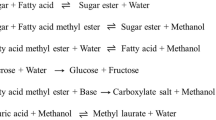Abstract
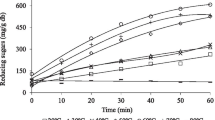
Multienzymatic conversion of sucrose into fructose and gluconic acid was studied through fed-batch and continuous (in a membrane reactor) processes. The law of substrate addition (sucrose or glucose) for the fed-batch process which led to a yield superior to 80% was the decreasing linear type, whose feeding rate (ϕ; L/h) was calculated through the equation: ϕ = ϕo − k.t, where ϕo (initial feeding rate, L/h), k (linear addition constant, L/h 2), and t (reaction time, h). In the continuous process, the yield of conversion of sucrose (Y) was superior to 70% under the following conditions: dilution rate = 0.33 h−1, total duration of 15 h, pH 5.0, 37 °C and initial sucrose concentration of 64 g/L (Y = 92%), 100 g/L (Y = 83%), or 150 g/L (Y = 76%).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goulas, A. K., Cooper, J. M., Grandison, A. S., & Rastall, R. A. (2004). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 88, 778–779.
Kennedy, J. F., Pimentel, M. C. B., Melo, E. H. M., & Lima-filho, J. L. (2007). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 87, 2266–2271.
Vaz, A. J., Takei, K., & Bueno, E. C. (2007). Immunoassays: fundamentals and applications (Guanabara Koogan, ed). Rio de Janeiro, 67.
Andreotti, D. Z., Tomotani, E. J., & Vitolo, M. (2010). European Biomass Conference and Exhibition from Research to Industry and Markets 18, 1367–1370. Lyon, France.
Tomotani, E. J., Vitolo, M., Felipe, M. G. A., & Arruda, P. V. (2010). International Congress on Biocatalysis, 5, from 29/08 to 02/09/2010, Hamburg, Germany. Biocat, 2010, 103–104.
Panke, S., & Wubbolts, M. G. (2005). Current Opin Chem Biol, 9, 188–194.
Sheu, D. C., Lio, P. J., Chen, S. T., Lin, C. T., & Duan, K. (2001). Biotechnology Letters, 23, 1499–1503.
Tomotani, E. J., & Vitolo, M. (2010). Brazilian. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 46(3), 571–577.
Neves, L. C. M., & Vitolo, M. (2007). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 136, 161–170.
Tomotani, E. J., & Vitolo, M. (2007). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 1020–1025.
Tomotani, E. J., Neves, L. C. M., & Vitolo, M. (2005). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 121, 149–162.
Sengupta, S., & Modak, J. M. (2001). Chemical Engineering Science, 56, 3315–3325.
Pérez-terrazas, J. E., Ibarra-junquera, V., & Rosu, H. C. (2008). Korean J Chemical Engineer, 25(3), 461–465.
Tomotani, E. J., & Vitolo, M. (2004). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 113, 145–159.
Taraboulsi, F. A., Jr., & Vitolo, M. (2010). Analytica, 8(47), 86–93.
Da Silva, A. R. (2010). Dissertation. Sao Paulo, Brazil: University of São Paulo, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Mansour, E. H., & Dawoud, M. (2003). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 83, 446–450.
Arruda, L. M., & Vitolo, M. (1999). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 8, 23–33.
Raba, J., & Mottola, H. A. (1995). Glucose oxidase as an analytical reagent. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 25(1), 1–42.
Fogarty, W. M., & Kelly, C. T. (1990). Microbial enzymes and biotechnology (2nd ed.). London: Elsevier Applied Science.
Wigley, R. C. (1996). Cheese and Whey. In T. Godfrey & S. West (Eds.), Industrial Enzymology (2nd ed., pp. 135–154). London: MacMillan LTDA.
Echegaray, O. F., Carvalho, J. C. M., Fernandes, A. N. R., Sato, S., Aquarone, E., & Vitolo, M. (2000). Biomass and Bioenergy, 19, 39–50.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial grant from CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa) and FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) and thank Philip Barsanti for revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taraboulsi, F.A., Tomotani, E.J. & Vitolo, M. Multienzymatic Sucrose Conversion into Fructose and Gluconic Acid through Fed-Batch and Membrane-Continuous Processes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 1708–1724 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9389-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9389-6