Abstract
Purpose of Review
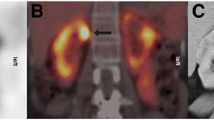
The majority of enhancing renal masses cannot be characterized through imaging as malignant or benign; however, such characterization could save patients from unnecessary surgery and/or biopsy and associated morbidity. Herein, we review the recent literature on the emerging use of 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT in preoperative differentiation of enhancing renal masses.
Recent Findings
Recent reports have shown that 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT imaging can differentiate mitochondrial-rich, benign, or indolent renal masses from renal cell carcinoma. These studies demonstrate good correlation between a positive 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT scan and a pathologically proven diagnosis of renal oncocytoma and hybrid oncocytic/chromophobe tumor. In addition, there is excellent correlation between a negative scan and a diagnosis of clear cell subtype of renal cell carcinoma.
Summary
Preoperative 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT offers a non-invasive method for differentiating renal lesions with low aggressiveness from other RCCs, in particular, clear cell renal cell carcinoma.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
Turner RM 2nd, Morgan TM, Jacobs BL. Epidemiology of the small renal mass and the treatment disconnect phenomenon. Urol Clin North Am. 2017;44(2):147–54.
Gordetsky J, Zarzour J. Correlating preoperative imaging with histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma and common mimickers. Curr Urol Rep. 2016;17(7):52.
Patel HD, Johnson MH, Pierorazio PM, Sozio SM, Sharma R, Iyoha E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and risks of biopsy in the diagnosis of a renal mass suspicious for localized renal cell carcinoma: systematic review of the literature. J Urol. 2016;195(5):1340–7.
Gorin MA, Rowe SP, Allaf ME. Oncocytic neoplasm on renal mass biopsy: a diagnostic conundrum. Oncology (Williston Park). 2016;30(5):426–35.
Campbell SC, Novick AC, Belldegrun A, Blute ML, Chow GK, Derweesh IH, et al. Guideline for management of the clinical T1 renal mass. J Urol. 2009;182(4):1271–9.
Johnson DC, Vukina J, Smith AB, Meyer AM, Wheeler SB, Kuo TM, et al. Preoperatively misclassified, surgically removed benign renal masses: a systematic review of surgical series and United States population level burden estimate. J Urol. 2015;193(1):30–5.
Violette P, Abourbih S, Szymanski KM, Tanguay S, Aprikian A, Matthews K, et al. Solitary solid renal mass: can we predict malignancy? BJU Int. 2012;110(11 Pt B):E548–52.
•• Sheikhbahaei S, Jones CS, Porter KK, Rowe SP, Gorin MA, Baras AS, et al. Defining the added value of 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT to conventional cross-sectional imaging in the characterization of enhancing solid renal masses. Clin Nucl Med. 2017;42(4):e188–e93. Demonstrated that the addition of 99m Tc-MIBI SPECT/CT uptake ratio to traditional cross-sectional imaging improves radiologists’ accuracy, confidence, and inter-reader agreement.
Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Sestamibi Injection package insert. http://www2mallinckrodtcom/Nuclear_Imaging/Tc-99m_Sestamibiaspx-sthashWi8PiTs7dpuf. Hazelwood: Mallinckrodt Inc; 2006.
Liddy S, Worsley D, Torreggiani W, Feeney J. Preoperative imaging in primary hyperparathyroidism: literature review and recommendations. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2017;68(1):47–55.
Taillefer R. The role of 99mTc-sestamibi and other conventional radiopharmaceuticals in breast cancer diagnosis. Semin Nucl Med. 1999;29(1):16–40.
Gormley TS, Van Every MJ, Moreno AJ. Renal oncocytoma: preoperative diagnosis using technetium 99m sestamibi imaging. Urology. 1996;48(1):33–9.
•• Rowe SP, Gorin MA, Gordetsky J, Ball MW, Pierorazio PM, Higuchi T, et al. Initial experience using 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT for the differentiation of oncocytoma from renal cell carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2015;40(4):309–13. Initial validation of the hypothesis that imaging with 99m Tc-MIBI SPECT/CT can differentiate benign solid renal tumors from ccRCCs.
Gorin MA, Rowe SP, Baras AS, Solnes LB, Ball MW, Pierorazio PM, et al. Prospective evaluation of (99m)Tc-sestamibi SPECT/CT for the diagnosis of renal oncocytomas and hybrid oncocytic/chromophobe tumors. Eur Urol. 2016;69(3):413–6.
•• Tzortzakakis A, Gustafsson O, Karlsson M, Ekstrom-Ehn L, Ghaffarpour R, Axelsson R. Visual evaluation and differentiation of renal oncocytomas from renal cell carcinomas by means of 99mTc-sestamibi SPECT/CT. EJNMMI Res. 2017;7(1):29. Independent corroboration of 99m Tc-MIBI SPECT/CT for differentiating benign solid renal tumors from ccRCCs.
Haake SM, Rathmell WK. Renal cancer subtypes: should we be lumping or splitting for therapeutic decision making? Cancer. 2017;123(2):200–9.
Delahunt B, Eble JN, McCredie MR, Bethwaite PB, Stewart JH, Bilous AM. Morphologic typing of papillary renal cell carcinoma: comparison of growth kinetics and patient survival in 66 cases. Hum Pathol. 2001;32(6):590–5.
Han G, Yu W, Chu J, Liu Y, Jiang Y, Li Y, et al. Oncocytic papillary renal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathological and genetic analysis and indolent clinical course in 14 cases. Pathol Res Pract. 2017;213(1):1–6.
Pierorazio PM, Hyams ES, Mullins JK, Allaf ME. Active surveillance for small renal masses. Rev Urol. 2012;14(1–2):13–9.
Pierorazio PM, Johnson MH, Ball MW, Gorin MA, Trock BJ, Chang P, et al. Five-year analysis of a multi-institutional prospective clinical trial of delayed intervention and surveillance for small renal masses: the DISSRM registry. Eur Urol. 2015;68(3):408–15.
Kawaguchi S, Fernandes KA, Finelli A, Robinette M, Fleshner N, Jewett MA. Most renal oncocytomas appear to grow: observations of tumor kinetics with active surveillance. J Urol. 2011;186(4):1218–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Andrew M. Reynolds and Kristin Kelly Porter each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on New Imaging Techniques
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynolds, A.M., Porter, K.K. Characterizing Indeterminate Renal Masses with Molecular Imaging: the Role of 99mTc-MIBI SPECT/CT. Curr Urol Rep 18, 86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-017-0737-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-017-0737-0