rats. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 47(4):577–588. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.650576
Ye DX, Ma YY, Zhao W, Cao HM, Kong JL, Xiong HM, Möhwald H (2016) ZnO-based nanoplatforms for labeling and treatment of mouse tumors without detectable toxic side effects. ACS Nano 10(4):4294–4300. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b07846
.Zhao XS, Ren X, Zhu R, Luo ZY, Ren BX (2016) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 180:56–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.09.013
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31402263 and 41301562).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Highlights
• The oral toxicity of 50 nm and other size of nano-ZnO is different.
• The oral LD50 of unmodified 50-nm ZnO was 5177-mg/kg·bw and the 95% confidence limits for the LD50 were 5116–5238-mg/kg·bw.
• Unmodified 50-nm ZnO showed apparent cumulative toxicity and the accumulation coefficient (K) was 1.9.
• The target organs for 50-nm ZnO acute oral exposure were the livers, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tracts.
• The target organs for 50-nm ZnO cumulative oral exposure were the liver, kidney, lung, and pancrea.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, T., Zhang, SH., Zhang, JL. et al. Acute and Cumulative Effects of Unmodified 50-nm Nano-ZnO on Mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 185, 124–134 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1233-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1233-6