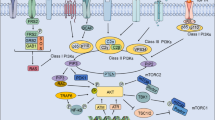
Abstract
The phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) pathway plays a critical role in cancer cell growth and survival. PI3K is activated in human cancers by elevated receptor tyrosine kinase activity, RAS mutation, as well as by mutation, amplification, and deletion of genes encoding components of the pathway. Additionally, PI3K pathway activation plays an important role in acquired resistance to both chemotherapy and targeted agents. The essential role of PI3K in human cancer has led to the development of PI3K pathway inhibitors that have shown promise in preclinical models and have entered phase 1 clinical trials. This article reviews preclinical and clinical data on members of this novel drug class, as well as data justifying the combination of PI3K inhibitors with other anticancer agents.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Engelman JA, Ji L, Cantley LC: The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet 2006, 7:606–619.
Hietakangas V, Cohen SM: Regulation of tissue growth through nutrient sensing. Annu Rev Genet 2009, 43:389–410.
• Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ: Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009, 8:627–644. This article provides an extremely informative review on the role of PI3K in cancer. It also reviews therapeutic approaches of targeting the PI3K pathway.
• Marone R, Cmiljanovic V, Giese B, Wymann MP: Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase: moving towards therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008, 1784:159–185. This excellent review thoroughly details the development of PI3K inhibitors.
Gupta S, Ramjaun AR, Haiko P, Wang Y, et al.: Binding of ras to phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110alpha is required for ras-driven tumorigenesis in mice. Cell 2007,129:957–968.
Fruman DA, Bismuth G: Fine tuning the immune response with PI3K. Immunol Rev 2009, 228:253–272.
Franke TF: PI3K/Akt: getting it right matters. Oncogene 2008, 27:6473–6488.
Amaravadi R, Thompson CB: The survival kinases Akt and Pim as potential pharmacological targets. J Clin Invest 2005, 115:2618–2624.
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM: Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell 2007, 12:9–22.
Carracedo A, Pandolfi PP: The PTEN-PI3K pathway: of feedbacks and cross-talks. Oncogene 2008, 27:5527–5541.
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, et al.: High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 2004, 304:554.
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9:550–562.
Martin-Berenjeno I, Vanhaesebroeck B: PI3K regulatory subunits lose control in cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 16:449–450.
Sujobert P, Bardet V, Cornillet-Lefebvre P, et al.: Essential role for the p110δ isoform in phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation and cell proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 106:1063–1066.
Zhao L, Vogt PK: Class I PI3K in oncogenic cellular transformation. Oncogene 2008, 27:5486–5496.
Jaiswal BS, Janakiraman V, Kljavin NM, et al.: Somatic mutations in p85alpha promote tumorigenesis through class IA PI3K activation. Cancer Cell 2009, 16:463–474.
Carpten JD, Faber AL, Horn C, et al.: A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature 2007, 448:439–444.
•• Faber AC, Li D, Song Y, et al.: Differential induction of apoptosis in HER2 and EGFR addicted cancers following PI3K inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106:19503–19508. This paper demonstrates that combination therapy with PI3K and MEK inhibitors can be effective in EGFR-addicted cancers.
• Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et al.: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316:1039–1043. This paper demonstrated that acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors can arise through MET amplification. The MET overexpression results in PI3K activation.
Engelman JA, Mukohara T, Zejnullahu K, et al.: Allelic dilution obscures detection of a biologically significant resistance mutation in EGFR-amplified lung cancer. J Clin Invest 2006, 116:2695–2706.
Jhawer M, Goel S, Wilson AJ, et al.: PIK3CA mutation/PTEN expression status predicts response of colon cancer cells to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cetuximab. Cancer Res 2008, 68:1953–1961.
Nagata Y, Lan KH, Zhou X, et al.: PTEN activation contributes to tumor inhibition by trastuzumab, and loss of PTEN predicts trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell 2004, 6:117–127.
Ihle NT, Williams R, Chow S, et al.: Molecular pharmacology and antitumor activity of PX-866, a novel inhibitor of phosphoinositide-3-kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 2004, 3:763–772.
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF: A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 1994, 269:5241–5248.
Garlich JR, De P, Dey N, et al.: A vascular targeted pan phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor prodrug, SF1126, with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res 2008, 68:206–215.
Ihle NT, Paine-Murrieta G, Berggren MI, et al.: The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor PX-866 overcomes resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib in A-549 human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 2005, 4:1349–1357.
Jimeno A, Hong DS, Hecker S, et al.: Phase I trial of PX-866, a novel phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI-3K) inhibitor. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2009, 27:3542.
Yu K, Lucas J, Zhu T, et al.: PWT-458, a novel pegylated-17-hydroxywortmannin, inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling and suppresses growth of solid tumors. Cancer Biol Ther 2005, 4:538–545.
Chiorean EG, Mahadevan D, Harris WB, et al.: Phase I evaluation of SF1126, a vascular targeted PI3K inhibitor, administered twice weekly IV in patients with refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2009, 27:2558.
Folkes AJ, Ahmadi K, Alderton WK, et al.: The identification of 2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-(4-methanesulfonyl-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-4-morpholin-4-yl-t hieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine (GDC-0941) as a potent, selective, orally bioavailable inhibitor of class I PI3 kinase for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 2008, 51:5522-5532.
Wagner AJ, Von Hoff DH, LoRusso PM, et al.: A first-in-human phase I study to evaluate the pan-PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 administered QD or BID in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2009, 27:3501.
Sarker D, Kristeleit R, Mazina KE, et al.: A phase I study evaluating the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of the oral pan-phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor GDC-0941. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2009, 27:3538.
Foster P: Potentiating the antitumor effects of chemotherapy with the selective PI3K inhibitor XL147. AACR Meeting Abstracts 2007, 2007:C199.
Shapiro G, Kwak E, Baselga J, et al.: Phase I dose-escalation study of XL147, a PI3K inhibitor administered orally to patients with solid tumors. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2009, 27:3500.
Faulkner N, LoRusso PM, Guthrie T, et al.: A phase 1 safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of the PI3K inhibitor XL147 (SAR245408) in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced solid tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 2009, 8:C197.
Wheler JJ, Traynor AM, Bailey HH, et al.: A phase 1 safety and pharmacokinectic (PK) study of the PI3K inhibitor XL147 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. Presented at the American Association for Cancer Research–National Cancer Institute–European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer International Conference on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics. Boston, MA; November 15–19, 2009:B247.
LoRusso P, Markman B, Tabernero J, et al.: A phase I dose-escalation study of the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics of XL765, a PI3K/TORC1/TORC2 inhibitor administered orally to patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2009, 27:3502.
Maira S-M, Stauffer Fdr, Brueggen J, et al.: Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther 2008, 7:1851–1863.
Eichhorn PJ, Gili M, Scaltriti M, et al.: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase hyperactivation results in lapatinib resistance that is reversed by the mTOR/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor NVP-BEZ235. Cancer Res 2008, 68:9221–9230.
Shaywitz AJ, Courtney KD, Patnaik A, Cantley LC: PI3K enters beta-testing. Cell Metabolism 2008, 8:179–181.
Billottet C, Grandage VL, Gale RE, et al.: A selective inhibitor of the p110delta isoform of PI 3-kinase inhibits AML cell proliferation and survival and increases the cytotoxic effects of VP16. Oncogene 2006, 25:6648–6659.
Uddin S, Hussain AR, Siraj AK, et al.: Role of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival. Blood 2006, 108:4178–4186.
•• Flinn IW, Byrd JC, Furman RR, et al.: Evidence of clinical activity in a phase 1 study of CAL-101, an oral P110δ isoform-selective inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, in patients with relapsed or refractory B-Cell malignancies. Presented at the 51st American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting. New Orleans, LA: December 5–8, 2009:922. This abstract describes preliminary results showing that single agent CAL-101 has produced several partial responses in B cell malignancies.
Gills JJ, Dennis PA: Perifosine: update on a novel Akt inhibitor. Curr Oncol Rep 2009, 11:102–110.
Tolcher AW, Yap TA, Fearen I, et al.: A phase I study of MK-2206, an oral potent allosteric Akt inhibitor (Akti), in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumor (ST). ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2009, 27:3503.
•• Brachmann SM, Hofmann I, Schnell C, et al.: Specific apoptosis induction by the dual PI3K/mTor inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 in HER2 amplified and PIK3CA mutant breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106:22299–22304. This paper demonstrates that NVP-BEZ235 is effective in HER2 amplified and PIK3CA mutant breast cancer cells. Importantly, it also shows that breast cancer cells with loss of PTEN function are resistant to NVP-BEZ235.
Sos ML, Fischer S, Ullrich R, Peifer M, Heuckmann JM, Koker M, et al.: Identifying genotype-dependent efficacy of single and combined PI3K- and MAPK-pathway inhibition in cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:18351-6.
Ozbay T, Durden DL, Liu T, et al.: In vitro evaluation of pan-PI3-kinase inhibitor SF1126 in trastuzumab-sensitive and trastuzumab-resistant HER2-over-expressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2009 Jul 28 (Epub ahead of print).
Junttila TT, Akita RW, Parsons K, et al.: Ligand-independent HER2/HER3/PI3K complex is disrupted by trastuzumab and is effectively inhibited by the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941. Cancer Cell 2009, 15:429–440.
•• Engelman JA, Chen L, Tan X, et al.: Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat Med 2008, 14:1351–1356. This paper shows that combined PI3K and MEK inhibition is effective in a RAS mutated model of murine lung cancer.
Hui RC, Gomes AR, Constantinidou D, et al.: The forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a increases phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt activity in drug-resistant leukemic cells through induction of PIK3CA expression. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28:5886–5898.
Ng SSW, Tsao MS, Chow S, Hedley DW: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 2000, 60:5451–5455.
Vasudevan KM, Barbie DA, Davies MA, et al.: AKT-independent signaling downstream of oncogenic PIK3CA mutations in human cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 16:21–32.
Toral-Barza L, Zhang WG, Lamison C, et al.: Characterization of the cloned full-length and a truncated human target of rapamycin: activity, specificity, and enzyme inhibition as studied by a high capacity assay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005, 332:304–310.
Disclosure
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cleary, J.M., Shapiro, G.I. Development of Phosphoinositide-3 Kinase Pathway Inhibitors for Advanced Cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 12, 87–94 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-010-0091-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-010-0091-6