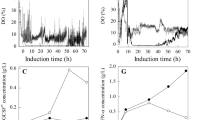
Abstract
In production of porcine interferon α (pIFN-α) by Pichia pastoris, improper glycerol feeding strategy leads to ethanol accumulation in the last stage of growth phase. In the present study, taking two runs with low ethanol accumulation under 2 g/L as control group, effects of long-term (>4 h) and instantaneous high ethanol concentration (>10 g/L) on pIFN-α production, and activities of key enzymes in carbon metabolism were discussed. As a result, compared with control group, pIFN-α expression level was decreased about 4~12 folds under long-term high ethanol concentration, from the level above 3 g/L to the level under 1 g/L; pIFN-α expression level was decreased about 8 folds under instantaneous high ethanol concentration, reaching to the low level of 0.42 g/L. The low production of pIFN-α was caused by the severe inhibitory effect of ethanol on these enzymes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, W. H., Bevins, M. A., Plantz, B. A., Smith, L. A., & Meagher, M. M. (2000). Modeling Pichia pastoris growth on methanol and optimizing the production of a recombinant protein, the heavy-chain fragment C of botulinum neurotoxin, serotype A. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 70, 1–8.
Chang, H. W., Jeng, C. R., Liu, J. J., Lin, T. L., Chang, C. C., Chia, M. Y., Tsai, Y. C., & Pang, V. F. (2005). Reduction of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infection in swine alveolar macrophages by porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2)-induced interferon-alpha. Veterinary Microbiology, 108, 167–177.
Chinsangaram, J., Koster, M., & Grubman, M. J. (2001). Inhibition of L-deleted foot-and-mouth disease virus replication by alpha/beta interferon involves double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Journal of Virology, 75, 5498–5503.
Jin, H., Liu, G., Ye, X., Duan, Z., Li, Z., & Shi, Z. (2010). Enhanced porcine interferon-alpha production by recombinant Pichia pastoris with a combinational control strategy of low induction temperature and high dissolved oxygen concentration. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 52, 91–98.
Crowley, J., Arnold, S. A., Wood, N., Harvey, L. M., & McNeil, B. (2005). Monitoring a high cell density recombinant Pichia pastoris fed-batch bioprocess using transmission and reflectance near infrared spectroscopy. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 36, 621–628.
Lopes, M., Belo, I., & Mota, M. (2013). Batch and fed-batch growth of Pichia pastoris under increased air pressure. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 36, 1267–1275.
Gao, M., Zheng, Z., Wu, J., Dong, S., Li, Z., Jin, H., Zhan, X., & Lin, C. (2012). Improvement of specific growth rate of Pichia pastoris for effective porcine interferon-alpha production with an on-line model-based glycerol feeding strategy. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 1437–1445.
Calik, P., Bayraktar, E., Inankur, B., Soyaslan, E. S., Sahin, M., Taspinar, H., Acik, E., Yilmaz, R., & Ozdamar, T. H. (2010). Influence of pH on recombinant human growth hormone production by Pichia pastoris. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 85, 1628–1635.
Ding, J., Gao, M., Hou, G., Liang, K., Yu, R., Li, Z., & Shi, Z. (2014). Stabilizing porcine interferon-α production by Pichia pastoris with an ethanol on-line measurement based DO-Stat glycerol feeding strategy. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 89, 1948–1953.
Inan, M., & Meagher, M. M. (2001). The effect of ethanol and acetate on protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 92, 337–341.
Sedmak, J. J., & Grossberg, S. E. (1977). A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Analytical Biochemistry, 79, 544–552.
Gao, M., Li, Z., Yu, R., Wu, J., Zheng, Z., Shi, Z., Zhan, X., & Lin, C. (2012). Methanol/sorbitol co-feeding induction enhanced porcine interferon-alpha production by P. pastoris associated with energy metabolism shift. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 35, 1125–1136.
Suye, S., Ogawa, A., Yokoyama, S., & Obayashi, A. (1990). Screening and identification of Candida methanosorbosa as alcohol oxidase producing methanol using yeast. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 54(5), 1297–1298.
Schute, H., Flossdorf, J., Sahm, H., & Kula, M. R. (1976). Purification and properties of formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase from Candida boidinii. European Journal of Biochemistry, 62, 151–160.
Li, X., Li, Z., Zheng, J., Shi, Z., & Li, L. (2012). Yeast extract promotes phase shift of bio-butanol fermentation by Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824 using cassava as substrate. Bioresource Technology, 125, 43–51.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial supports from the Natural Science Foundation of China (#31301408), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (#BK20130122), and the 111 Project (No. 111–2–06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, J., Gao, M., Hou, G. et al. Effect of Ethanol Accumulation on Porcine Interferon-α Production by Pichia pastoris and Activities of Key Enzymes in Carbon Metabolism. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 1964–1974 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1693-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1693-0