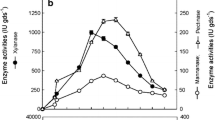
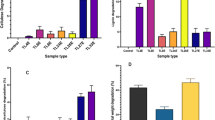
Abstract
Multi-strain mixed fermentation can provide a relatively complete lignocellulosic enzyme system compared with single-strain fermentation. This study was firstly to screen strains which have a strong ability to hydrolyse rice straw (RS) enzymatically and enrich true protein (TP). Then, the conditions in the process of SSF, including the optimum inoculum size of mixed strains, inoculation ratio, and different inoculation time of N. crassa 14–8, were optimized. The experimental results showed that the highest TP content could be obtained by using N. crassa 14–8, C. utilis, and P. chrysosporium as mixed strains, and 5 mM Mn2+ and 50 mM veratryl alcohol were used as inducers of lignin peroxidase (LiP) to improve the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis. When N. crassa 14–8 was inoculated 1 day later than P. chrysosporium, the total inoculum size was 10%, and the optimum ratio of N. crassa 14–8 to P. chrysosporium was 1:2, the maximum TP yield (8.89%) was obtained, with 123.37% of its increase rate. This work proposed a technique with potential application in large-scale feedstuff protein conversion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu, O. A., Tewe, O. O., Losel, D. M., & Onifade, A. A. (2000). Changes in lipid, fatty acids and protein composition of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) after solid-state fungal fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 72(2), 189–192.
Aggelopoulos, T., Katsieris, K., Bekatorou, A., Pandey, A., Banat, I. M., & Koutinas, A. A. (2014). Solid state fermentation of food waste mixtures for single cell protein, aroma volatiles and fat production. Food Chemistry, 145, 710–716.
Asgher, M., Ahmed, N., & Iqbal, H. M. N. (2011). Hyperproductivity of extracellular enzymes from indigenous white rot fungi (P. chrysosporium IBL-03) by utilizing agro-wastes. Bioresources, 6, 4454–4467.
Bader, J., Mast-Gerlach, E., Popovi, M. K., Bajpai, R., & Stahl, U. (2010). Relevance of microbial coculture fermentations in biotechnology. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 109(2), 371–387.
Bak, J. S., Ko, J. K., Choi, I. G., Park, Y. C., Seo, J. H., & Kim, K. H. (2009). Fungal pretreatment of lignocellulose by Phanerochaete chrysosporium to produce ethanol from rice straw. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 104(3), 471–482.
Bonugli-Santos, R. C., Durrant, L. R., Silva, M. D., & Sette, L. D. (2010). Production of laccase, manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase by Brazilian marine-derived fungi. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 46(1), 32–37.
Chen, S. L. (2010). Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosics: Potential, progress and challenges. Biofuels, 1(1), 177–199.
Danesh, A., Mamo, G., & Mattiasson, B. (2011). Production of haloduracin by Bacillus halodurans using solid-state fermentation. Biotechnology Letters, 33(7), 1339–1344.
Dias, A. A., & Rui, M. B. (2003). In vivo and laccase-catalysed decolourization of xenobiotic azo dyes by a basidiomycetous fungus: Characterization of its ligninolytic system. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19(9), 969–975.
Dobozi, M. S., Szakács, G., & Bruschi, C. V. (1992). Xylanase activity of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58(11), 3466–3471.
Eberhart, B. M., Beck, R. S., & Goolsby, K. M. (1977). Cellulase of Neurospora crassa. Journal of Bacteriology, 130(1), 181–186.
Elshafei, A. M. (1990). Cellulase and hemicellulase formation by fungi using corn Stover as the substrate. Biological Wastes, 32(3), 209–218.
Froehner, S. C., & Eriksson, K. E. (1974). Induction of Neurospora crassa laccase with protein synthesis inhibitors. Journal of Bacteriology, 120(1), 450–457.
Garrido, S. M., Kitamoto, N., Watanabe, A., Shintani, T., & Gomi, K. (2012). Functional analysis of FarA transcription factor in the regulation of the genes encoding lipolytic enzymes and hydrophobic surface binding protein for the degradation of biodegradable plastics in Aspergillus oryzae. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 113(5), 549–555.
Garrote, G., Dominguez, H., & Parajo, J. C. (2002). Autohydrolysis of corncob: Study of non-isothermal operation for xylooligosaccharide production. Journal of Food Engineering, 52(3), 211–218.
Gassara, F., Brar, S. K., Tyagi, R. D., John, R. P., Verma, M., & Valero, J. R. (2011). Parameter optimization for production of ligninolytic enzymes using agro-industrial wastes by response surface method. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 16(2), 343–351.
Ghose, T. K. (2009). Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 59, 257–268.
Huang, D. L., Zeng, G. M., Feng, C. L., Shuang, H., Zhao, M. H., Cui, L., Yu, Z., Jiang, X. Y., & Liu, H. L. (2010). Mycelial growth and solid-state fermentation of lignocellulosic waste by white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium under lead stress. Chemosphere, 81(9), 1091–1097.
Huang, X., Wang, D., Liu, C., Hu, M., Qu, Y., & Gao, P. (2003). The roles of veratryl alcohol and nonionic surfactant in the oxidation of phenolic compounds by lignin peroxidase. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 311(2), 491–494.
Irfan, M., Nazir, M. I., Nadeem, M., Gulsher, M., Syed, Q., & Baig, S. (2011). Optimization of process parameters for the production of single cell biomass of Candida utilis in solid state fermentation. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, 10, 264–270.
Kirk, T. K., & Farrell, R. L. (1987). Enzymatic "combustion": The microbial degradation of lignin. Annual Review of Microbiology, 41(1), 465–501.
Lio, J. Y., & Wang, T. (2012). 75.Solid-state fermentation of soybean and corn processing coproducts for potential feed improvement. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(31), 7702–7709.
Mahadevan, P. R., & Eberhart, B. (1964). The Beta-glucosidase system of Neurospora Crassa. Ii. Purification and characterization of aryl beta-glucosidase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 108(1), 22–29.
Mishra, C., Keskar, S., & Rao, M. (1984). Production and properties of extracellular Endoxylanase from Neurospora crassa. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 48(1), 224–228.
Perez, J., & Jeffries, T. W. (1993). Role of organic acid chelators in manganese regulation of lignin degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 39-40(1), 227–238.
Rajoka, M. I., Kiani, M. A. T., Khan, S., Awan, M. S., & Hashmi, A. S. (2004). Production of single cell protein from rice polishings using Candida utilis. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 20(3), 297–301.
Saha, B. C. (2003). Hemicellulose bioconversion. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30(5), 279–291.
Sanchez, C. (2009). Lignocellulosic residues: Biodegradation and bioconversion by fungi. Biotechnology Advances, 27(2), 185–194.
Santos, M. M. D., & Rosa, A. S. D. (2004). Thermal denaturation: Is solid-state fermentation really a good technology for the production of enzymes? Bioresource Technology, 93(3), 261–268.
Shi, J., Sharma-Shivappa, R. R., Chinn, M., & Howell, N. (2009). Effect of microbial pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of cotton stalks for ethanol production. Biomass and Bioenergy, 33(1), 88–96.
Singh, P., Sulaiman, O., Hashim, R., Peng, L. C., & Singh, R. P. (2013). Evaluating biopulping as an alternative application on oil palm trunk using the white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 82, 96–103.
SKC, C. (2010). Protein Analysis (2nd ed.). USA: Aspen Publishers Inc.
Talaeipour, M., Hemmasi, A. H., Kasmani, J. E., Mirshokraie, S. A., & Khademieslam, H. (2010). Effects of fungal treatment on structural and chemical features of hornbeam chips. Bioresources, 5, 477–487.
Ten, H. R., & Teunissen, P. J. (2001). Oxidative mechanisms involved in lignin degradation by white-rot fungi. Chemical Reviews, 101, 3397.
Van Soest, P. J. (1963). Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds. 1. Preparation of fiber residues of low nitrogen content. Journal of the Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, 46, 825–829.
Xiao, L., Yang, L. Y., Zhang, Y., Gu, Y. F., Jiang, L. J., & Qin, B. Q. (2009). Solid state fermentation of aquatic macrophytes for crude protein extraction. Ecological Engineering, 35(11), 1668–1676.
Zhao, L., Cao, G. L., Wang, A. J., Ren, H. Y., Dong, D., Liu, Z. N., Guan, X. Y., Xu, C. J., & Ren, N. Q. (2012). Fungal pretreatment of cornstalk with Phanerochaete chrysosporium for enhancing enzymatic saccharification and hydrogen production. Bioresource Technology, 114, 365–369.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key R&D Program of Jiangsu Province (Modern Agriculture), China (BE2017355); the Agricultural Sci-Tech Self-Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, CX(17)3044, China; the Open Funding Project of National Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering; and Jiangsu Special Research and Development Grant for Northern Jiangsu Area, China (SZ-YC2017001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, J., Chen, H., Wu, B. et al. Protein Production Through Microbial Conversion of Rice Straw by Multi-Strain Fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 187, 253–265 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2792-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2792-5