Abstract
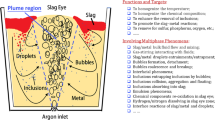
In the ladle metallurgy process, the bubble movement and slag layer behavior is very important to the refining process and steel quality. For the bubble–liquid flow, bubble movement plays a significant role in the phase structure and causes the unsteady complex turbulent flow pattern. This is one of the most crucial shortcomings of the current two-fluid models. In the current work, a one-third scale water model is established to investigate the bubble movement and the slag open-eye formation. A new mathematical model using the large eddy simulation (LES) is developed for the bubble–liquid-slag-air four-phase flow in the ladle. The Eulerian volume of fluid (VOF) model is used for tracking the liquid-slag-air free surfaces and the Lagrangian discrete phase model (DPM) is used for describing the bubble movement. The turbulent liquid flow is induced by bubble–liquid interactions and is solved by LES. The procedure of bubble coming out of the liquid and getting into the air is modeled using a user-defined function. The results show that the present LES–DPM–VOF coupled model is good at predicting the unsteady bubble movement, slag eye formation, interface fluctuation, and slag entrainment.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C D :
-
Drag force coefficient
- C VM :
-
Virtual mass force coefficient
- C S :
-
Smagorinsky constant
- d :
-
Distance to the closest wall
- d p :
-
Bubble diameter
- F D :
-
Momentum exchange coefficient
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{VM}} \) :
-
Virtual mass force
- \( \vec{F}_{\text{PG}} \) :
-
Pressure gradient force
- \( \vec{g} \) :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- L s :
-
Mixing length for subgrid scales
- n :
-
Number of bubbles
- P :
-
Pressure
- Q :
-
Gas flow rate
- Re :
-
Relative Reynolds number
- S :
-
Rate-of-strain tensor
- t :
-
Time
- \( \vec{u} \) :
-
Velocity
- V :
-
Cell volume
- α :
-
Volume fraction
- ρ :
-
Density
- τ :
-
Subgrid-scale stress
- μ :
-
Viscosity
- μ t :
-
Turbulent viscosity
- κ :
-
Von Kármán constant
- \( \delta_{\text{ij}} \) :
-
Dirac function
References
J.W. Han, S.H. Heo, D.H. Kam, B.D. You, J.J. Pak, and H.S. Song, ISIJ Int. 41, 1165 (2001).
K. Yonezawa and K. Schwerdtfeger, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 30B, 411 (1999).
V. Sahajwalla, A.H. Castillejos, and J.K. Brimacombe, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 21B, 71 (1990).
D. Mazumdar and J.W. Evans, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 35B, 400 (2004).
K. Krishnapisharody and G.A. Irons, ISIJ Int. 48, 1807 (2008).
B.K. Li, H.B. Yin, C.Q. Zhou, and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 48, 1704 (2008).
C.A. Llanos, S. Garcia, J.A. Ramos-Banderas, J.D.J. Barreto, and G. Solorio, ISIJ Int. 50, 396 (2010).
D. Guo and G.A. Irons, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 31B, 1457 (2000).
S.W.P. Cloete, J.J. Eksteen, and S.M. Bradshaw, Prog. Comput. Fluid Dynam. 9, 345 (2009).
H. Liu, Z. Qi, and M. Xu, Steel Res. Int. 82, 440 (2011).
Z.Q. Liu, B.K. Li, M.F. Jiang, and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 53, 484 (2013).
Z.Q. Liu, L.M. Li, B.K. Li, and M.F. Jiang, JOM 66, 1184 (2014).
F. Wang, B.K. Li, and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 47, 568 (2007).
A.B. Liu, D. Mather, and R.D. Reitz, Modeling the Effects of Drop Drag and Breakup on Fuel Sprays, SAE Technical Paper 930072 (Warrendale, PA: SAE, 1993).
J. Smagorinsky, Month. Wea. Rev. 91, 99 (1963).
M. Germano, U. Piomelli, P. Moin, and W.H. Cabot, Phys. Fluids A 3, 1760 (1991).
D.K. Lilly, Phys. Fluids A 4, 633 (1992).
M.T. Dhotre and B.L. Smith, Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 6615 (2007).
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China for support of this research (Grant No. 51210007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Liu, Z., Cao, M. et al. Large Eddy Simulation of Bubbly Flow and Slag Layer Behavior in Ladle with Discrete Phase Model (DPM)–Volume of Fluid (VOF) Coupled Model. JOM 67, 1459–1467 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1465-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1465-x