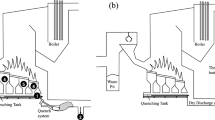
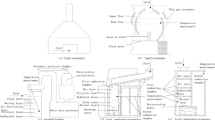
Abstract
The continuously increasing production of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash (MSWIBA) has promoted its utilization as construction material and raised environmental concern. The physico-chemical properties and leaching behavior of MSWIBA were studied, and ecotoxicological testing using a luminescent bacterium bioassay was performed to assess the ecological pollution risks associated with its leached constituents. The MSWIBA was leached by two types of leachants, H2SO4/HNO3 and HAc solution, at different liquid to solid ratios and contact times. The concentrations of heavy metals and anions in the leachates were analyzed. Multivariate statistical analyses, including principle component analysis, Pearson’s correlation analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis, were used to evaluate the contributions of the constituents to the toxicity (EC 50) of the MSWIBA leachate. The statistical analyses of the ecotoxicological results showed that the Ba, Cr, Cu, Pb, F−and total organic carbon (TOC) concentrations were closely correlated with the EC 50 value, and these substances were the main contributors to the ecotoxicity of the MSWIBA leachate. In addition, the cluster of these variables indicated similar leaching behaviors. Overall, the research demonstrated that the ecotoxicological risks resulting from MSWIBA leaching could be assessed before its utilization, which provides crucial information for the adaptation of MSWIBA as alternative materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang M B, Chung Y T. Dioxin contents in fly ashes of MSW incineration in Taiwan. Chemosphere, 1998, 36(9): 1959–1968
Wan X, Wang W, Ye T M, Guo Y W, Gao X B. A study on the chemical and mineralogical characterization of MSWI fly ash using a sequential extraction procedure. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 134(1–3): 197–201
National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistical Press, 2014 (in Chinese)
Yu J, Sun L, Xiang J, Jin L, Hu S, Su S, Qiu J. Physical and chemical characterization of ashes from a municipal solid waste incinerator in China. Waste Management & Research, 2013, 31(7): 663–673
Zhang H, He P J, Shao L M. Fate of heavy metals during municipal solid waste incineration in Shanghai. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 156(1–3): 365–373
Belevi H, Langmeier M. Factors determining the element behavior in municipal solid waste incinerators. 2. Laboratory experiments. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(12): 2507–2512
Chen P W, Liu Z S,WunMJ, Ran C L. Evaluating the mutagenicity of leachates obtained from the bottom ash of a municipal solid waste incinerator by using a Salmonella reverse mutation assay. Chemosphere, 2015, 124: 70–76
Dijkstra J J, van der Sloot H A, Comans R N J. The leaching of major and trace elements from MSWI bottom ash as a function of pH and time. Applied Geochemistry, 2006, 21(2): 335–351
Shim Y S, Rhee S W, Lee W K. Comparison of leaching characteristics of heavy metals from bottom and fly ashes in Korea and Japan. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2005, 25(5): 473–480
Feng S, Wang X, Wei G, Peng P, Yang Y, Cao Z. Leachates of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash from Macao: Heavy metal concentrations and genotoxicity. Chemosphere, 2007, 67(6): 1133–1137
Arickx S, Van Gerven T, Boydens E, L’hoëst P, Blanpain B, Vandecasteele C. Speciation of Cu in MSWI bottom ash and its relation to Cu leaching. Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 2(12): 3642–3650
Radetski C M, Ferrari B, Cotelle S, Masfaraud J F, Ferard J F. Evaluation of the genotoxic, mutagenic and oxidant stress potentials of municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash leachates. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 333(1–3): 209–216
Fan H J, Shu H Y, Yang H S, Chen W C. Characteristics of landfill leachates in central Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 361(1–3): 25–37
Barreto-Rodrigues M, Silva F T, Paiva T C B. Characterization of wastewater from the Brazilian TNT industry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 164(1): 385–388
Sponza D T, Oztekin R. Destruction of some more and less hydrophobic PAHs and their toxicities in a petrochemical industry wastewater with sonication in Turkey. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(22): 8639–8648
Zhang X X, Sun S L, Zhang Y, Wu B, Zhang Z Y, Liu B, Yang L Y, Cheng S P. Toxicity of purified terephthalic acid manufacturing wastewater on reproductive system of male mice (Mus musculus). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 176(1–3): 300–305
Farre M, Barcelo D. Toxicity testing of wastewater and sewage sludge by biosensors, bioassays and chemical analysis. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2003, 22(5): 299–310
Körner S, Das S K, Veenstra S, Vermaat J E. The effect of pH variation at the ammonium/ammonia equilibrium in wastewater and its toxicity to Lemna gibba. Aquatic Botany, 2001, 71(1): 71–78
Lah B, Vidic T, Glasencnik E, Cepeljnik T, Gorjanc G, Marinsek- Logar R. Genotoxicity evaluation of water soil leachates by Ames test, comet assay, and preliminary Tradescantia micronucleus assay. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2008, 139(1–3): 107–118
Huerta B B, Ferrer M P, Ribe V, Larsson M, Engwall M, Wojciechowska E, Waara S. Hazard assessment of sediments from a wetland system for treatment of landfill leachate using bioassays. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 97: 255–262
Stiernstrom S, Enell A, Wik O, Borg H, Breitholtz M. An ecotoxicological evaluation of aged bottom ash for use in constructions. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2014, 34(1): 86–92
Thomulka K W, McGee D J, Lange J H. Use of the bioluminescent bacterium Photobacterium phosphoreum to detect potentially biohazardous materials in water. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1993, 51(4): 538–544
Al-Mutairi N Z. Coagulant toxicity and effectiveness in a slaughterhouse wastewater treatment plant. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2006, 65(1): 74–83
Ren S. Assessing wastewater toxicity to activated sludge: recent research and developments. Environment International, 2004, 30(8): 1151–1164
Ye Z, Zhao Q, Zhang M, Gao Y. Acute toxicity evaluation of explosive wastewater by bacterial bioluminescence assays using a freshwater luminescent bacterium, Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. Nov. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2–3): 1351–1354
Zhu W, Wang J, Chen X, Zhaxi C, Yang Y, Song Y. A new species of luminous bacteria Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. Nov. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1994, 25: 273–280 (in Chinese)
Ma M, Tong Z, Wang Z, Zhu W. Acute toxicity bioassay using the freshwater luminescent bacterium Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. Nov.- Q67. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1999, 62(3): 247–253
Zhang H, He P J, Shao L M, Li X J. Leaching behavior of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash and its geochemical modeling. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2008, 10(1): 7–13
ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Assessing the Microbial Detoxification of Chemically Contaminated Water and Soil Using a Toxicity Test with a Luminescent Marine Bacterium. ASTM D56–96, Pennsylvania, United States, 2009
Fernández-Alba A R, Hernando Guil M D, López G D, Chisti Y. Comparative evaluation of the effects of pesticides in acute toxicity luminescence bioassays. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2002, 451(2): 195–202
Quevauviller P, Thomas O, van der Beken A. Wastewater Quality Monitoring and Treatment. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, England, 2006
Zheng W, Phoungthong K, Lü F, Shao L M, He P J. Evaluation of a classification method for biodegradable solid wastes using anaerobic degradation parameters. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2013, 33(12): 2632–2640
European Committee for Standardization. Unbound Mixtures- Specifications. CEN EN 1 3285, 2004
Chinese Standard. Standard for pollution control on the municipal solid waste incineration. GB 1 8485, 2014 (in Chinese)
Li X G, Lv Y, Ma B G, Chen Q B, Yin X B, Jian S W. Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash in blended cement. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2012, 32: 96–100
Rendek E, Ducom G, Germain P. Influence of waste input and combustion technology on MSWI bottom ash quality. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2007, 27(10): 1403–1407
Chang C Y, Wang C F, Mui D T, Cheng M T, Chiang H L. Characteristics of elements in waste ashes from a solid waste incinerator in Taiwan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1–3): 1351–1354
Rocca S, van Zomeren A, Costa G, Dijkstra J J, Comans R N J, Lombardi F. Characterisation of major component leaching and buffering capacity of RDF incineration and gasification bottom ash in relation to reuse or disposal scenarios. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2012, 32(4): 759–768
Ni M, Du Y, Lu S, Peng Z, Li X, Yan J, Cen K. Study of ashes from a medical waste incinerator in China: physical and chemical characteristics on fly ash, ash deposits and bottom ash. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2013, 32(3): 496–504
Li M, Xiang J, Hu S, Sun L S, Su S, Li P S, Sun X X. Characterization of solid residues from municipal solid waste incinerator. Fuel, 2004, 83(10): 1397–1405
Haykiri-Acma H, Yaman S, Ozbek N, Kucukbayrak S. Mobilization of some trace elements from ashes of Turkish lignites in rain water. Fuel, 2011, 90(11): 3447–3455
Saikia N, Kato S, Kojima T. Compositions and leaching behaviours of combustion residues. Fuel, 2006, 85(2): 264–271
Chang E E, Chiang P C, Lu P H, Ko Y W. Comparisons of metal leachability for various wastes by extraction and leaching methods. Chemosphere, 2001, 45(1): 91–99
Chiang K Y, Tsai C C, Wang K S. Comparison of leaching characteristics of heavy metals in APC residue from an MSW incinerator using various extraction methods. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2009, 29(1): 277–284
US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). RCRA training modules, Introduction to hazardous waste identification. Washington, DC., USA, 2003
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEP). Identification standards for hazardous wastes- Identification for extraction toxicity. GB 5085.3–2007. Beijing, China, 2007 (in Chinese)
Skodras G, Grammelis P, Prokopidou M, Kakaras E, Sakellaropoulos G. Chemical, leaching and toxicity characteristics of CFB combustion residues. Fuel, 2009, 88(7): 1201–1209
Barbosa R, Dias D, Lapa N, Lopes H, Mendes B. Chemical and ecotoxicological properties of size fractionated biomass ashes. Fuel Processing Technology, 2013, 109: 124–132
Ore S, Todorovic J, Ecke H, Grennberg K, Lidelöw S, Lagerkvist A. Toxicity of leachate from bottom ash in a road construction. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 2007, 27(11): 1626–1637
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phoungthong, K., Xia, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Leaching toxicity characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 10, 399–411 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0819-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0819-5