Abstract
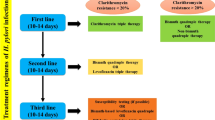
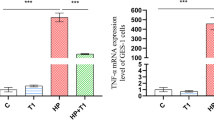
Probiotic lactic acid bacteria are being proposed to cure peptic ulcers by reducing colonization of Helicobacter pylori within the stomach mucosa and by eradicating already established infection. In lieu of that, in vitro inhibitory activity of pediocin-producing probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici BA28 was evaluated against H. pylori by growth inhibition assays. Further, chronic gastritis was first induced in two groups of C57BL/6 mice by orogastric inoculation with H. pylori with polyethylene catheter, and probiotic P. acidilactici BA28 was orally administered to study the eradication and cure of peptic ulcer disease. H. pylori and P. acidilactici BA28 were detected in gastric biopsy and fecal samples of mice, respectively. A probiotic treatment with P. acidilactici BA28, which is able to eliminate H. pylori infection and could reverse peptic ulcer disease, is being suggested as a co-adjustment with conventional antibiotic treatment. The study provided an evidence of controlling peptic ulcer disease, by diet modulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Correia, M., Michel, V., Matos, A. A., Carvalho, P., Oliveira, M. J., Ferreira, R. M., et al. (2012). PLoS ONE, 7(4), e35072. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035072.
Kuster, J. G., Vliet, A. H. M., & Kuipers, E. J. (2006). Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 19(3), 449–490.
Prasad, S., Mathan, M., Chandy, G., Rajan, D. P., Venkateswaran, S., Ramakrishna, B. S., et al. (1994). Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 9, 501–506.
Kang, G., Rajan, D. P., Patra, S., Chacko, A., & Mathan, M. M. (1999). Indian Journal Medical Research, 110, 86–90.
Jais, M., & Barua, S. (2004). Journal of Communication Disorders, 36, 132–135.
NIH. (1994). Journal of the American Medical Association, 272, 659.
Megraud, F., Bonnet, F., Garnier, M., & Lamouliatte, H. (1985). Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 22, 1007–1010.
Lopez-Brea, M., Alarcon, T., Domingo, D., & Diaz- Reganon, J. (2008). Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 61, 139–142.
Karen Collins, R. D. (2007). American Institute Cancer Research, 50(7), 1365–1374.
Ljungh, A., & Wadstrom, T. (2006). Current Issues in Intestinal Microbiology, 7, 73–89.
Reid, G., Beuerman, D., Heinemann, C., & Bruce, A. W. (2001). FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology, 32, 37–41.
Reid, G., & Bruce, A. W. (2006). World Journal of Urology, 24, 28–32.
Falagas, M. E., Betsi, G. I., & Tokas, T. (2006). Journal of Microbial Information, 12, 2772.
Kaur, B., Balgir, P. P., Mittu, B., Chauhan, A., Kumar, B., & Garg, N. (2013). American Journal of Drug Diseases Development, 3(1), 1–12. doi:10.3923/ajdd.2013.
Szajewska, H., & Mrukowicz, J. Z. (2005). Paediatric Drugs, 7, 111–122.
Chenoll, E., Casinos, B., Bataller, E., Astals, P., & Echevarria, P. J. (2011). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77, 1335–1343.
Lin, W. H., Wu, C. R., Fang, T. J., Guo, J. T., Huang, S. Y., Lee, M. S., et al. (2011). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 91, 1424–1431.
Kaur, B., Garg, N., Sachdev, A., Kumar, B., Mittu, B., & Chauhan, A. (2012). Open Access Scientific Reports, 1(6), 323.
Kaur, B. and Garg, N. (2013) Mintage Journal Pharmaceutical Medicine Science 17–20.
Yang, R., Johnson, M. C., & Ray, B. (1992). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 3355.
Pucci, M. J., Vedamuthu, E. R., Kunka, B. S., & Vandenbergh, P. A. (1988). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54, 2349.
Toba, T., Yoshioka, E., & Itoh, T. (1991). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 12, 106–108.
Parisi, J. T., Baldwin, J. N., & Sottile, M. (1973). Applied Microbiology, 25(4), 558–561.
Lee, A., O’Rourke, J., Ungria, M., Robertson, B., Daskalopoulos, G., & Dixon, M. F. (1997). Gastroenterology, 112, 1386–1397.
Ferrero, R., Thiberge, J., Huerre, M., & Labigne, A. (1998). Infection and Immunity, 66, 1349–1355.
Eaton, K. A., Radin, M. J., & Krakowka, S. (1995). Veterinary Pathology, 32, 489–497.
Patel, S. K., Pratap, C. B., Verma, A. K., Jain, A. K., Dixit, V. K., & Nath, G. (2013). World Journal of Gastroenterology, 19(7), 1056–1067.
Smoot, D. T. (1997). Gastroenterology, 113, 31–34.
Kim, T. S., Hur, J. W., Yu, M. A., Cheigh, C. I., Kim, K. N., Hwang, J. K., et al. (2003). Journal of Food Protection, 66(1), 3–12.
Simova, E. D., Beshkova, D. B., & Dimitrov, Z. H. P. (2009). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 106(10), 692–701.
Pingitore, E. V., Salvucci, E., Sesma, F., & Nader-Macías, M. E. (2007). Communicating Current Research Educational Topics Trends Applied Microbiology, 1, 557–568.
Cats, A., Kuipers, E. J., Bosschaert, M. A. R., Pot, R. G. J., Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C. M. J. E., & Kusters, J. G. (2003). Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 17, 429–435.
Motlagh, A. M., Johnson, M. C., & Ray, B. (1991). Journal of Food Protection, 54, 873–878.
Mahler, M., Janke, C., Wagner, S., & Hedrich, H. J. (2002). Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 37, 267–278.
Zhou, J. S., Shu, Q., Rutherfurd, K. J., Prasad, J., Birtles, M. J., Gopal, P. K., et al. (2000). International Journal of Food Microbiology, 56, 87–96.
Matsuzaki, T., Yamazaki, R., Hashimoto, S., & Yokokura, T. (1998). Journal of Dairy Science, 81, 48–53.
Matsuzaki, T., & Chin, J. (2000). Immunology and Cell Biology, 78, 67–73.
Kirjavainen, P. V., El-Nezami, H. S., Salminen, S. J., Ahokas, J. T., & Wright, P. F. (1999). FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology, 26, 131–135.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the contribution extended by Mrs. Nimpi Samplay, Department of Pharmacology, CT Institute, Jalandhar, Punjab, India during animal experimentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, B., Garg, N., Sachdev, A. et al. Effect of the Oral Intake of Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici BA28 on Helicobacter pylori Causing Peptic Ulcer in C57BL/6 Mice Models. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 973–983 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0585-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0585-4