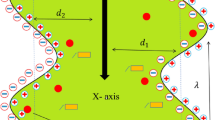
Abstract
Bioconvection plays an inevitable role in introducing sustainable and environment-friendly fuel cell technologies. Bio-mathematical modelling of such designs needs continuous refinements to achieve strong agreements in experimental and computational results. Actually, microorganisms transport a miscellaneous palette of ingredients in manufacturing industrial goods particularly in fertilizer industries. Heat transfer characteristics of molecular structure are measured by a physical phenomenon which is allied with the transpiration of heat within matter. Motivated by bio-inspired fuel cells involved in near-surface flow phenomena, in the present article, we examine the transverse swimming of motile gyrotactic microorganisms numerically in a rheological Jeffery fluid near a stretching wall. The leading physical model is converted in a nonlinear system of ODEs through proper similarity alterations. A numerical technique called shooting method with R-K Fehlberg is applied via mathematical software and graphical presentations are obtained. The influence of all relative physical constraints on velocity, temperature, concentration, and volume fraction of gyrotactic microorganisms is expressed geometrically. It is found that heat and mass flux at the surface as well as density of motile microorganism’s declines for Brownian motion and thermophoresis parameter. Comparison in tabular form is made with existing literature to validate the results for limiting cases with convective boundary conditions.
摘要
生物对流在可持续、环境友好型燃料电池技术中具有重要作用。这种设计的生物数学模型需要不断的改进,以在实验和计算结果中取得强有力的一致性。实际上,微生物在工业产品的制造过程中,特别是在肥料工业中,运输各种成分。通过与物质散热相关的物理现象来测量分子结构的传热特性。受仿生燃料电池近壁流动现象的启发,本文运用数值方法研究了在靠近伸展壁面的流变性Jeffery流体中运动的旋控微生物的横向游动。通过适当的相似度变换,将主导物理模型转化为非线性ODE 系统。采用R-K Fehlberg 打靶法在数学软件上进行数值模拟,得到所有物理条件对旋控微生物的速度、温度、浓度和体积分数的影响。结果表明,由于布朗运动和热泳参数的影响,表面的热通量和质量通量以及运动微生物的密度均有所下降。与已有文献进行比较,验证对流边界条件下极限情况结果的有效性。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HUSSAIN A, ZETOON R, ALI S, NADEEM S. Magnetically driven flow of pseudoplastic fluid across a sensor surface [J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2019, 41(4): 185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1691-1.
MEHMOOD R, NADEEM S, SALEEM S, AKBAR N S. Flow and heat transfer analysis of Jeffery nano fluid impinging obliquely over a stretched plate [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 74: 49–58. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.02.001.
ABD EL-AZIZ M, AFIFY A A. Influences of slip velocity and induced magnetic field on MHD stagnation-point flow and heat transfer of casson fluid over a stretching sheet [J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018: 9402836. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9402836.
VAJRAVELU K, SREENADH S, LAKSHMINARAYANA P. The influence of heat transfer on peristaltic transport of a Jeffrey fluid in a vertical porous stratum [J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2011, 16(8): 3107–3125. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2010.11.001.
SIVAIAH R, RAVIKUMAR S, HEMADRI REDDY R, SURESH GOUD J, SARAVANA R. Physical significance of rotation and hall current effects on hemodynamic physiological jeffery fluid with porous medium through a tapered channel [M]// Advances in Fluid Dynamics. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2020: 573–587. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4308-1_45.
ZHANG Li-jun, BHATTI M M, MARIN M, MEKHEIMER K S. Entropy analysis on the blood flow through anisotropically tapered arteries filled with magnetic zincoxide (ZnO) nanoparticles [J]. Entropy, 2020, 22(10): 1070. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101070.
HAYAT T, SHEHZAD S A, QASIM M, OBAIDAT S. Thermal radiation effects on the mixed convection stagnation-point flow in a jeffery fluid [J]. Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung A, 2011, 66(10, 11): 606–614. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5560/zna.2011-0024.
BABU D H, NARAYANA P V S. Joule heating effects on MHD mixed convection of a Jeffrey fluid over a stretching sheet with power law heat flux: A numerical study [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2016, 412: 185–193. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.04.011.
BHATTACHARYYA K, VAJRAVELU K. Stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet [J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2012, 17(7): 2728–2734. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.11.011.
MAHAPATRA T R, DHOLEY S, GUPTA A S. Heat transfer in oblique stagnation-point flow of an incompressible viscous fluid towards a stretching surface [J]. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 43(8): 767–773. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-006-0116-8.
SIAVASHI M, KARIMI K, XIONG Qin-gang, DORANEHGARD M H. Numerical analysis of mixed convection of two-phase non-Newtonian nanofluid flow inside a partially porous square enclosure with a rotating cylinder [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2019, 137(1): 267–287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7945-9.
GAROOSI F, GAROOSI S, HOOMAN K. Numerical simulation of natural convection and mixed convection of the nanofluid in a square cavity using Buongiorno model [J]. Powder Technology, 2014, 268: 279–292. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.08.006.
RANA S, MEHMOOD R, AKBAR N S. Mixed convective oblique flow of a Casson fluid with partial slip, internal heating and homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2016, 222: 1010–1019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.07.137.
ABU-NADA E, CHAMKHA A J. Mixed convection flow in a lid-driven inclined square enclosure filled with a nanofluid [J]. European Journal of Mechanics — B/Fluids, 2010, 29(6): 472–482. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2010.06.008.
KUMARI M. Variable viscosity effects on free and mixed convection boundary-layer flow from a horizontal surface in a saturated porous medium-variable heat flux [J]. Mechanics Research Communications, 2001, 28(3): 339–348. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0093-6413(01)00182-3.
IZADI A, SIAVASHI M, XIONG Qin-gang. Impingement jet hydrogen, air and CuH2O nanofluid cooling of a hot surface covered by porous media with non-uniform input jet velocity [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(30): 15933–15948. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.176.
MERKIN J H. Natural-convection boundary-layer flow on a vertical surface with Newtonian heating [J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 1994, 15(5): 392–398. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-727X(94)90053-1.
HAYAT T, FAROOQ M, ALSAEDI A. Homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in the stagnation point flow of carbon nanotubes with Newtonian heating [J]. AIP Advances, 2015, 5(2): 027130. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4908602.
QASIM M, KHAN I, SHAFIE S. Heat transfer in a micropolar fluid over a stretching sheet with Newtonian heating [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(4): e59393. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059393.
HAYAT T, KHAN M I, WAQAS M, ALSAEDI A. Newtonian heating effect in nanofluid flow by a permeable cylinder [J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 256–262. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.11.047.
IZADI A, SIAVASHI M, RASAM H, XIONG Qin-gang. MHD enhanced nanofluid mediated heat transfer in porous metal for CPU cooling [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 168: 114843. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114843.
SOLTANGHEIS S, SIAVASHI M, IZADI A A, XIONG Qingang. Semi-analytical study of impingement cooling of metal foam heat sinks of CPUs with air and hydrogen jets under LTNE condition [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2021, 145(4): 1801–1816. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10772-9.
SELİMEFENDİGİL F, ÖZCAN ÇOBAN S, ÖZTOP H F. Electrical conductivity effect on MHD mixed convection of nanofluid flow over a backward-facing step [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(5): 1133–1145.
NAYAK M K, MEHMOOD R, MAKINDE O D, MAHIAN O, CHAMKHA A J. Magnetohydrodynamic flow and heat transfer impact on ZnO-SAE50 nanolubricant flow over an inclined rotating disk [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(5): 1146–1160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4077-8.
JAVED M, FAROOQ M, AHMAD S, ANJUM A. Melting heat transfer with radiative effects and homogeneous: Heterogeneous reaction in thermally stratified stagnation flow embedded in porous medium [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(11): 2701–2711. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3947-9.
HAYAT T, MUHAMMAD K, ALSAEDI A, FAROOQ M. Features of Darcy-Forchheimer flow of carbon nanofluid in frame of chemical species with numerical significance [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(5): 1260–1270. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4085-8.
AHMED N, ABBASI A, KHAN U, ZAIDI S Z A, FAISAL I, MOHYUD-DIN S T. Heat transfer intensification in hydromagnetic and radiative 3D unsteady flow regimes: A comparative theoretical investigation for aluminum and γ-aluminum oxides nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(5): 1233–1249. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4083-x.
ZHANG Li-jun, BHATTI M M, MICHAELIDES E E. Electro-magnetohydrodynamic flow and heat transfer of a third-grade fluid using a Darcy-Brinkman-Forchheimer model [J]. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2021, 31(8): 2623–2639. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/hff-09-2020-0566.
KUZNETSOV A V. Thermo-bioconvection in a suspension of oxytactic bacteria [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2005, 32(8): 991–999. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2004.11.005.
KUZNETSOV A V. Investigation of the onset of bioconvection in a suspension of oxytactic microorganisms subjected to high-frequency vertical vibration [J]. Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2006, 20(2): 73–87. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-006-0007-0.
ALLOUI Z, NGUYEN T H, BILGEN E. Numerical investigation of thermo-bioconvection in a suspension of gravitactic microorganisms [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(7–8): 1435–1441. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2006.09.008.
ABDUL LATIFF N A, UDDIN M J, BÉG O A, ISMAIL A I. Unsteady forced bioconvection slip flow of a micropolar nanofluid from a stretching/shrinking sheet [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part N: Journal of Nanomaterials, Nanoengineering and Nanosystems, 2016, 230(4): 177–187. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1740349915613817.
TABAEI A, SADEGHI S, HOSSEINZADEH S, BIDABADI M, XIONG Qin-gang, KARIMI N. A simplified mathematical study of thermochemical preparation of particle oxide under counterflow configuration for use in biomedical applications [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2020, 139(4): 2769–2779. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08917-y.
RANA S, MEHMOOD R, NADEEM S. Bioconvection through interaction of Lorentz force and gyrotactic microorganisms in transverse transportation of rheological fluid [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2021, 145(5): 2675–2689. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09830-5.
GHORAI S, HILL N A. Gyrotactic bioconvection in three dimensions [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2007, 19(5): 054107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2731793.
BÉG O A, PRASAD V R, VASU B. Numerical study of mixed bioconvection in porous media saturated with nanofluid containing oxytactic microorganisms [J]. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 2013, 13(4): 1350067. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1142/s021951941350067x.
MEHMOOD R, TABASSUM R, KUHARAT S, BÉG O A, BABAIE M. Thermal slip in oblique radiative nano-polymer gel transport with temperature-dependent viscosity: Solar collector nanomaterial coating manufacturing simulation [J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2019, 44(2): 1525–1541. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3599-y.
TLILI I, WAQAS H, ALMANEEA A, KHAN S U, IMRAN M. Activation energy and second order slip in bioconvection of oldroyd-B nanofluid over a stretching cylinder: A proposed mathematical model [J]. Processes, 2019, 7(12): 914. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120914.
SIAVASHI M, RASAM H, IZADI A. Similarity solution of air and nanofluid impingement cooling of a cylindrical porous heat sink [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2019, 135(2): 1399–1415. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7540-0.
MEHMOOD R, NADEEM D S, AKBAR N. Oblique stagnation flow of Jeffery fluid over a stretching convective surface [J]. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2015, 25(3): 454–471. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/hff-01-2014-0019.
MAKINDE O D, AZIZ A. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with a convective boundary condition [J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2011, 50(7): 1326–1332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2011.02.019.
KHAN W A, POP I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(11, 12): 2477–2483. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.01.032.
WANG C Y. Free convection on a vertical stretching surface [J]. ZAMM-Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1989, 69(11): 418–420. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.19890691115.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Siddra RANA and Rashid MEHMOOD provided the concept and edited the draft of manuscript. M. M. BHATTI conducted the literature review and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Mohsan HASSAN edited the draft of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
Siddra RANA, Rashid MEHMOOD, M. M. BHATTI, Mohsan HASSAN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, S., Mehmood, R., Bhatti, M.M. et al. Swimming of motile gyrotactic microorganisms and suspension of nanoparticles in a rheological Jeffery fluid with Newtonian heating along elastic surface. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 3279–3296 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4855-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4855-y