Abstract
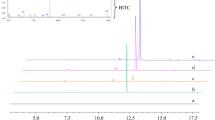
This paper studied the effects of different cooking conditions (methods, temperatures and time) on the retention rate of 4-(methylthio)-3-butenyl isothiocyanate (MTBITC) in Chinese white radish by using a method of ultrasound extraction coupled with gas chromatography—flame ionization detector (GC-FID). Results showed that the retention rate of MTBITC decreased with increasing cooking time and temperatures. The retention rate of MTBITC declined dramatically after holding for 1 min at 85 or 95 °C. The fitted equations demonstrated that the degradation of MTBITC followed an exponential decay pattern for non-microwave (water bath or steam stove) cooking, while for microwave cooking, the degradation of MTBITC followed approximately a linear decay.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, A., Boulaaba, A., Pingen, S., Krischek, C., & Klein, G. (2016). Low temperature cooking of pork meat—physicochemical and sensory aspects. Meat Science, 118, 82–88.
Blahovec, J., Kouřím, P., & Kindl, M. (2015). Low-temperature carrot cooking supported by pulsed electric field—DMA and DETA thermal analysis. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(10), 2027–2035.
Coogan, R. C., & Wills, R. B. H. (2002). Effect of drying and salting on the flavour compound of Asian white radish. Food Chemistry, 77, 305–307.
Cui, Z.-W., Xu, S.-Y. and Sun, D.-W. (2003). Dehydration of garlic slices by combined microwave-vacuum and air drying. Drying Technology, 21(7), 1173–1184.
Cui, Z.-W., Xu, S.-Y. and Sun, D.-W. (2004a). Effect of microwave-vacuum drying on the carotenoids retention of carrot slices and chlorophyll retention of Chinese chive leaves. Drying Technology, 22(3), 563–575.
Cui, Z.-W., Xu, S.-Y. and Sun, D.-W. (2004b). Microwave–vacuum drying kinetics of carrot slices. Journal of Food Engineering, 65(2), 157–164.
Ji, Y. L., Shen, Q., Lin, G. Q., Wang, L. Z., & Wang, S. T. (1996). Determination of MTB-GSL in radish by gas chromatography. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 19(4), 92–94.
Li, J., Xie, B. J., Yan, S. L., Li, H., & Wang, Q. Z. (2015). Extraction and determination of 4-methylthio-3-butenyl isothiocyanate in Chinese radish (Raphanussativus L.) roots. LWT–Food Science and Technology, 60(22), 1080–1087.
Okano, K., Asano, J., & Ishii, G. (1990). A rapid method for determining the pungent principle in Japanese radish (Raphanussativus L.). Journal of the Japanese Society for Horticultural Science, 59(3), 545–550.
Sang, J. P., Minchinton, I. R., Johnstone, P. K., & Truscott, R. J. W. (1984). Glucosinolate profiles in the seed, root, and leaf tissue of cabbage, mustard, radish and swede. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 64, 77–93.
Song, D., Liang, H., Kuang, P. Q., Tang, P. W., Hu, G. F., & Yuan, Q. P. (2013). Instability and structural change of 4-methylsulfinyl-3-butenyl isothiocyanate in the hydrolytic process. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(21), 5097–5102.
Visentin, M., Tava, A., & Iori, R. (1992). Isolation and identification of trans-4-(methylthio)-3-butenylglucosinolate from radish roots (Raphanussativus L.). Journal Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 40, 1687–1691.
Wang, P., Wei, M., Liu, X. X., Xu, W. L., Fu, W. M., Wang, C., & Wang, S. F. (2014). Study on influences of different fertilization treatments on flavor components in radish by GC-MS. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 46(9), 74–77.
Yasushi, N., Takako, I., Atsuo, T., Jun, K., & Tomoaki, M. (2001). 4-(methylthio)-3-butenyl isothiocyanate, a principal antimutagen in daikon (raphanussativus; Japanese white radish). Journal Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49, 5755–5760.
Yasushi, N., Kei, N., Yumi, A., Toyoaki, W., Kiwamu, T., Tomoaki, M., Shigehisa, O., Johan, M., Yasuki, K., Akiyoshi, N., Eun, Y. P., Kenji, S., & Kozo, O. (2008). Comparison of the glucosinolate-myrosinase systems among daikon (Raphanussativus, Japanese white radish) varieties. Journal Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56, 2702–2707.
You, H., Hao, R., Li, R., Zhang, L., Zhu, Y., & Luo, Y. B. (2015). The effect of radish sourced 4-(methylthio)-3-butenyl isothiocyanate on ameliorating the severity of high fat diet inducted nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 8(9), 15910–15919.
Zhang, W. Q. (1990). Determination of raphanin. Shandong Agricultural Science, 2, 10–13.
Zhang D. M. (2009) Radish fermentation with lactic acid bacteria as starter culture and volatile flavor components. MSc Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Key Projects of Administration of Ocean and Fisheries of Guangdong Province (A201401C04), the Collaborative Innovation Major Special Projects of Guangzhou City (201508020097), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2014A030313244), the International S&T Cooperation Program of China (2015DFA71150), the International S&T Cooperation Program of Guangdong Province (2013B051000010) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (2015ZM159). The authors also gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Guangdong Province Government (China) through the program “Leading Talent of Guangdong Province (Da-Wen Sun)” and the support of the collaborative research program between the Midea Group and South China University of Technology. In addition, the authors wish to acknowledge the contribution of Paul B McNulty, Emeritus Professor of Biosystems Engineering, University College Dublin, Ireland, who assisted in editing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhong Han and He Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Z., Li, H., Yu, XC. et al. Effects of Low Temperature Cooking on the Retention of 4-(Methylthio)-3-Butenyl Isothiocyanate (MTBITC) of Chinese White Radish (Raphanussativus L.). Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 1640–1647 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1787-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1787-x