Abstract
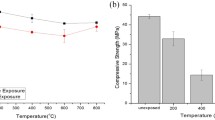
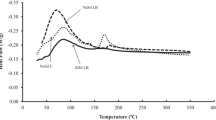
A comparative study of the influence of elevated temperature on foam geopolymer using circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash (CFA) was reported. Foam geopoymers were prepared with different amounts of foam agent and different SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratios of 3.1, 3.4, and 3.8. The mechanical, thermo-physical properties and microstructure of the foam geopolymers before and after exposure to elevated temperature of 800, 1000, and 1200 °C were investigated. The specimen with SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratio of 3.8 exhibits the highest compressive strength, better microstructure and dimension stability before and after firing. Carnegeite, nepheline, and zeolite crystalline phases appearing after exposure may contribute to the good post-exposure strength. Low weight foam geopolymer using CFA can increase strength and maintain higher stability as high as 1000 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DAVIDOVITS J. Geopolymer chemistry and applications [M]. Saint-Quentin (France): Institute Geopolymer, 2008: 2–20.
KOMNITSAS K, ZAHARAKI D. Geopolymerisation: A review and prospects for the minerals industry [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20: 1261–1277.
DUXSON P, PROVIS J L, LUKEY G C, van DEVENTER J S J. The role of inorganic polymer technology in the development of ‘green concrete’ [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2007, 37(12): 1590–1597.
LEE B K. Solid-gel interactions in geopolymers [D]. Melbourne: University of Melbourne, 2002.
SIDDIQUE R, KHAN M I. Supplementary cementing materials [M]. New York: Springer, 2011: 1–66.
SHI X S, COLLINS F G, ZHAO X L, WANG Q Y. Mechanical properties and microstructure analysis of fly ash geopolymeric recycled concrete [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 237–238: 20–29.
HAJI-ESMAEILI H. Admixtures for use in geopolymers [D]. Thunder Bay: Lakehead University, 2012.
NATALI A, MANZI S, BIGNOZZI M C. Novel fiber-reinforced composite materials based on sustainable geopolymer matrix [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 21: 1124–1131.
LIU Ze, SHAO Ning-ning, WANG Dong-min, QIN Jun-feng, HUANG Tian-yong, SONG Wei, LIN Mu-xi, YUAN Jin-sha, WANG Zhen. Fabrication and properties of foam geopolymer using circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash [J]. International Journal of Minerals: Metallurgy and Materials, 2014, 21(1): 89–93.
ABDULLAH M M A B, HUSSIN K, BNHUSSAIN M, ISMAIL K N, YAHYA Z, RAZAK R A. Fly ash-based geopolymer lightweight concrete using foaming agent [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2012, 13: 7186–7198.
THO-IN T, SATA V, CHINDAPRASIRT P, JATURAPITAKKUL C. Pervious high-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 30: 366–371.
RIAHI S, NAZARI A. The effects of nanoparticles on early age compressive strength of ash-based geopolymers [J]. Ceramics International, 2012, 38(6): 4467–4476.
DUXSON P, LUKEY G C, van DEVENTER J S J. Thermal evolution of metakaolin geopolymers: Part 1-Physical evolution [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2006, 352: 5541–5555.
DUXSON P, LUKEY G C, VAN DEVENTER J S J. Thermal conductivity of metakaolin geopolymers used as a first approximation for determining gel interconnectivity [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2006, 45: 7781–7788.
PROVIS J L, van DEVENTER J S J. Direct measurement of the kinetics of geopolymerisation by in-situ energy dispersive X-ray diffractometry [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42: 2974–2981.
NATH S K, KUMAR S. Influence of iron making slags on strength and microstructure of fly ash geopolymer [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 38: 924–930.
ZHANG Yao-jun, WANG Ya-chao, XU De-long, LI Sheng. Mechanical performance and hydration mechanism of geopolymer composite reinforced by resin [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 6574–6580.
BARBOSA V F F, MACKENZIE K J D. Thermal behaviour of inorganic geopolymers and composites derived from sodium polysialate [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2003, 38(2): 319–331.
HE Pei-gang, JIA De-chang, LIN Tie-song, WANG Mei-rong, ZHOU Yu. Effects of high-temperature heat treatment on the mechanical properties of unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced geopolymer composites [J]. Ceramics International, 2010, 36: 1447–1453.
KONG D L Y, SANJAYAN J G, SAGOE-CRENTSIL K. Comparative performance of geopolymers made with metakaolin and fly ash after exposure to elevated temperatures [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2007, 37: 1583–1589.
BAKHAREV T. Thermal behaviour of geopolymers prepared using class F fly ash and elevated temperature curing [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2006, 36: 1134–1147.
RICKARD W D A, TEMUUJIN J, van RIESSEN A. Thermal analysis of geopolymer pastes synthesised from five fly ashes of variable composition [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2012, 358: 1830–1839.
DOMBROWSKI K, BUCHWALD A, WEIL M. The influence of calcium content on the structure and thermal performance of fly ash based geopolymers [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(9): 3033–3043.
RICKARD W D A, VICKERS L, van RIESSEN A. Performance of fibre reinforced, low density metakaolin geopolymers under simulated fire conditions [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2012, 73: 71–77.
ZHAO Ye-long, YE Jun-wei, LU Xiao-bin, LIU Man-gang, LIN Yuan, GONG Wei-tao, NING Gui-ling. Preparation of sintered foam materials by alkali-activated coal fly ash [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174: 108–112.
PRUDHOMME E, MICHAUD P, JOUSSEIN E, CLACENS J M, ARII-CLACENS S, SOBRADOS I, PEYRATOUT C, SMITH A, SANZ J, ROSSIGNOL S. Structural characterization of geomaterial foams-Thermal behavior [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2011, 357: 3637–3647.
MASI G, RICKARD W D A, VICKERS L, BIGNOZZI M C, van RIESSEN A. A comparison between different foaming methods for the synthesis of light weight geopolymers [J]. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(9): 13891–13902.
LIEFKE E. Industrial applications of foamed inorganic polymers[C]// DAVIDOVITS J, DAVIDOVITS R, JAMES C. Proceeding of Geopolymer’ 99, Second International Conference. France, 1999: 189–195.
KHALE D, CHAUDHARY R. Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development: A review [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42: 729–746.
SILVA P D, SAGOE-CRENSTIL K. Medium-term phase stability of Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O geopolymer systems [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2008, 38: 870–876.
LIU Ze, SHAO Ning-ning, HUANG Tian-yong, QIN Jun-feng, WANG Dong-min, YANG Yu. Effect of SiO2/Na2O ratio on the properties of the foam geopolymer using circulating fluidized bed fly ash [J]. International Journal of Minerals: Metallurgy and Materials, 2014, 21(6): 620–626.
ZHANG Zu-hua, PROVIS J L, REID A, WANG Hao. Geopolymer foam concrete: An emerging material for sustainable construction [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 56: 113–127.
KONG D L Y, SANJAYAN J G, SAGOE-CRENSTIL K. Factors affecting the performance of metakaolin geopolymers exposed to elevated temperatures [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2008, 43(3): 824–831.
RICKARD W D A, WILLIAMS R, TEMUUJIN J, van RIESSEN A. Assessing the suitability of three Australian fly ashes as an aluminosilicate source for geopolymers in high temperature applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 3390–3397.
FERNANDEZ-JIMENEZ A, PALOMO A, PASTOR J Y, MARTIN A. New cementitious materials based on alkali-activated fly ash: Performance at high temperatures [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(10): 3308–3314.
WANG Hong-ling, LI Hai-hong, YAN Feng-yuan. Synthesis and mechanical properties of metakaolinite-based geopolymer [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2005, 268: 1–6.
DUXSON P, LUKEY G C, van DEVENTER J S J. Physical evolution of Na-geopolymer derived from metakaolin up to 1000 °C [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(9): 3044–3054.
DUXSON P, LUKEY G C, VAN DEVENTER J S J. The thermal evolution of metakaolin geopolymers: Part 2-Phase stability and structural development [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2007, 353: 2186–2200.
RICKARD W D A, van RIESSEN A, WALLS P. Thermal character of geopolymers synthesized from class F fly ash containing high concentrations of iron and a-quartz [J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2010, 7(1): 81–88.
PROVIS J L, HARREX R M, BERNAL S A, DUXSON P, van DEVENTER J S J. Dilatometry of geopolymers as a means of selecting desirable fly ash sources [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2012, 358: 1930–1937.
RAHIER H, WASTIELS J, BIESEMANS M, WILLEM R, van ASSCHE G, van MELE B. Reaction mechanism, kinetics and high temperature transformations of geopolymers [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42: 2982–2996.
BARBOSA V F F, MACKENZIE K J D, THAUMATURGO C. Synthesis and characterisation of materials based on inorganic polymers of alumina and silica: sodium polysialate polymers [J]. International Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2000, 2(4): 309–317.
GUNZLER H, GREMLICH H. IR spectroscopy: An introduction [M]. Germany: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, 2002: 203–214.
CHINDAPRASIRT P, JATURAPITAKKUL C, CHALEE W, RATTANASAK U. Comparative study on the characteristics of fly ash and bottom ash geopolymers [J]. Waste Management, 2009, 29: 539–543.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(20120023110011) supported by Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China; Projects(2009KH09, 2009QH02) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Shao, Nn., Qin, Jf. et al. Strength and thermal behavior of low weight foam geopolymer using circulating fluidized bed combustion fly ash. J. Cent. South Univ. 22, 3633–3640 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2904-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2904-0