Abstract
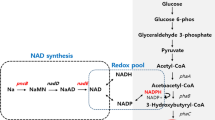
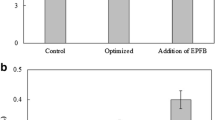
Previously, we presented a novel approach for increasing the consumption of xylose and the lipid yield by overexpressing the genes coding for xylose isomerase (XI) and xylulokinase (XK) in Mucor circinelloides. In the present study, an in-depth analysis of lipid accumulation by xylose metabolism engineered M. circinelloides strains (namely Mc-XI and Mc-XK) using corn straw hydrolysate was to be explored. The results showed that the fatty acid contents of the engineered M. circinelloides strains were, respectively, increased by 19.8% (in Mc-XI) and 22.3% (in Mc-XK) when compared with the control strain, even though a slightly decreased biomass in these engineered strains was detected. Moreover, the xylose uptake rates of engineered strains in the corn straw hydrolysate were improved significantly by 71.5% (in Mc-XI) and 68.8% (in Mc-XK), respectively, when compared with the control strain. Maybe the increased utilization of xylose led to an increase in lipid synthesis. When the recombinant M. circinelloides strains were cultured in corn straw hydrolysate medium with the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio) of 50 and initial pH of 6.0, at 30 °C and 500 rpm for 144 h, a total biomass of 12.6–12.9 g/L with a lipid content of 17.2–17.7% (corresponding to a lipid yield of 2.17–2.28 g/L) was achieved. Our study provides a foundation for the further application of the engineered M. circinelloides strains to produce lipid from lignocelluloses.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin, M., Slininger, P. J., Dien, B. S., Waghmode, S., Moser, B. R., Orjuela, A., Sousa Lda, C., & Balan, V. (2015). Microbial lipid-based lignocellulosic biorefinery: Feasibility and challenges. Trends in Biotechnology, 33(1), 43–54.
Yu, Y., Xu, Z., Chen, S., & Jin, M. (2020). Microbial lipid production from dilute acid and dilute alkali pretreated corn stover via Trichosporon dermatis. Bioresource Technology, 295, 122253.
Tang, S., Dong, Q., Fang, Z., Cong, W. J., & Zhang, H. (2020). Microbial lipid production from rice straw hydrolysates and recycled pretreated glycerol. Bioresource Technology, 312, 123580.
Bjorklund, G., Dadar, M., Dosa, M. D., Chirumbolo, S., & Pen, J. J. (2020). Insights on dietary omega-6/omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) ratio in oxidative metabolic pathways of oncological bone disease and global health. Current Medicinal Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867327666200427095331.
Hayashi, S., Satoh, Y., Ogasawara, Y., & Dairi, T. (2020). Recent advances in functional analysis of polyunsaturated fatty acid synthases. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 59, 30–36.
Ferreira, J. A., & Taherzadeh, M. J. (2020). Improving the economy of lignocellulose-based biorefineries with organosolv pretreatment. Bioresource Technology, 299, 122695.
Özdenkçi, K., De Blasio, C., Muddassar, H. R., Melin, K., Oinas, P., Koskinen, J., Sarwar, G., & Järvinen, M. (2017). A novel biorefinery integration concept for lignocellulosic biomass. Energy Conversion and Management, 149, 974–987.
Brandenburg, J., Poppele, I., Blomqvist, J., Puke, M., Pickova, J., Sandgren, M., Rapoport, A., Vedernikovs, N., & Passoth, V. (2018). Bioethanol and lipid production from the enzymatic hydrolysate of wheat straw after furfural extraction. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(14), 6269–6277.
Slininger, P. J., Dien, B. S., Kurtzman, C. P., Moser, B. R., Bakota, E. L., Thompson, S. R., O'Bryan, P. J., Cotta, M. A., Balan, V., Jin, M., Sousa Lda, C., & Dale, B. E. (2016). Comparative lipid production by oleaginous yeasts in hydrolyzates of lignocellulosic biomass and process strategy for high titers. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 113(8), 1676–1690.
Zheng, Y., Yu, X., Zeng, J., & Chen, S. (2012). Feasibility of filamentous fungi for biofuel production using hydrolysate from dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of wheat straw. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 5(1), 50.
Fei, X., Jia, W., Wang, J., Chen, T., & Ling, Y. (2020). Study on enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency and physicochemical properties of cellulose and lignocellulose after pretreatment with electron beam irradiation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 145, 733–739.
Carvalho, A. K., Rivaldi, J. D., Barbosa, J. C., & de Castro, H. F. (2015). Biosynthesis, characterization and enzymatic transesterification of single cell oil of Mucor circinelloides--a sustainable pathway for biofuel production. Bioresource Technology, 181, 47–53.
Carvalho, A. K. F., Bento, H. B. S., Rivaldi, J. D., & De Castro, H. F. (2018). Direct transesterification of Mucor circinelloides biomass for biodiesel production: effect of carbon sources on the accumulation of fungal lipids and biofuel properties. Fuel, 234, 789–796.
Reis, C. E., Zhang, J., & Hu, B. (2014). Lipid accumulation by pelletized culture of Mucor circinelloides on corn stover hydrolysate. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174(1), 411–423.
Andrade, G. S. S., Carvalho, A. K. F., Romero, C. M., Oliveira, P. C., & de Castro, H. F. (2014). Mucor circinelloides whole-cells as a biocatalyst for the production of ethyl esters based on babassu oil. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 37(12), 2539–2548.
Chu, L., Zan, X., Tang, X., Zhao, L., Chen, H., Chen, Y. Q., Chen, W., & Song, Y. (2016). The role of a xylose isomerase pathway in the conversion of xylose to lipid in Mucor circinelloides. RSC Advances, 6(81), 77944–77952.
Zhang, Y., Luan, X., Zhang, H., Garre, V., Song, Y., & Ratledge, C. (2017). Improved gamma-linolenic acid production in Mucor circinelloides by homologous overexpressing of delta-12 and delta-6 desaturases. Microbial Cell Factories, 16(1), 113.
Jo, S., Yoon, J., Lee, S. M., Um, Y., Han, S. O., & Woo, H. M. (2017). Modular pathway engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum to improve xylose utilization and succinate production. Journal of Biotechnology, 258, 69–78.
Hou, J., Qiu, C., Shen, Y., Li, H., & Bao, X. (2017). Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the efficient co-utilization of glucose and xylose. FEMS Yeast Research, 17(4). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fox034.
Guaman, L. P., Oliveira-Filho, E. R., Barba-Ostria, C., Gomez, J. G. C., Taciro, M. K., & da Silva, L. F. (2018). xylA and xylB overexpression as a successful strategy for improving xylose utilization and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate production in Burkholderia sacchari. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 45(3), 165–173.
Sanchez Nogue, V., & Karhumaa, K. (2015). Xylose fermentation as a challenge for commercialization of lignocellulosic fuels and chemicals. Biotechnology Letters, 37(4), 761–772.
Brodeur, G., Yau, E., Badal, K., Collier, J., Ramachandran, K. B., & Ramakrishnan, S. (2011). Chemical and physicochemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: A review. Enzyme Research, 2011, 787532.
Zhang, T., Jiang, D., Zhang, H., Lee, D. J., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Q., Jing, Y., Zhang, Y., & Xia, C. (2020). Effects of different pretreatment methods on the structural characteristics, enzymatic saccharification and photo-fermentative bio-hydrogen production performance of corn straw. Bioresource Technology, 304, 122999.
Baral, N. R., Li, J., & Jha, A. K. (2014). Perspective and prospective of pretreatment of corn straw for butanol production. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172(2), 840–853.
Robak, K., Balcerek, M., Dziekonska-Kubczak, U., & Dziugan, P. (2019). Effect of dilute acid pretreatment on the saccharification and fermentation of rye straw. Biotechnology Progress, 35(3), e2789.
Liu, Z., Li, L., Liu, C., & Xu, A. (2018). Pretreatment of corn straw using the alkaline solution of ionic liquids. Bioresource Technology, 260, 417–420.
Den, W., Sharma, V. K., Lee, M., Nadadur, G., & Varma, R. S. (2018). Lignocellulosic biomass transformations via greener oxidative pretreatment processes: Access to energy and value-added chemicals. Frontiers in Chemistry, 6, 141.
Zhang, Y., Fu, X., & Chen, H. (2012). Pretreatment based on two-step steam explosion combined with an intermediate separation of fiber cells--optimization of fermentation of corn straw hydrolysates. Bioresource Technology, 121, 100–104.
Truong, N. P. V., & Kim, T. H. (2018). Effective saccharification of corn stover using low-liquid aqueous ammonia pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis. Molecules, 23(5), 1050.
Zhang, J., Zhu, Z., Wang, X., Wang, N., Wang, W., & Bao, J. (2010). Biodetoxification of toxins generated from lignocellulose pretreatment using a newly isolated fungus, Amorphotheca resinae ZN1, and the consequent ethanol fermentation. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 3(1), 26.
Shao, L., Chen, H., Li, Y., Li, J., Chen, G., & Wang, G. (2020). Pretreatment of corn stover via sodium hydroxide-urea solutions to improve the glucose yield. Bioresource Technology, 307, 123191.
Yan, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, K., Si, M., Liu, M., Chai, L., Liu, X., & Shi, Y. (2017). Bacteria-enhanced dilute acid pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol, 245(Pt A), 419–425.
Jonsson, L. J., Alriksson, B., & Nilvebrant, N. O. (2013). Bioconversion of lignocellulose: inhibitors and detoxification. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 6(1), 16.
Kim, D. (2018). Physico-chemical conversion of lignocellulose: Inhibitor effects and detoxification strategies: A Mini Review. Molecules, 23(2), 309.
Martinez, A., Rodriguez, M. E., Wells, M. L., York, S. W., Preston, J. F., & Ingram, L. O. (2001). Detoxification of dilute acid hydrolysates of lignocellulose with lime. Biotechnology Progress, 17(2), 287–293.
Krishnani, K. K. (2016). Lignocellulosic wheat straw-derived ion-exchange adsorbent for heavy metals removal. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 178(4), 670–686.
He, Y., Zhang, J., & Bao, J. (2016). Acceleration of biodetoxification on dilute acid pretreated lignocellulose feedstock by aeration and the consequent ethanol fermentation evaluation. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 9(1), 19.
Xie, Y., Hu, Q., Feng, G., Jiang, X., Hu, J., He, M., et al. (2018). Biodetoxification of phenolic inhibitors from lignocellulose pretreatment using Kurthia huakuii LAM0618(T) and subsequent lactic acid fermentation. Molecules, 23(10), 2626.
Senatham, S., Chamduang, T., Kaewchingduang, Y., Thammasittirong, A., Srisodsuk, M., Elliston, A., Roberts, I. N., Waldron, K. W., & Thammasittirong, S. N. (2016). Enhanced xylose fermentation and hydrolysate inhibitor tolerance of Scheffersomyces shehatae for efficient ethanol production from non-detoxified lignocellulosic hydrolysate. Springerplus, 5(1), 1040.
Sanda, T., Hasunuma, T., Matsuda, F., & Kondo, A. (2011). Repeated-batch fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysate to ethanol using a hybrid Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain metabolically engineered for tolerance to acetic and formic acids. Bioresource Technology, 102(17), 7917–7924.
He, Y., Zhang, J., & Bao, J. (2014). Dry dilute acid pretreatment by co-currently feeding of corn stover feedstock and dilute acid solution without impregnation. Bioresource Technology, 158, 360–364.
Zhang, J., Wang, X., Chu, D., He, Y., & Bao, J. (2011). Dry pretreatment of lignocellulose with extremely low steam and water usage for bioethanol production. Bioresource Technology, 102(6), 4480–4488.
Aussant, J., Guiheneuf, F., & Stengel, D. B. (2018). Impact of temperature on fatty acid composition and nutritional value in eight species of microalgae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(12), 5279–5297.
Fadhlaoui, M., Laderriere, V., Lavoie, I., & Fortin, C. (2020). Influence of temperature and nickel on algal biofilm fatty acid composition. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 39(8), 1566–1577.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Shandong Province (2018GSF121013), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR201910220031), Zibo City and University Integration Project (2017ZBXC169), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31670064 and 31972851), and Taishan Industry Leading Talent Project (LJNY201606).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Song, Y. Lipid Accumulation by Xylose Metabolism Engineered Mucor circinelloides Strains on Corn Straw Hydrolysate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193, 856–868 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03427-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03427-2