Abstract
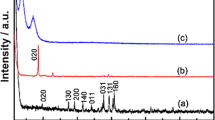
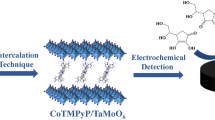
A novel sandwich-structured nanocomposite based on Ti2NbO7− nanosheets and cobalt porphyrin (CoTMPyP) was fabricated through electrostatic interaction, in which CoTMPyP has been successfully inserted into the lamellar spacing of layered titanoniobate. The resultant Ti2NbO7/CoTMPyP nanocomposite was characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, EDS, FT-IR, and UV-vis. It is demonstrated that the intercalated CoTMPyP molecules were found to be tilted approximately 63° against Ti2NbO7− layers. The glass carbon electrode (GCE) modified by Ti2NbO7/CoTMPyP film showed a fine diffusion-controlled electrochemical redox process. Furthermore, the Ti2NbO7/CoTMPyP-modified electrode exhibited excellent electrocatalytic oxidation activity of ascorbic acid (AA). Differential pulse voltammetric studies demonstrated that the intercalated nanocomposite detects AA linearly over a concentration range of 4.99 × 10−5 to 9.95 × 10−4 mol L−1 with a detection limit of 3.1 × 10−5 mol L−1 at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.0.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, X., Wei, S., Chen, S., Yuan, D., & Zhang, W. (2014). Graphene-multiwall carbon nanotube-gold nanocluster composites modified electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173(7), 1717–1726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0959-2
Liu, C., Han, R., Ji, H., Sun, T., Zhao, J., Chen, N., Chen, J., Guo, X., Hou, W., & Ding, W. (2016). S-doped mesoporous nanocomposite of HTiNbO5 nanosheets and TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18(2), 801–810. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP06555K
Zhang, X., Li, D., Yin, F., Gong, J., Yang, X., Tong, Z., & Xu, X. (2014). Characterization of a layered methylene blue/vanadium oxide nanocomposite and its application in a reagentless H2O2 biosensor. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 172(1), 176–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0528-0
Zhai, Z., Hu, C., Yang, X., Zhang, L., Liu, C., Fan, Y., & Hou, W. (2012). Nitrogen-doped mesoporous nanohybrids of TiO2 nanoparticles and HTiNbO5 nanosheets with a high visible-light photocatalytic activity and a good biocompatibility. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(36), 19122–19131. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm32338a
Zhai, Z., Huang, Y., Xu, L., Yang, X., Hu, C., Zhang, L., Fan, Y., & Hou, W. (2011). Thermostable nitrogen-doped HTiNbO5 nanosheets with a high visible-light photocatalytic activity. Nano Research, 4(7), 635–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0119-8
Liu, C., Sun, T., Wu, L., Liang, J., Huang, Q., Chen, J., & Hou, W. (2015). N-doped Na2Ti6O13@TiO2 core–shell nanobelts with exposed {1 0 1} anatase facets and enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance. Applied Catalysis B, 170, 17–24.
Zhai, Z., Yang, X., Xu, L., Hu, C., Zhang, L., Hou, W., & Fan, Y. (2012). Novel mesoporous NiO/HTiNbO5 nanohybrids with high visible-light photocatalytic activity and good biocompatibility. Nanoscale, 4(2), 547–556. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1NR11091H
Hervieu, M., & Raveau, B. (1980). A layer structure: the titanoniobate CsTi2NbO7. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 32(2), 161–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(80)90562-9
Rebbah, H., Hervieu, M., & Raveau, B. (1981). The CsTi2NbO7 type layer oxides: ion exchange properties. Materials Research Bulletin, 16(2), 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(81)90075-1
Dias, A. S., Lima, S., Carriazo, D., Rives, V., Pillinger, M., & Valente, A. A. (2006). Exfoliated titanate, niobate and titanoniobate nanosheets as solid acid catalysts for the liquid-phase dehydration of D-xylose into furfural. Journal of Catalysis, 244(2), 230–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2006.09.010
Akatsuka, K., Takanashi, G., Ebina, Y., Haga, M. A., & Sasaki, T. (2012). Electronic band structure of exfoliated titanium-and/or niobium-based oxide nanosheets probed by electrochemical and photoelectrochemical measurements. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 116(23), 12426–12433. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp302417a
Xie, K., Wei, W., & Yu, H. (2016). A novel layered titanoniobate as anode material for long-life sodium-ion batteries. RSC Advances, 6(42), 35746–35750. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA02530G
Catti, M., Pinus, I., Ruffo, R., Salamone, M. M., & Mari, C. M. (2016). A novel layered lithium niobium titanate as battery anode material: crystal structure and charge-discharge properties. Solid State Ionics, 295, 72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2016.08.001
Takagaki, A., Yoshida, T., Lu, D., Kondo, J. N., Hara, M., Domen, K., & Hayashi, S. (2004). Titanium niobate and titanium tantalate nanosheets as strong solid acid catalysts. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 108(31), 11549–11555. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp049170e
Tanaka, T., Fukuda, K., Ebina, Y., Takada, K., & Sasaki, T. (2004). Highly organized self-assembled monolayer and multilayer films of titania nanosheets. Advanced Materials, 16(11), 872–875. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200306470
Liu, L., Ma, J., Shao, F., Zhang, D., Gong, J., & Tong, Z. (2012). A nanostructured hybrid synthesized by the intercalation of CoTMPyP into layered titanate: direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis. Electrochemistry Communications, 24, 74–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2012.08.021
Ma, J., Yang, M., Chen, Y., Liu, L., Zhang, X., Wang, M., Zhang, D., & Tong, Z. (2015). Sandwich-structured composite from the direct coassembly of layered titanate nanosheets and Mn porphyrin and its electrocatalytic performance for nitrite oxidation. Materials Letters, 150, 122–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.03.039
Ma, J., Wu, J., Gu, J., Liu, L., Zhang, D., Xu, X., Yang, X., & Tong, Z. (2012). Fabrication and spectroscopic, electrochemical, and catalytic properties of a new intercalation compound of K4Nb6O17 with cationic cobalt porphyrin. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 357, 95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2012.01.025
Ma, J., Wu, J., Zheng, J., Liu, L., Zhang, D., Xu, X., Yang, X., & Tong, Z. (2012). Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical behavior of cationic iron porphyrin intercalated into layered niobate. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 151, 325–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.10.016
Pan, B., Zhao, W., Zhang, X., Li, J., Xu, J., Ma, J., Liu, L., Zhang, D., & Tong, Z. (2016). Research on self-assembly of exfoliated perovskite nanosheets (LaNb2O7 −) and cobalt porphyrin utilized for electrocatalytic oxidation of ascorbic acid. RSC Advances, 6(52), 46388–46393. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA06429A
Zhang, X., Liu, L., Ma, J., Yang, X., Xu, X., & Tong, Z. (2013). A novel metalloporphyrin intercalated layered niobate as an electrode modified material for detection of hydrogen peroxide. Materials Letters, 95, 21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.12.061
Barnes, M. J. (1975). Function of ascorbic acid in collagen metabolism. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 258(1 Second Confer), 264–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29287.x
Smith, A. R., Visioli, F., & Hagen, T. M. (2002). Vitamin C matters: increased oxidative stress in cultured human aortic endothelial cells without supplemental ascorbic acid. FASEB Journal, 16(9), 1102–1104. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.01-0825fje
Kyaw, A. (1978). A simple colorimetric method for ascorbic acid determination in blood plasma. Clinica Chimica Acta, 86(2), 153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(78)90128-6
Marques, I. D. H. C., Marques, E. T. A., Silva, A. C., Ledingham, W. M., Melo, E. H. M., Da Silva, V. L., & Lima Filho, J. L. (1994). Ascorbic acid determination in biological fluids using ascorbate oxidase immobilized on alkylamine glass beads in a flow injection potentiometric system. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 44(1), 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02921853
Speek, A. J., Schrijver, J., & Schreurs, W. H. P. (1984). Fluorometric determination of total vitamin C in whole blood by high-performance liquid chromatography with pre-column derive atization. Journal of Chromatography, 305, 53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(00)83313-7
Sun, C., Lee, H., Yang, J., & Wu, C. (2011). The simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using graphene/size-selected Pt nanocomposites. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 26(8), 3450–3455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.01.023
Pournaghi-Azar, M. H., Razmi-Nerbin, H., & Hafezi, B. (2002). Amperometric determination of ascorbic acid in real samples using an aluminum electrode, modified with nickel hexacyanoferrate films by simple electroless dipping method. Electroanalysis, 14(3), 206–212. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4109(200202)14:3<206::AID-ELAN206>3.0.CO;2-M
Deng, K., Zhou, J., & Li, X. (2013). Noncovalent nanohybrid of cobalt tetraphenylporphyrin with graphene for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Electrochimica Acta, 114, 341–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.09.164
Liu, X., Wei, S., Chen, S., Yuan, D., & Zhang, W. (2014). Graphene-multiwall carbon nanotube-gold nanocluster composites modified electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173(7), 1717–1726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0959-2
Vance Jr., T. B., & Seff, K. (1975). Hydrated and dehydrated crystal structures of seven-twelfths cesium-exchanged zeolite a. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 79, 2163–2167.
Yao, K., Nishimura, S., Imai, Y., Wang, H., Ma, T., Abe, E., Tateyama, H., & Yamagishi, A. (2003). Spectroscopic and photoelectrochemical study of sensitized layered niobate K4Nb6O17. Langmuir, 19(2), 321–325. https://doi.org/10.1021/la026065s
Machado, A. M., Wypych, F., Drechsel, S. M., & Nakagaki, S. (2002). Study of the catalytic behavior of montmorillonite/iron (III) and Mn (III) cationic porphyrins. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 254(1), 158–164. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8488
Halma, M., de Freitas Castro, K. A. D., Taviot-Gueho, C., Prévot, V., Forano, C., Wypych, F., & Nakagaki, S. (2008). Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic activity of anionic iron (III) porphyrins intercalated into layered double hydroxides. Journal of Catalysis, 257(2), 233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2008.04.026
Chen, S., & Chiu, S. (2001). The catalytic and photocatalytic autoxidation of Sx 2− to SO4 2− by water-soluble cobalt porphyrin. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 166(2), 243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1169(00)00471-4
Ma, J., Jiang, H., Zhuo, N., Li, J., Lu, J., Gong, J., Xu, X., & Tong, Z. (2011). Fabrication of polypyrrole/layered niobate nanocomposite and its electrochemical behavior. Journal of Materials Science, 46(21), 6883–6888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5652-z
Pisoschi, A. M., Pop, A., Serban, A. I., & Fafaneata, C. (2014). Electrochemical methods for ascorbic acid determination. Electrochimica Acta, 121, 443–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.12.127
Sternson, A. W., McCreery, R., Feinberg, B., & Adans, R. N. (1973). Electrochemical studies of adrenergic neurotrans-mitters and related compounds. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 46(2), 313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(73)80139-1
Rusling, J. F., & Zuman, P. (1980). Effects of buffers on polarographic reduction of pyridinecarboxaldehydes. Analytical Chemistry, 52(13), 2209–2211. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50063a049
Qu, F., Li, N., & Jiang, Y. (1998). Electrochemical studies of NiTMPyP and interaction with DNA. Talanta, 45(5), 787–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(97)00154-9
Harris, F. L., & Toppen, D. L. (1978). Kinetics and mechanism of reactions of water-soluble ferriporphyrins. 2. Reduction by ascorbic acid. Inorganic Chemistry, 17(1), 74–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic50179a016
Deakin, M. R., Kovach, P. M., Stutts, K. J., & Wightman, R. M. (1986). Heterogeneous mechanisms of the oxidation of catechols and ascorbic acid at carbon electrodes. Analytical Chemistry, 58(7), 1474–1480. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00298a046
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Fund of Jiangsu Province (BK20161294), HHIT Research Project (Z2015011), Lianyungang Science Project (CG1602), and the Natural Science Foundation of Huaihai Institute of Technology (Z2014004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 620 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Xu, J., Zhang, X. et al. Fabrication of a New Self-assembly Compound of CsTi2NbO7 with Cationic Cobalt Porphyrin Utilized as an Ascorbic Acid Sensor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 185, 834–846 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2701-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2701-y