Opinion statement
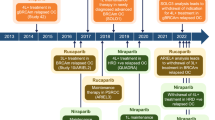
The treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is one of the great success stories in the field of oncology, which was revolutionized with the development of therapies aimed at disrupting crucial pathways. Tumor biology of RCC has provided insight into the disease through elucidation of the role of vascular endothelial growth-factor (VEGF) and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Targeted agents against VEGF and mTOR, as well as agents targeting relevant immunomodulatory pathways, have shown clinical benefit for advanced disease. The targeted agents are highly effective in achieving a response and survival, particularly in high-risk patients. These include the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) axitinib and cabozantinib, and programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) nivolumab and pembrolizumab. There is a wealth of evidence investigating different therapeutic options and combinations for first-line treatment of advanced RCC including the CheckMate 214 study, KEYNOTE-426, JAVELIN Renal 101, and CheckMate 9ER. Dual ICI and combination agents targeting the programmed cell death protein 1/programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (PD1/PDL1) and VEGF, began to demonstrate superiority over previously accepted standards in advanced clear-cell RCC. Data from a number of clinical studies are available to help physicians with evidence-based decisions for the sequence of second-line and future treatments for patients with progressive RCC. In this review, we focus on essentials for clinicians treating patients with clear-cell RCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: the 2019 update. Eur Urol. 2019;75(5):799–810.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Smaldone MC, Fung C, Uzzo RG, et al. Adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapies in high-risk renal cell carcinoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2011;25(4):765–91.
Sun M, Marconi L, Eisen T, et al. Adjuvant vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur Urol. 2018;74(5):611–20.
Correa AF, Jegede O, Haas NB, et al. Predicting renal cancer recurrence: defining limitations of existing prognostic models with prospective trial-based validation. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(23):2062–71.
Appleman LJ, Puligandla M, Pal SK, et al. Randomized, double-blind phase III study of pazopanib versus placebo in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who have no evidence of disease following metastasectomy: a trial of the ECOG-ACRIN cancer research group (E2810): American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2019.
Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(5):706–20.
Linehan WM, Walther MM, Zbar B. The genetic basis of cancer of the kidney. J Urol. 2003;170(6 Pt 1):2163–72.
Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(4):354–66.
Shen C, Kaelin WG Jr. The VHL/HIF axis in clear cell renal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013;23(1):18–25.
Sato Y, Yoshizato T, Shiraishi Y, et al. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2013;45(8):860–7.
Barata PC, Rini BI. Treatment of renal cell carcinoma: current status and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(6):507–24.
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(34):5794–9.
Rini BI, Dorff TB, Elson P, et al. Active surveillance in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a prospective, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(9):1317–24.
Harrison MR, Costello BA, Bhavsar NA, et al. Active surveillance of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from a prospective observational study (MaRCC). Cancer. 2021;127(13):2204–12.
Liu J, Blake SJ, Yong MC, et al. Improved efficacy of neoadjuvant compared to adjuvant immunotherapy to eradicate metastatic disease. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(12):1382–99.
Bhindi B, Abel EJ, Albiges L, et al. Systematic review of the role of cytoreductive nephrectomy in the targeted therapy era and beyond: an individualized approach to metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2019;75(1):111–28.
Méjean A, Ravaud A, Thezenas S, et al. Sunitinib Alone or after Nephrectomy in Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(5):417–27.
Lara PN Jr, Evans CP. Cytoreductive Nephrectomy in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer: Not All That It's Cut Out to Be. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(2):171–2.
Bakouny Z, Xie W, Dudani S, et al. Cytoreductive nephrectomy (CN) for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) or targeted therapy (TT): a propensity score-based analysis: American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2020.
Fallah J, Gittleman H, Weinstock C, et al. Survival benefit of nephrectomy prior to immunotherapy-based combinations in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an FDA pooled analysis: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2021.
Runcie K, Singer EA, Ornstein MC, et al. Cyto-KIK: A phase II trial of cytoreductive surgery in kidney cancer plus immunotherapy (nivolumab) and targeted kinase inhibition (cabozantinib): Wolters Kluwer Health; 2021.
Psutka SP, Master VA. Role of metastasis-directed treatment in kidney cancer. Cancer. 2018;124(18):3641–55.
Dragomir A, Nazha S, Wood LA, et al. Outcomes of complete metastasectomy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients: the Canadian Kidney Cancer information system experience. Urol Oncol. 2020;38(10):799.e1-.e10.
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, et al. Prognostic impact of metastasectomy in renal cell carcinoma in the postcytokine therapy era. Urol Oncol. 2021;39(1):77.e17-77.e25.
Bowman IA, Bent A, Le T, et al. Improved survival outcomes for kidney cancer patients with brain metastases. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019;17(2):e263–e72.
Wardak Z, Christie A, Bowman A, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases from renal-cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019;17(2):e273–e80.
Emamekhoo H, Olsen M, Carthon BC, et al. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab plus ipilimumab (NIVO+ IPI) in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC) with brain metastases: Interim analysis of CheckMate 920: American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2019.
Choueiri TK, Halabi S, Sanford BL, et al. Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of poor or intermediate risk: the Alliance A031203 CABOSUN Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(6):591–7.
McKay RR, Lin X, Perkins JJ, et al. Prognostic significance of bone metastases and bisphosphonate therapy in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2014;66(3):502–9.
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(22):2271–81.
Tykodi SS, Donskov F, Lee J-L, et al. First-line pembrolizumab (pembro) monotherapy in advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC): Updated results for KEYNOTE-427 cohort A: American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2019.
Donskov F, McDermott D, Lee J, et al. KEYNOTE-427 cohort A: pembrolizumab monotherapy as first-line therapy in advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Ann Oncol. 2018;29:viii307.
Atkins MB, Jegede O, Haas NB, et al. Phase II study of nivolumab and salvage nivolumab+ ipilimumab in treatment-naïve patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC)(HCRN GU16-260): American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2020.
Grimm M-O, Schmidinger M, Martinez ID, et al. Tailored immunotherapy approach with nivolumab in advanced renal cell carcinoma (TITAN-RCC). Ann Oncol. 2019;30:v892.
McKay RR, Xie W, McGregor BA, et al. Optimized management of nivolumab (Nivo) and ipilimumab (Ipi) in advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC): a response-based phase II study (OMNIVORE): American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2020.
Choueiri TK, Kluger HM, George S, et al. FRACTION-RCC: innovative, high-throughput assessment of nivolumab+ ipilimumab for treatment-refractory advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC): American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2020.
Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, et al. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(7):2105–16.
McDermott DF, Atkins MB. Application of IL-2 and other cytokines in renal cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004;4(4):455–68.
Dutcher JP, Schwartzentruber DJ, Kaufman HL, et al. High dose interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin) - expert consensus on best management practices-2014. J Immunother Cancer. 2014;2(1):26.
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(14):1277-90. This trial showed an efficacy and overall survival benefit of nivolumab plus ipilimumab over sunitinib in the first-line treatment of intermediate- or poor-risk advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma.
Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(12):1116-27. Based on these data, pembrolizumab plus axitinib indicated for use as first line therapy for patients with advanced RCC.
Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J, et al. Avelumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(12):1103-15. Axitinib plus avelumab improved progression-free survival, but not overall survival, in all patient subgroups relative to sunitinib.
Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):829-41. Based on these data, nivolumab + cabozantinib was FDA approved as first-line treatment for patients with advanced RCC.
Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY, et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(14):1289-300. For patients with treatment-naïve advanced RCC, the combination of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab improved both OS and PFS in a randomized phase III trial.
Motzer R, Tannir N, McDermott D, et al. 661P Conditional survival and 5-year follow-up in CheckMate 214: first-line nivolumab+ ipilimumab (N+ I) versus sunitinib (S) in advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). Annals of Oncology. 2021;32:S685–S7.
Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, et al. Pembrolizumab (pembro) plus axitinib (axi) versus sunitinib as first-line therapy for advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC): results from 42-month follow-up of KEYNOTE-426: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2021.
Motzer RJ, Choueiri TK, Powles T, et al. Nivolumab+ cabozantinib (NIVO+ CABO) versus sunitinib (SUN) for advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC): outcomes by sarcomatoid histology and updated trial results with extended follow-up of CheckMate 9ER: American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2021.
Motzer RJ, Porta C, Eto M, et al. Phase 3 trial of lenvatinib (LEN) plus pembrolizumab (PEMBRO) or everolimus (EVE) versus sunitinib (SUN) monotherapy as a first-line treatment for patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC)(CLEAR study): American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2021.
Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10189):2404–15.
Iacovelli R, Ciccarese C, Bria E, et al. Patients with sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma - re-defining the first-line of treatment: a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur J Cancer. 2020;136:195–203.
Schmidt A, Azad A, Goh J, et al. Treatment selection for first-line metastatic renal cell carcinoma in Australia: impact of new therapy options. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019;15(Suppl 10):3–10.
Naito S, Ichiyanagi O, Kato T, et al. Effect of third- and fourth-line systemic therapies for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15451.
Fischer S, Gillessen S, Rothermundt C. Sequence of treatment in locally advanced and metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Transl Androl Urol. 2015;4(3):310–25.
Deniz B, Ambavane A, Yang S, et al. Treatment sequences for advanced renal cell carcinoma: a health economic assessment. PLoS One. 2019;14(8):e0215761.
Albiges L, Voss MH, Rini BI, et al. Outcomes of patients who progressed while receiving avelumab+ axitinib (A+ Ax) and received subsequent treatment (Tx) in JAVELIN Renal 101: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2021.
Kotecha RR, Motzer RJ, Voss MH. Towards individualized therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16(10):621–33.
Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature. 2013;499(7456):43-9.
Emberley E, Bennett M, Chen J, et al., editors. CB-839, a selective glutaminase inhibitor, has anti-tumor activity in renal cell carcinoma and synergizes with cabozantinib and everolimus. Keystone Symposia, Tumor Metabolism: Mechanisms and Targets, Whistler Canada; 2017.
Tannir NM, Agarwal N, Porta C, et al. CANTATA: Primary analysis of a global, randomized, placebo (Pbo)-controlled, double-blind trial of telaglenastat (CB-839)+ cabozantinib versus Pbo+ cabozantinib in advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) patients (pts) who progressed on immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) or anti-angiogenic therapies. Wolters Kluwer Health; 2021.
Ornstein MC, Pal SK, Wood LS, et al. Individualised axitinib regimen for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma after treatment with checkpoint inhibitors: a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(10):1386–94.
Procopio G, Pircher C, Claps M, et al. A phase II open-label study of cabozantinib after first-line treatment including an immune-checkpoint combination in patients with advanced or unresectable renal cell carcinoma: The BREAKPOINT trial (MeetUro trial 03-EudraCT number 2018-000582-36). American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2021.
Powles T, Motzer RJ, Escudier B, et al. Outcomes based on prior therapy in the phase 3 METEOR trial of cabozantinib versus everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2018;119(6):663–9.
Marteau F, Harrow B, McCarthy C, et al. Cabozantinib versus other TKIs after CPI treatment in the real-world management of patients with mRCC: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2021.
Rini BI, Pal SK, Escudier BJ, et al. Tivozanib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (TIVO-3): a phase 3, multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(1):95–104.
Ravi P, Mantia C, Su C, et al. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of immunotherapy rechallenge in patients with renal cell carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(10):1606–10.
Gul A, Stewart TF, Mantia CM, et al. Salvage ipilimumab and nivolumab in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma after prior immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(27):3088–94.
Laccetti AL, Garmezy B, Xiao L, et al. Combination antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibition and anti-PD1 immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of safety, tolerance, and clinical outcomes. Cancer Med. 2021;10(7):2341–9.
Lee C-H, Shah AY, Hsieh JJ, et al. Phase II trial of lenvatinib (LEN) plus pembrolizumab (PEMBRO) for disease progression after PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mccRCC): American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2020.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Glen H, et al. Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(15):1473–82.
Bauer TM, Choueiri TK, Papadopoulos KP, et al. The oral HIF-2 α inhibitor MK-6482 in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC): updated follow-up of a phase I/II study: American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2021.
Choueiri TK, Bauer TM, McDermott DF, et al. Phase 2 study of the oral hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) inhibitor MK-6482 in combination with cabozantinib in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC): American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2021.
Haas NB, Manola J, Uzzo RG, et al. Adjuvant sunitinib or sorafenib for high-risk, non-metastatic renal-cell carcinoma (ECOG-ACRIN E2805): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10032):2008–16.
Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, et al. Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(23):2246–54.
Choueiri TK, Tomczak P, Park SH, et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as post-nephrectomy adjuvant therapy for patients with renal cell carcinoma: randomized, double-blind, phase III KEYNOTE-564 study. Am Soc Clin Oncol; 2021. Pembrolizumab is a potential new standard of care for patients with renal cell cancer with the risk of disease recurrence after surgery in the adjuvant setting.
Zehir A, Benayed R, Shah RH, et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):703–13.
Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Polak P, et al. Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature. 2013;499(7457):214–8.
Hsieh JJ, Chen D, Wang PI, et al. Genomic Biomarkers of a Randomized Trial Comparing First-line Everolimus and Sunitinib in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2017;71(3):405–14.
Voss MH, Reising A, Cheng Y, et al. Genomically annotated risk model for advanced renal-cell carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(12):1688–98.
Braun DA, Ishii Y, Walsh AM, et al. Clinical validation of PBRM1 alterations as a marker of immune checkpoint inhibitor response in renal cell carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(11):1631–3.
Braun DA, Hou Y, Bakouny Z, et al. Interplay of somatic alterations and immune infiltration modulates response to PD-1 blockade in advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med. 2020;26(6):909–18.
McDermott DF, Huseni MA, Atkins MB, et al. Clinical activity and molecular correlates of response to atezolizumab alone or in combination with bevacizumab versus sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med. 2018;24(6):749–57.
Choueiri TK, Albiges L, Haanen JB, et al. Biomarker analyses from JAVELIN Renal 101: Avelumab+ axitinib (A+ Ax) versus sunitinib (S) in advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2019.
Giannakis M, Li H, Jin C, et al. Metabolomic correlates of response in nivolumab-treated renal cell carcinoma and melanoma patients. American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2017.
Li H, Bullock K, Gurjao C, et al. Metabolomic adaptations and correlates of survival to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Bulent Cetin declares that he has no conflict of interest. Chiara A. Wabl declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ozge Gumusay declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the authors.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Genitourinary Cancers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cetin, B., Wabl, C.A. & Gumusay, O. Reshaping Treatment Paradigms for Advanced Renal Cell Cancer Patients and Improving Patient Management. Curr. Treat. Options in Oncol. 23, 609–629 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-022-00966-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-022-00966-0