Abstract
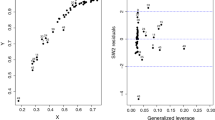
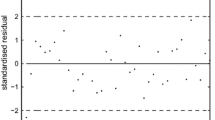
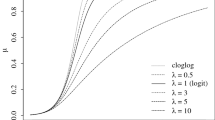
In this article, we consider the issue of assessing influence of observations in the general class of beta regression models introduced by Simas et al. (Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 54:348–366, 2010), which is very useful in situations in which the response is restricted to the standard unit interval (0,1). Our results generalize those in Espinheira et al. (Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 52:4417–4431, 2008a; J. Appl. Stat. 35:407–419, 2008b), which only apply to linear beta regression models. We define some residuals, and a Portmanteau test for serial correlation. Further, some influence methods, such as the global, local, and total local influence of an individual and generalized leverage, are discussed. Moreover, we also derive the normal curvatures of local influence under various perturbation schemes. Finally, simulation results and an application to real data show the usefulness of our results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson AC (1985) Plots, transformation and regression. Clarendon, Oxford
Cook RD (1977) Detection of influential observations in linear regression. Technometrics 19:15–18
Cook RD (1986) Assessment of local influence (with discussion). J R Stat Soc B 48:133–169
Cox DR, Hinkley DV (1974) Theoretical statistics. Chapman & Hall, London
Cook RD, Weisberg S (1982) Residuals and influence in regression. Chapman & Hall, London
Doornik JA (2006) Ox: an object-oriented matrix language. Timberlake Consultants Press, London
Espinheira PL, Ferrari SLP, Cribari-Neto F (2008a) Influence diagnostics in beta regression. Comput Stat Data Anal 52:4417–4431
Espinheira PL, Ferrari SLP, Cribari-Neto F (2008b) On beta regression residuals. J Appl Stat 35:407–419
Ferrari SLP, Cribari-Neto F (2004) Beta regression for modeling rates and proportions. J Appl Stat 31:799–815
Huet S, Bouvier A, Poursat MA, Jolivet E (2003) Statistical tools for nonlinear regression: a practical guide with S-PLUS and R. Springer, Berlin
Jørgensen B (1997) The theory of dispersion models. Chapman & Hall, London
Kieschnick R, McCullough B (2003) Regression analysis of variates observed on (0,1): Percentages, proportions, and fractions. Stat Model 3:193–213
Lawrance AJ (1988) Regression transformation diagnostic using local influence. J Am Stat Assoc 83:1067–1072
Leiva V, Barros M, Paula GA, Galea M (2007) Influence diagnostics in log-Birnbaum–Saunders regression models with censored data. Comput Stat Data Anal 51:5694–5707
Lemonte AJ (2009) Influence diagnostics in Birnbaum–Saunders nonlinear regression models. Working paper. arXiv:0904.4139
Lesaffre E, Verbeke G (1998) Local influence in linear mixed model. Biometrics 54:570–583
Li WK (1991) Testing model adequacy for some Markov regression models for time series. Biometrika 78:83–89
McCullagh P, Nelder J (1989) Generalized linear models, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, London
Paula GA (1993) Assessing local influence in restricted regression models. Comput Stat Data Anal 16:63–79
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (1992) Numerical recipes in C: the art of scientific computing, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Rocha AV, Cribari-Neto F (2009) Beta autoregressive moving average models. Test 18:529–545
Simas AB, Barreto-Souza W, Rocha AV (2010) Improved estimators for a general class of beta regression models. Comput Stat Data Anal 54:348–366
Thomas W, Cook RD (1990) Assessing influence on predictions from generalized linear models. Technometrics 32:59–65
Verbeke G, Molenberghs G (2000) Linear mixed models for longitudinal data. Springer, New York
Wei BC (1998) Exponential family nonlinear models. Springer, Singapore
Wei BC, Hu YQ, Fung WK (1998) Generalized leverage and its applications. Scand J Stat 25:25–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, A.V., Simas, A.B. Influence diagnostics in a general class of beta regression models. TEST 20, 95–119 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-010-0189-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-010-0189-z