Abstract
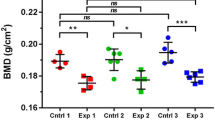
Bone deformation and fragility are common signs of skeletal fluorosis. Disorganisation of bone tissue and presence of inflammatory foci were observed after fluoride (F−) administration. Most information about F− effects on bone has been obtained in adult individuals. However, in fluorosis areas, children are a population very exposed to F− and prone to develop not only dental but also skeletal fluoroses. The aim of this work was to evaluate the bone parameters responsible for the effect of different doses of F− on fracture load of the trabecular and cortical bones using multivariate analysis in growing rats. Twenty-four 21-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups: F0, F20, F40 and F80, which received orally 0, 20, 40 or 80 μmol F−/100 g bw/day, respectively, for 30 days. After treatment, tibiae were used for measuring bone histomorphometric and connectivity parameters, bone mineral density (BMD) and bone cortical parameters. The femurs were used for biomechanical tests and bone F− content. Trabecular bone volume was significantly decreased by F−. Consistently, we observed a significant decrease in fracture load and Young’s modulus (YM) of the trabecular bone in F−-treated groups. However, cortical bone parameters were not significantly affected by F−. Moreover, there were no significant differences in cortical nor trabecular BMD. Multivariate analysis revealed a significant correlation between the trabecular fracture load and YM but not with bone volume or BMD. It is concluded that when F− is administered as a single daily dose, it produces significant decrease in trabecular bone strength by changing the elasticity of the trabecular bone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (1970) Fluoride and human health. World Health Organization, Geneva
Cook HA (1969) Fluoride and tea. Lancet 2:329
Kramer L, Osis D, Wiatrowski E, Spencer H (1974) Dietary fluoride in different areas in the United States. Am J Clin Nutr 27(6):590–594
Fina BL, Lupo M, Dri N, Lombarte M, Rigalli A (2016) Comparison of fluoride effects on germination and growth of Zea mays, Glycine max and Sorghum vulgare. J Sci Food Agric 96(11):3679–3687. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7551
Caverzasio J, Palmer G, Bonjour JP (1998) Fluoride: mode of action. Bone 22:585–589
Gazzano E, Bergandi L, Riganti C, Aldieri E, Doublier S, Costamagna C, Bosia A, Ghigo D (2010) Fluoride effects: the two faces of Janus. Curr Med Chem 17(22):2431–2441. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710791698503
Opydo-Szymaczek J, Gerreth K (2015) Developmental enamel defects of the permanent first molars and incisors and their association with dental caries in the region of Wielkopolska, Western Poland. Oral Health Prev Dent 13:461–469. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.ohpd.a33088
Everett ET (2011) Fluoride’s effects on the formation of teeth and bones, and the influence of genetics. J Dent Res 90(5):552–560. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034510384626
Moudgil A, Srivastava RN, Vasudev A, Bagga A, Gupta A (1986) Fluorosis with crippling skeletal deformities. Indian Pediatr 23(10):767–773
Posner AS, Eanes ED, Harper RA, Zipkin I (1963) X-ray diffraction analysis of the effect of fluoride on human bone apatite. Arch Oral Biol 8(4):549–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9969(63)90071-2
Grynpas MD (1990) Fluoride effects on bone crystals. J Bone Miner Res 5(S1):S169–S175. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.5650051362
Mousny M, Omelon S, Wise L, Everett ET, Dumitriu M, Holmyard DP, Banse X, Devogelaer JP, Grynpas MD (2008) Fluoride effects on bone formation and mineralization are influence by genetics. Bone 43(6):1067–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2008.07.248
Farr JN, Khosla S (2015) Skeletal changes through the lifespan-from growth to senescence. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2015.89
Golden NH, Abrams SA (2014) Optimizing bone health in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 134(4):e1229–e1243. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-2173
Teotia M, Teotia SP, Singh KP (1998) Endemic chronic fluoride toxicity and dietary calcium deficiency interaction syndromes of metabolic bone disease and deformities in India: year 2000. Indian J Pediatr 65(3):371–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02761130
Vilasrao GS, Kamble KM, Sabat RN (2014) Child fluorosis in Chhattisgarh, India: a community-based survey. Indian Pediatr 51(11):903–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-014-0525-6
De Almeida BS, Da Silva Cardoso VE, Buzalaf MAR (2007) Fluoride ingestion from toothpaste and diet in 1- to 3-year-old Brazilian children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 35(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0528.2007.00328.x
García-Camba de la Muela JM, García-hoyos F, Varela Morales M, González Sanz A (2009) Demonstration of fluoride systemic absorption secondary to toothbrusing with fluoride dentifrice in children. Rev Esp Salud Publica 83(3):415–425. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1135-57272009000300007
Guo XE (2008) What is nanomechanics of bone and why is it important? J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 8(7301):327–328. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.322.7301.1536
Willems HME, van den Heuvel EGHM, Castelein S, Buisman JK, Bronckers ALJJ, Bakker AD, Klein-Nulend J (2011) Fluoride inhibits the response of bone cells to mechanical loading. Odontology 99(2):112–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-011-0013-6
Stein ID, Granik G (1980) Human vertebral bone: relation of strength, porosity, and mineralization to fluoride content. Calcif Tissue Int 32(1):189–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02408540
Brun LR, Roma SM, Pérez F, Rigalli A (2012) Inflamación en el tejido óseo de ratas inducida por fluoruro de sodio. Actual Osteol 8:19–28
Fina BL, Lombarte M, Rigalli JP, Rigalli A (2014) Fluoride increases superoxide production and impairs the respiratory chain in ROS 17/2.8 osteoblastic cells. PLoS One 9(6):e100768. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100768
Harriss DJ, Atkinson G (2011) Update—ethical standards in sport and exercise science research. Int J Sports Med 32(10):819–821. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1237378
Olfert ED, Cross BM, McWilliam A (1993) Guide to the care and use of experimental animals. Canadian C, Ottawa
Beinlich AD, Brun LRM, Rigalli A, Puche RC (2003) Intestinal absorption of disodium monofluorophosphate in the rat as affected by concurrent administration of calcium. Arzneimittel-forsch Drug Res 53(08):584–589. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1297153
Li W, Jiang B, Cao X, Xie Y, Huang T (2017) Protective effect of lycopene on fluoride-induced ameloblasts apoptosis and dental fluorosis through oxidative stress-mediated Caspase pathways. Chem Biol Interact 261:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.11.021
Pulungan ZSA, Sofro ZM, Partadiredja G (2016) Sodium fluoride does not affect the working memory and number of pyramidal cells in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Anat Sci Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-016-0384-4
Dempster DW, Compston JE, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR, Parfitt AM (2013) Standardized nomenclature, symbols, and units for bone histomorphometry: a 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res 28(1):2–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1805
Harrar K, Hamami L (2013) An interconnectivity index for osteoporosis assessment using X-ray images. J Med Biol Eng 33(6):569–575. https://doi.org/10.5405/jmbe.1294
Brun LR, Brance ML, Lombarte M, Maher MC, di Loreto VE, Rigalli A (2015) Effects of yerba mate (IIex paraguariensis) on histomorphometry, biomechanics, and densitometry on bones in the rat. Calcif Tissue Int 97(5):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-015-0043-0
Brun LR, Pera LI, Rigalli A (2010) Bone morphometry and differences in bone fluorine containing compounds in rats treated with NaF and MFP. Biomed Pharmacother 64(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2008.10.009
Moreno H, Lombarte M, Di Loreto VE (2009) Bones and bone tissue. In: Rigalli A, Di Loreto VE (eds) Experimental surgical models in the laboratory rat. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, pp 229–232. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420093278.ch43
Hoggarth CR, Bennett R, Daley-Yates PT (1991) The pharmacokinetics and distribution of pamidronate for a range of doses in the mouse. Calcif Tissue Int 49(6):416–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02555853
Hogan HA, Ruhmann SP, Sampson HW (2000) The mechanical properties of cancellous bone in the proximal tibia of ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res 15(2):284–292. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.2.284
Rigalli A, Alloatti R, Puche RC (1999) Measurement of total and diffusible serum fluoride. J Clin Lab Anal 13(4):151–157. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-2825
Development Core Team R (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Vestergaard P, Jorgensen NR, Schwarz P, Mosekilde L (2008) Effects of treatment with fluoride on bone mineral density and fracture risk—a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 19(3):257–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-007-0437-6
Lombarte M, Brun LR, Brance ML et al (2014) Efecto diferencial del ácido zoledrónico sobre el hueso trabecular y cortical de ratas ovariectomizadas. Actual Osteol 10:238–246
Kaseva ME (2006) Contribution of trona (magadi) into excessive fluorosis—a case study in Maji ya Chai ward, northern Tanzania. Sci Total Environ 366(1):92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.08.049
Zhang L, Huang D, Yang J, Wei X, Qin J, Ou S, Zhang Z, Zou Y (2017) Probabilistic risk assessment of Chinese residents’ exposure to fluoride in improved drinking water in endemic fluorosis areas. Environ Pollut 222:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.074
Paoloni JD, Fiorentino CE, Sequeira ME (2003) Fluoride contamination of aquifers in the southeast subhumid pampa, Argentina. Environ Toxicol 18(5):317–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.10131
de la Sota M, Puche R, Rigalli A, Fernández LM, Benassati S, Boland R (1997) Changes in bone mass and in glucose homeostasis in subjects with high spontaneous fluoride intake. Medicina (B Aires) 57(4):417–420
Lupo M, Fina BL, Aguirre MC, Armendariz M, Rigalli A (2012) Determination of water fluoride concentration and the influence of the geographic coordinate system and time. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(8):5221–5225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1273-7
Blanes PS, Buchhamer EE, Giménez MC (2011) Natural contamination with arsenic and other trace elements in groundwater of the Central-West region of Chaco, Argentina. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 46(11):1197–1206. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2011.598774
Seeman E (2008) Bone quality: the material and structural basis of bone strength. J Bone Miner Metab 26(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-007-0793-5
Rigalli A, Alloatti R, Menoyo I, Puche RC (1995) Comparative study of the effect of sodium fluoride and sodium monofluorophosphate on glucose homeostasis in the rat. Arzneimittelforschung 45(3):289–292
Rigalli A, Ballina JC, Puche RC (1992) Bone mass increase and glucose tolerance in rats chronically treated with sodium fluoride. Bone Miner 16(2):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-6009(92)90880-M
Lou D-D, Guan Z-Z, Liu Y-J, Liu YF, Zhang KL, Pan JG, Pei JJ (2013) The influence of chronic fluorosis on mitochondrial dynamics morphology and distribution in cortical neurons of the rat brain. Arch Toxicol 87(3):449–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0942-z
Lupo M, Afonso M, Buzalaf R, Rigalli A (2011) Effect of fluoridated water on plasma insulin levels and glucose homeostasis in rats with renal deficiency. Biol Trace Elem Res 140(2):198–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8690-5
de Carvalho JG, de Oliveira RC, Buzalaf MAR (2006) Plasma as an indicator of bone fluoride levels in rats chronically exposed to fluoride. J Appl Oral Sci 14(4):238–241. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1678-77572006000400005
Lobo JGVM, Leite AL, Pereira HABS, Fernandes MS, Peres-Buzalaf C, Sumida DH, Rigalli A, Buzalaf MAR (2015) Low-level fluoride exposure increases insulin sensitivity in experimental diabetes. J Dent Res 94(7):990–997. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034515581186
Everett ET, McHenry MAK, Reynolds N, Eggertsson H, Sullivan J, Kantmann C, Martinez-Mier EA, Warrick JM, Stookey GK (2002) Dental fluorosis: variability among different inbred mouse strains. J Dent Res 81(11):794–798. https://doi.org/10.1177/0810794
Alliston T (2014) Biological regulation of bone quality. Curr Osteoporos Rep 12(3):366–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-014-0213-4
Schnitzler CM, Wing JR, Mesquita JM et al (1990) Risk factors for the development of stress fractures during fluoride therapy for osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 5(S1):S195–S200. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.5650051330
Orcel P, De Vernejoul MC, Prier A et al (1990) Stress fractures of the lower limbs in osteoporotic patients treated with fluoride. J Bone Miner Res 5(S1):S191–S194. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.5650051392
Schnitzler CM, Wing JR, Gear KA, Robson HJ (1990) Bone fragility of the peripheral skeleton during fluoride therapy for osteoporosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 261:268–275
de Cássia Alves Nunes R, Chiba FY, Pereira AG et al (2016) Effect of sodium fluoride on bone biomechanical and histomorphometric parameters and on insulin signaling and insulin sensitivity in ovariectomized rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 173(1):144–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0642-2
Franke J, Runge H, Grau P, Fengler F, Wanka C, Rempel H (1976) Physical properties of fluorosis bone. Acta Orthop Scand 47(1):20–27. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453677608998967
Ghanizadeh G, Babaei M, Naghii MR, Mofid M, Torkaman G, Hedayati M (2014) The effect of supplementation of calcium, vitamin D, boron, and increased fluoride intake on bone mechanical properties and metabolic hormones in rat. Toxicol Ind Health 30(3):211–217. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233712452775
Nakahara H (1995) The effect of sodium fluoride on bone mineral density and bone strength in ovariectomized rats. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi 69(11):1182–1192
Sreenivasan D, Watson M, Callon K, Dray M, Das R, Grey A, Cornish J, Fernandez J (2013) Integrating micro CT indices, CT imaging and computational modelling to assess the mechanical performance of fluoride treated bone. Med Eng Phys 35(12):1793–1800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2013.07.013
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Hilda Moreno for technical assistance.
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) (PIP 112-200801-00341). CONICET had no role in the design, analysis or writing of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The animals were treated according to the accepted international standards for animal care, and the study has been approved by the Ethical Committee of the School of Medicine of Rosario National University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fina, B.L., Lupo, M., Da Ros, E.R. et al. Bone Strength in Growing Rats Treated with Fluoride: a Multi-dose Histomorphometric, Biomechanical and Densitometric Study. Biol Trace Elem Res 185, 375–383 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1229-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1229-2