Abstract
Background
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are widely used expensive medications.
Aims
We performed a cross-sectional study to determine the extent and indication of PPI use in Irish acute medical wards.
Methods
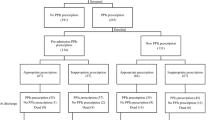
Fifty-five medical charts were reviewed at the beginning and end of 1 month.
Results and conclusions
Thirty-three patients were prescribed PPIs; 26 prior to admission. The prescribing of PPIs was concordant with guideline recommendations in only 30% of cases. Two-thirds of PPI use was unlicensed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HSE Primary Care Reimbursements Service. Statistical analysis of claims and payments 2006
British Medical Association and Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. British National Formulary, March 2006, p 48
Cunningham R, Dial S (2008) Is over-use of proton pump inhibitors fuelling the current epidemic of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea? J Hosp Infect 70:1–6
Laheij RJ, Sturkenboom MC, Hassing RJ, Dielman J, Stricker BH, Jansen JB (2004) Risk of community-acquired pneumonia and use of gastric acid-suppressive drugs. JAMA 292:1955–1960
Yang YX, Lewis JD, Epstein S, Metz DC (2006) Long-term PPI therapy and risk of hip fracture. JAMA 296(24):2947–2953
Gilard M, Arnaud B, Cornily JC et al (2008) Influence of omeprazole on the antiplatelet action of clopidogrel associated with aspirin: the randomized, double-blind OCLA (Omeprazole Clopidogrel Aspirin) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:256–260
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (2000) Guidance on the use of proton pump inhibitors for dyspepsia. http://www.nice.org.uk
Naunton M, Peterson GM, Bleasel MD (2000) Overuse of proton pump inhibitors. J Clin Pharm Ther 25:333–340
Sebastian SS, Kernan N, Qasim A, O’Morain CA, Buckley M (2003) Appropriateness of gastric antisecretory therapy in hospital practice. Ir J Med Sci 172(3):115–117
Van Vliet EP, Otten HJ, Rudolphus A et al (2008) Inappropriate prescription of proton pump inhibitors on two pulmonary medicine wards. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20(7):608–612
Mat Saad AZ, Collins N, Lobo M, O’Connor HJ (2005) Proton pump inhibitors: a survey of prescribing in an Irish General hospital. Int J Clin Pract 59(1):31–34
Reilly JP (1999) Safety profile of the proton-pump inhibitors. Am J Health Syst Pharm 56(23 Suppl 4):S11–S17
Laine L, Ahnen D, McClain C et al (2000) Review article: potential gastrointestinal effects of long-term acid suppression with proton pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 14:651–668
Mouly S, Charlemagne A, Le Jeunne P, Fagnani F (2008) General practitioners’ management of gastroesophageal reflux in France in 2005: a pharmacoeconomic study. Presse Med 37(10):1397–1406
Ryan G, Glynn L (2009) Overcoming barriers to rational prescribing. Forum J ICGP 26(2):40–42
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Murali Sayana, SpR, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Waterford Regional Hospital for the valuable suggestions in the writing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
D. Molloy and A. Molloy contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molloy, D., Molloy, A., O’Loughlin, C. et al. Inappropriate use of proton pump inhibitors. Ir J Med Sci 179, 73–75 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-009-0426-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-009-0426-1