Abstract
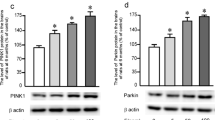
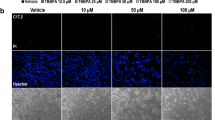
This study aims to clarify the molecular mechanism of fluorine exposure that leads to nerve injury. PC12 cells were treated with fluorine at different concentrations (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 mM). Cytoactivity was detected at different time points (2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24, and 48 h). After 2 h, DCF was used to detect and mark the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) within cells. After 24 h, cellular metamorphosis was observed using an inverted microscope. After 2 h, Hoechst-33342 was used to detect apoptosis. After 24 h, Western blot analysis was performed to detect apoptosis-related poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) protein, p-elF, and expression of the endoplasmic reticulum stress-related X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1). The results showed that Fluorine exposure resulted in a reduction of cell viability, which was negatively correlated with fluorine dose. Within certain fluorine exposure duration, the ROS level within the cell and the apoptotic level are linearly related to fluorine exposure level. XBP-1 and PARP protein are sensitive to variations in fluorine concentration, which indicates that oxidative stress from fluorine exposure can lead to apoptosis. XBP-1 and PARP may be the key proteins during the entire process. These results provide a valid basis for fluorine-induced free radical injury theory.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shanthakumari D, Srinivasalu S, Subramanian S (2004) Effeet of fluoride intoxication on lipidperoxidation and antioxidatnt status in experimental rats. Toxicology 204(2–3):219–228
Li GS, Xu H (2005) Secondary discussion of chronical fluorosis and oxidative stress. Chin J Endemiol 24(1):3–4
Reddy GB, Khandare AL, Reddy PY, et al. (2003) Antioxidant defence system and lipid peroxidation in patients with skeletal fluorosis and in fluoride-intoxicated rabbits. Toxicol Sci 72:363
Wu Y, Zhao Q, Zhang ZG (2010) Protective effect of selenium on liver impairments induced by sodium fluoride in rats. J Environ Health 27(11):955–958
Zhao Q, Wu Y, Zhang ZG (2011) Protective effect of selenium on fluoride-induced renal impairments in rats. Chin J Endemiol 30(2):137–141
Feng P, Wei JR, Zhang ZG (2011) Intervention of selenium on chronic fluorosis-induced injury of blood antioxidant capacity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:1024–1031
Feng P, Wei JR, Zhang ZG (2012) Influence of selenium and fluoride on blood antioxidant capacity of rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:565–568
Zhang L, Yang SY, Zhang ZG (2012) Intervention of selenium on liver impairment induced by chronic fluorosis in rats. J Hygiene Res 41(4):141–145
Zhang SM, Zheng XR, Zhang ZG, et al. (2015) Alterations in oxidative stress and apoptosis in cultured PC12 cells exposed to fluoride. Fluoride 48(3):213–222
Guan LY (2008) Reactive oxygen activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway mediated selenite-induced apoptosis of NB4 cells. Chinese Peking Union Medical College
Xu XL, Zhang ZG, Shen XY (2001) The influence of fluorosis on learning-memory behaviors of mice and the activities of SOD and the content of MDA in the brain. China Public Health 17(1):8–10
Wang JM, Liu HT, Ma JJ (2006) Fluorosis and application of interrelated technology in it. Prog Vet Med 27(3):51–54
Hefnawy G, Pérez T (2010) The importance of selenium and the effects of its deflciency in animal health. Small Ruminant Res 89:185–192
Barbier O, Mendoza LA, del Razo LM (2010) Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 188:319–333
Zhou YT, Xiao HB, Bi MG (2011) ROS and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin 27(5):597–600
He P, Zhang M, He WH (2006) Effects of fluoride on oxidative stress and apoptosis in primary rat hippocampal neurons.chinese. J Endemiol 25(3):264–267
Kubota K, Lee DH, Tsuchiya M (2005) Fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in ameloblasts responsible for dental enamel formation. J Biol Chem 280(24):23194–23202
Zhang QX, Zhao H, Zhang C (2013) Wind, tonify deficiency medicine caspase 3 on cerebral ischemia rats and the effects of PARP expression. J Beijing Univ Chin Med 36(4):246–249
Song XY, Hu JF, Chen NH (2012) Neural cell apoptosis with cerebral ischemia disease. Chin Pharmacol 28(3):307–310
Feng LJ, Wang HP, et al. (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the degeneration of neurons. Chinese Pharmacology 23(4):428–432
Sharma R et al. (2008) Fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibits protein synthesis and secretion. Environ Health Perspect 9(116):1142–1146
Li GS (2003) Calcium from the “contradiction” look at the mechanism of skeletal fluorosis. National conference on fluorine and arsenic, Harbin: Chinese journal of endemiology newsroom
Xiong XZ, Liu JL, He WH, et al. (2007) Dose-effect relationship between drinking warer fluoride levels and damage to liver and kidney functions in children. Environ Mental Res 103(1):112–116
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number: 81273015, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number: 81573101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, L., Zheng, X., Sun, Y. et al. Effects of Sodium Fluoride on Lipid Peroxidation and PARP, XBP-1 Expression in PC12 Cell. Biol Trace Elem Res 173, 161–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0641-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0641-3