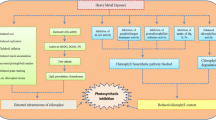
Abstract
Transport of photoassimilates linking functionally plant, as a whole system, is discussed as a target for different environmental stresses. Anatomical, physiological and biochemical aspects of phloem transport, phloem loading and unloading are taken into consideration. In the light of modern theoríes of assimilate transport some historical hypotheses are also shown, due to their input into the progress of transport science.
The role of phloem unloading in plant acclimation to environment stress is not clear, however changes in source/sink ratio was often observed as the effect of stress. The blockage of sieve tubes found as the result of given stress may be of secondary importance. On the other hand, phloem loading process seems to be an important target for different environmental stresses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloni B, Daie J, Wyse RE. 1986. Enhancement of [14C]sucrose from source leaves of Vicia faba by gibberellic acid. Plant Physiol. 82: 962–6.
Aikman D.P., Anderson W.P. 1971. A quantitative investigation of a peristaltic model for model translocation. Ann. Bot. 35:761–22.
Ameziane R., Limani M.A., Noctor G., Morot-Gaudry J.-F. 1995. Effect of nitrate concentration during growth on carbon partitioning and sink strength in chicory. J. Exp. Bot. 46: 1423–1428.
Anderson W.P. 1973. The mechanisms of phloem translocation. In: “Transport at the cellular level”, Eds. M.A. Sleigh, D.H. Jenings, Symp. Soc.Exp. Biol. No. 28.
Angelov M.N., Sung S.-J.S, Doong R.L., Harms W.R., Kormanik P.P., Black C.C. Jr. 1996. Long- and short-term flooding effects on survival and sink-source relationships of swamp-adapted tree species. Tree Physiol. 16: 477–484.
Basshman D.C., Raikhel N.V. 1996. Transport proteins in the plasma membrane and the secretory system. Trends in plant science. 1:15–20.
Behnke H.-D. 1995. Sieve-element characters of the Proteaceae and Elaeagnaceae: nuclear crystals, phloem proteins and sieve-element plastids. Bot. Acta 108: 467–538.
Blakeley S.D., Dennis D.T. 1993. Molecular approaches to the manipulation of carbon allocation in plants. Can. J. Bot. 71:765–778.
Boote K.J., Pickering N.B. 1993. Modeling photosynthesis of row crop canopies. Hort Sci. 29: 1423–1434.
Botha C.E.J 1992. Plasmodesmatal distribution, structure and frequency in relation to assimilation in C3 and C4 grasses in southern. Africa. Planta. 187:348–358.
Botha C.E.J., van Bel A.J.E. 1992. Quantification of symplastic continuity as visualised by plasmodesmograms: diagnostic value for phloem-loading pathways. Planta. 187:359–366.
Botha C.E.J., Cross R.H.M. 1997. Plasmodesmatal frequency in relation to short-distance transport and phloem loading in leaves of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Phloem is not loaded directly from the symplast. Physiol. Planta. 99: 355–362.
Bourquin S., Bonnemain J.-L., Delrot S. 1990. Inhibition of loading of 14C assimilates by p-chloromercuribenzene-sulfonic acid. Plant Physiol. 92: 97–102.
Bush D.R. 1993. Proton-coupled sugar and amino acid transporters in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44: 513–542.
Cakmak I., Hegeler Ch., Marschner H. 1994. Partitioning of shoot and root dry matter and carbohydrates in bean suffering from phosphorus, potassium and magnesium deficiency. J. Exp. Bot. 45: 1245–1250.
Cakmak I., Hengeler Ch., Marschner H. 1994. Changes in phloem export of sucrose in leaves in response to phosphorus, potassium, magnesium deficiency in bean plants. J. Exp. Bot. 45: 1251–1257.
Ciereszko I., Gniazdowska A., Mikulska M., Rychter A.M. 1996. Assimilate translocation in bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) during phosphate deficiency. J. Plant. Physiol. 149: 343–348.
Cote R., Thompson R.G., Grodziński B. 1992. Phothosynthetic oxygen production facilitates translocation of C-labelled photoassimilates from tendrils and leaflets of Pisum sativum L. J. Exp. Bot. 43: 819–829.
Cronshaw J. 1981. Phloem structure and function. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 32:465–84
Dannenhoffer J.M., Schulz A., Skaggs M.I., Bostwick D.E., Thompson G.A. 1997. Expresion of the phloem lecitin is developmentally linked to vascular differentiation in cucurbits. Planta. 201: 405–414.
DeJong T.M., Grossman Y.L. 1994. A supply and demand approach to modelling annual reproductive and vegetative growth of decidous fruit trees. Hort Sci. 29: 1435–1442.
Delucia E.H., Sasek T.W., Strain B.R. 1985. Photosynthetic inhibition after long-term exposure to elevated levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Photosynth. Res. 7: 175–184.
Dinar M., Rudich J., Zamski E. 1983. Effects of heat stress on carbon transport from tomato leaves. Ann. Bot. 51: 97–103
Du Y.Ch., Tachibana S. 1994. Photosinthesis, photosynthate translocation and metabolism in cucumber roots held at supraoptimal temperature. J. Japan. Soc. Hort. Sci. 63: 401–408.
Ehret D.L., Jolliffe P.A. 1985. Photosynthetic carbon dioxide exchange of bean plants grown at elevated carbon dioxide concentrations. Can. J. Bot. 63: 2026–2030.
Engels C. 1994. Effect of root and shoot meristem temperature on shoot to root dry matter partitioning and the internal concentrations of nitrogen and carbohydrates in maize and wheat. Ann. Bot. 73: 211–219.
Evert R.F. 1986. Phloem loading in maize. In: “Regulation of carbon and nitrogen reduction and utilization in maize”. Eds. J.C. Shannon, D.P. Knievel, C.D. Boyer, ch. 6.
Evert R.F., Mierzawa R.J. 1989. The cell wall-plasmalemma interface in sieve tubes of barley. Planta. 177: 24–34.
Farrar J.F. 1988. Temperature and the partitioning and translocation of carbon. In: “Plants and temperature” Eds. S.P. Long, F.I. Woodward. Symposia of the Society of Experimental Biology. 42. Cambridge: Company of Biologists. pp. 203–235.
Farrar J., van der Schoot, C., Drent P., van Bel A.J.E. 1992. Symplastic transport of lucifer yellow in mature leaf blades of barley: Potential mesophyll-to-sieve-tube transfer. New Phytol. 120: 191–196
Fellows R.J., Egli D.B., Leggett J.E. 1979. Rapid changes in translocation patterns in soybeans following source-sink alterations. Plant Physiol. 64: 652–655.
Fensom D.S. 1972. A theory of translocation in phloem of Heracleum by contactile protein microfibrillar material. Can. J. Bot. 50:479–97.
Fensom D.S., Williams E.J. 1974. A note on Allen’s suggestion for long-distance translocation in the phloem of plants. Nature 250:490–92.
Fondy B.R., Geiger D.R. 1980. Effect of rapid changes in sink-source ratio on export and distribution of products of photosynthesis in leaves of Beta vulgaris L. and Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 66: 945–949.
Fritz E., Evert R.F., Heyser W. 1983. Microautoradiographic studies of phloem loading and transport in the leaf of Zea mays. Planta. 159: 193–206.
Fromm J. 1991. Control of phloem unloading by action potentials in Mimosa. Physiol. Plant. 83: 529–533.
Galtier N., Foyer Ch.H., Murchine E., Alred R., Quick P., Voelker T.A., Thepenier C., Lasceve G., Betsche T. 1995. Effects of light and atmospheric carbon dioxide enrichment on photosynthesis and carbon partitioning in the leaves of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) plants over-expressing sucrose phosphate synthase. J. Exp. Bot. 46:1335–1344.
Gamalei Y.V. 1989. Structure and function of leaf minor veins in trees and herbs. A taxonomic review. Trees 3: 96–110.
Gamalei Y.V. 1991. Phloem loading and its development related to plant evolution from trees to herbs. Trees 5: 50–64.
Gamalei Y.V., van Bel A.J.E., Pakhomova M.V., Sjutkina A.V. 1994. Effects of temperature on the conformation of the endoplasmic reticulum and on starch accumulation in leaves with the symplasmic minor-vein configuration. Planta 194: 443–453.
Gedroc J.J., McConnaughay K.D.M., Coleman J.S. 1996. Plasticity in root/shoot partitioning: optimal, ontogenetic, or both? Functional Ecology. 10: 44–50.
Geiger D.B. 1974. Phloem loading and associated processes. In: “Phloem transport”. Eds. S.A. Aronoff, J. Dainty, P.R. Gorham, L.M. Srivastava, C.A. Swanson. New York. Plenum Press. pp. 251–281.
Geiger D.R., Sovonick S.S. 1975. Effects of temperature, anoxia and other metabolic inhibitors on translocation. In: “Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology”, New Series, vol. 1. Eds M.H. Zimmermann, J.A. Milburn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. pp. 256–287
Giaquinta R.T. 1983. Phloem loading of sucrose. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 34: 347–87.
Giaquinta R., Geiger D.R. 1977. Mechanism of cyanide inhibition of phloem translocation. Plant Physiol. 59: 178–180.
Gifford R.M., Evans L.T. 1981. Photosynthesis, carbon partitioning and yield. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 32: 485–509.
Gilder J., Cronshaw J. 1973. The distribution of adenosine triphosphatase activity in differentiating and mature phloem cells of Nicotiona tabacum and its relationship in phloem transport. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 44:388–404.
Goeschl J.D., Magnuson C.E., Fares Y., Jaeger C.H., Nelson C.E., Strain B.R. 1984. Spontaneous and induced blocking and unblocking of phloem transport. Plant, Cell Env. 7: 607–613.
Gould R.P., Minchin P.E.H., Young P.C. 1988. The effects of sulphur dioxide on phloem transport in two cereals. J. Exp. Bot. 39: 997–1007.
Grusak M.A., Lucas W.J. 1984. Recovery of cold-inhibited phloem translocation in sugar beet. J.Exp.Bot. 35:389–402.
Grusak M., Lucas W.J. 1985. Cold-inhibited phloem translocation in sugar beet. J. Exp. Bot. 36: 745–755.
Haritatos E., Keller F., Turgeon R. 1996. Raffinose oligosaccharide concentrations measured in individual cell and issue types in Cucumis melo L. leaves: implications for phloem loading. Planta. 198: 614–622.
Hejnowicz Z. 1970. Propagated disturbances of transverse potential gradient in intracellular fibrils as the source of motive forces for longitudinal transport in cells. Protoplasma. 71: 343–364
Herren T., Feller U. 1997. Influence of increased zinc levels on phloem transport in wheat shoots. J. Plant Physiol. 150: 228–231.
Heuvelink E. 1996. Re-interpretation of an experiment on the role of assimilate transport resistance in partitioning in tomato. Ann. Bot. 78: 467–470.
Ho L.C. 1988. Metabolism and compartmentation of imported sugars in sink organs in relation to sink strength. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 39: 355–378
Hoddinott J. 1983. The influence of light quality on carbohydrate translocation within corn leaf strips. New Phytol. 94: 351–358.
Hoddinott J., Ehret D.L., Gorham P.R. 1979. Rapid influences of water stress on photosynthesis and translocation in Phaeolus vulgaris. Can J. Bot. 57: 768–776.
Hole C.C., Dearman J. 1994. Sucrose uptake by the phloem parenchyma of carrot storage root. J. Exp. Bot. 45:7–15.
Huber S.C. 1983. Role of sucrose phosphate synthase in partitioning of carbon in leaves. Plant Physiol. 71:818–821.
Johnson R.P.C. 1968. Microfilaments in pores between froze-etched sieve elements. Planta 81:314–32
Jones R.J., Griffith S.M., Brenner M.L. 1986. Sink regulation of source activity by hormonal control. In: “Regulation of carbon and nitrogen reduction and utilization in maize”. Eds. J.C. Shannon, D.P. Knievel, C.D. Boyer. ch.17.
Kacperska A. 1998. Plant responses to low temperature stress: signalling pathways involved. In.: “Crop development for cool and wet European climate”. Eds. P. Sowinski, B. Zagdańska, A. Anioł. Brussels: European Cooperation in the Field of Scientific and Technical Research (COST), pp. 133–146. ISBN 92-828-1810-1.
Kaiser W.M., Martinoia E. 1985. Absence of an apoplasmic step in assimilate transport to the phloem? A comparison of assimilate efflux from leaf slices, mesophyll protoplasts and a unicellular green alga. J. Plant Physiol. 121: 463–474.
Kalt-Torres W., Kerr P.S., Usuda H., Huber S.C. 1987. Diurnal changes in maize leaf photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 83: 283–288.
Khamis S., Chaillou S., Lamaze T. 1990. CO2 assimilation and partitioning of carbon in maize plants deprived of orthophosphate. J. Exp.Bot. 41: 1619–1625.
Komor E., Orlich G., Weig A., Kockenberger W. 1996. Phloem loading — not metaphysical, only complex: towards a unified model of phloem loading. J. Exp. Bot. 47: 1155–1164.
Korner Ch., Pelaez-Riedl S., van Bel A.J.E. 1995. CO2 responsiveness of plants: a possible link to phloem loading. Plant, Cell Env. 18: 595–600.
Kuhn Ch., Franceschi V.R., Schulz A., Lemoine R., Frommer W.B. 1997. Macromolecular trafficking indicated by localization and turnover of sucrose transporters in enucleate sieve elements. Science. 275: 1298–1300.
Kuhn C., Quick W.P., Schulz A., Riesmeier J.W., Sonnewald U., Frommer W.B. 1996. Companion cell-specific inhibition of the potato sucrose transporter SUT1. Plant, Cell Env. 19: 1115–1123.
Kursanov, A.I. 1997. Plant Physiology in the system of biological disciplines. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 44: 694–696.
Lang A. 1983. Turgor — regulated translocation. Plant, Cell and Env. 6: 683–689.
Lee D.R., Arnold D.C. Fensom D.S. 1971. Some microscopical observations of functioning sieve tubes of Heracleum using Nomarski optics. J.Exp.Bot. 22:35–38
Lemoine R., Kuhn C., Thiele N., Delrot S., Frommer W.B. 1996. Antisense inhibition of sucrose transporter in potato: effects on amount and activity. Plant, Cell and Env. 19: 1124–1131.
Lenton J.R. 1984. Are plant growth substances involved in the partitioning of assimilate to developing reproductive sincs? Plant Growth Regulation. 2:267–276.
Levitt J. 1972. Responses of plants to environmental stress. Ed. T.T. Kozłowski, Academic Press, New York, pp. 1–43.
Lorenc-Plucińska G. 1993. SO2 modification of sugar movement in source leaves of Robinia pseudoacacia L. Arboretum Kórnickie. 38: 65–74.
Lorenz-Plucińska G., Ziegler H. 1987. Effect of sulfite and sufhydryl reagents on the phloem loading in cotyledons of Ricinus communis L. J. Plant. Phisiol. 128: 417–424.
Lorenz-Plucińska G., Ziegler H. 1993. Inhibition of phloem loading by sulfite affects sugar distribution in pea leaves. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 62: 175–178.
Lorenz-Plucińska G., Ziegler H. 1994. Sulfite sensitivity of sugar uptake by isolated veins of Pisum sativum. Photosynthetica. 30: 101–106.
Lucas W.J. 1985. Phloem-loading: A metaphysical phenomenon? In: “Regulation of carbon partitioning in photosynthetic tissue” Eds. R.L. Heath, J. Preiss. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville and Waverly Press, Baltimore, pp. 254–271.
MacRobie E.A.C. 1971. Phloem translocation. Facts and mechanisms: a comparative survey. Biol. Rev. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 46: 429–81.
Madore M.A., Webb J.A. 1981. Leaf free space analysis and vein loading in Cucurbita pepo. 59: 2550–2557.
Madore M.A., Oross J.W., Lucas W.J. 1986. Symplastic transport in Ipomea tricolor source leaves. Demonstration of functional symplastic connections from mesophyll to minor veins by novel dye-tracer method. Plant Physiol. 82: 432–42.
Marschner H., Kirkby E.A., Cakmak I. 1996. Effect of mineral nutrition status on shoot-root partitioning of photoassimilates and cycling of mineral nutrients. J. Exp. Bot. 47:1255–1263.
Maurosset L., Bonnemain J.-L. 1990. Mechanism of the inhibition of phloem loading by sodium sulfite: Effect of the pollutant on the transmembrane potential difference. Physiol. Plant. 80: 233–237.
Maynard J.W., Lucas W.J. 1982. Sucrose and glucose uptake into Beta vulgaris leaf tissues: A case for general (apoplastic) retrieval systems. Plant Physiol. 70: 1436–1443.
Martinez-Cortina C, Sanz, A. 1994. Effect of hormones on sucrose uptake and on ATPase activity of Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck leaves. Ann. Bot. 73: 331–5.
Mäkëla A.A., Sievanen R.P. 1987. Comparison of two shoot — root partitioning models with respect to substrate utilisation and functional balance. Ann. Bot. 59: 129–140.
McKinion J.M., Sequeira R.A. 1994. Mechanics of model building. Hort Sci. 29: 1413–1415.
Milburn J.A. 1980. The measurement of turgor pressure in sieve tubes. Ber. Deitsch. Bot. Ges. Bd. 93: 153–166.
Minchin P.E.H., Gould R. 1986. Effect of SO2 on phloem loading. Plant Science. 43:179–183.
Minchin P.E.H., Thorpe M.R. 1987. Is phloem transport due to a hydrostatic pressure gradient? Supporting evidence from pressure chamber experiments. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 14: 397–402.
Moing A., Carbonne F., Zipperlin B., Svanella L., Gaudillere J.-P. 1997. Phloem loading in peach: symplastic or apoplastic? Physiol. Plant. 101: 489–496.
Morris D.A. 1996. Hormonal regulation of source-sink relationships: an overview of potential control mechanisms. Photoassimilate distribution in plants and crops. 19: 441–465.
Münch E. 1930. Die Stoffbewegungen in der Pflanze. Gustav Fischer, Jena.
Neuhaus H.E., Quick W.P., Siegl G., Sitt M. 1990. Control of photosynthate partitioning in spinach leaves. Planta. 181: 583–592.
Ng C.K.Y. Hew Ch.S.H. 1996. Pathway of phloem loading in the C3 tropical orchid hybrid Oncidium Goldiana. J. Exp. Bot. 47: 1935–1939.
Niklas K.J., O’Rourke T.D. 1982. Growth patterns of plants that maximise vertical growth and minimize internal stress. Ann. J. Bot. 69: 1367–1374
Oparka K.J. 1990. What is phloem unloading? Plant Physiol. 94: 393–396.
Orlich G., Komor E. 1992. Phloem loading in Ricinus cotyledons: sucrose pathways via the mesophyll and apoplasm. Planta 187: 460–474.
Patrick J.W. 1997. Phloem unloading: sieve element unloading and post-sieve element transport. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Mol. Biol. 48: 191–222.
Patrick J.W., Offler C.E. 1995. Post-sieve element transport of sucrose in developing seeds. Aust. J. Plant. Physiol. 22: 681–702.
Pausch R.C., Mulchi Ch.L., Lee E.H., Foseth I.N., Slaughter. 1996. Use of 13C and 15N isotopes to investigate O3 effects on C and N metabolism in soybeans. Part 1. C fixation and translocation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 59: 69–80.
Potvin C., Goeschl J.D., Strain B.R. 1984. Effects of temperature and CO2 enrichment on carbon translocation of plants of the C4 grass species Echinochloa crusgalli (L.) Beauv. from cool and warm environments. Plant Physiol. 75: 1054–1057.
Reddy V.R., Pachepsky L.B., Acock B. 1994. Response of crop photosynthesis to carbon dioxide, temperature, and light: experimentation and modelling. Hort Sci. 29: 1415–1422.
Rentsch D., Frommer W.B. 1996. Molecular approaches towards an understanding of loading and unloading of assimilates in higher plants. J. Exp. Bot. 47.: 1199–1204.
Robidoux J., Sandborn E.B., Fensom D.S. Cameron M.L., 1973. Plasmatic filaments and particles in mature sieve elements of Heracleum sphondylium under the electron microscope. J.Exp.Bot. 24:349–59
Romberger J.A., Hejnowicz Z., Hill J.F. 1993. Plant structure: function and development. A treatise on anatomy and vegetative development with special reference to woody plants. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, London, Paris, Tokyo, Hong Kong, Barcelona, Budapest
Sakuth T., Schobert Ch., Pecsvaradi A., Eichholz A., Komor E., Orlich G. 1993. Specific proteins in the sieve-tube exudate of Ricinus communis L. seedlings: separation, characterization and in-vivo labelling. Planta. 191: 207–213.
Sasek T.W. Delucia E.H., Strain B.R. 1985. Reversibility of photosynthetic inhibition in cotton after long-term exposure to elevated CO2 concentrations. Physiol. Plant. 78: 619–622.
Schulz A. 1994. Phloem transport and differential in pea seedlings after source and sink manipulations. Planta. 192: 239–248.
Schulz A. 1995. Plasmodesmal widening accompanies the short-term increase in symplasmic phloem unloading in pea root tips under osmotic stress. Protoplasma. 188: 22–37.
Singh B.P. 1994. Modelling photosynthesis and carbon partitioning: Introduction to the workshop. Hort Sci. 29: 1412–1413.
Sjölund R.D. 1997. The phloem sieve element: A river runs through it. Plant Cell. 9: 1137–1146.
Slack G., Calvert A. 1977. The effect of truss removal on the yield of early sown tomatoes. J. Hort. Sci. 52: 309–315.
Smith J.A.C., Milburn J.A. 1980. Water stress and phloem loading. Ber. Deutsch. Bot. Bd. 93: 269–280.
Smith J.A.C., Milburn J.A. 1980. Osmoregulation and the control of phloem-sap composition in Ricinus communis L. Planta. 148: 28–34.
Sowiński P. 1992. Zmiany klimatu a rolnictwo. Biul. IHAR. 182: 21–30.
Sowiński P. 1995. Transport of assimilates from leaves to roots in chilling-treated maize seedlings. Acta Physiol. Plant. 17: 341–8.
Sowiński P. 1998a. Assimilate transport in maize seedlings treated with the moderate chilling. In: “Crop development for cool and wet European Climate”. Eds. P. Sowinski, B. Zagdańska, A. Anioł. Brussels: European Cooperation in the Field of Scientific and Technical Research (COST), pp. 65–69. ISBN 92-828-1810-1.
Sowiński P. 1998b. The effect of irradiance, p-chloromercuribenzensulphonic acid and fusicoccin on the long distance transport in Zea mays L. seedlings. Acta Physiol. Plant. 20:79–84.
Sowiński P, Królikowski Z. 1995. Chilling sensitivity in maize seedlings. III. Relations between growth and functioning at low temperatures and during post-stress recovery. Acta Physiol. Plant. 17, 219–24.
Sowiński P., Malaszewski S. 1989. Chiling-sensitivity in maize seedlings. I. Growth and functioning of shoots and roots. Acta Phisiol. Plant. 11: 165–171.
Sowiński P., Maleszwski S. 1990. Chilling-sensitivity in maize seedlings. II. Effect of low temperature on transport of 14C-assimilates from leaves to roots. Acta Physiol. Plant. 12: 35–40.
Sowiński P., Parys E., Dembiński E., Falfus J., Romanowska E., Ślaski J. 1991. Rośliny w zmieniającym się klimacie: efekt szklarniowy. Wiad. Bot.. 35:17–34.
Sowiński P., Richner W., Soldati A., Stamp P. 1998. Assimilate transport in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings at vertical low temperature gradients in the root zone. J. Exp. Bot. 49: 747–752.
Spanner D.C. 1975. The electroosmotic flow. In: “Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology”. Eds. M.H. Zimmermann, J.A. Milburn. vol. 1. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp. 301–327.
Spanner D.C. 1979. The electroosmotic theory of phloem transport: a final restatement. Plant, Cell and Env. 2: 107–121.
Stadler R., Brandner J., Schulz A., Gahrtz M., Sauer N. 1995. Phloem loading by the PmSUC2 sucrose carrier from Plantago major occurs into companion cells. Plant Cell. 7: 1545–1554.
Stadler R., Sauer N. 1996. The Arabidopsis thaliana AtSUC2 Gene is specifically expressed in companion cells. Bot. Acta. 109: 261–340.
Starck Z. 1995. Współzalezność pomiędzy fotosyntezą i dystrybucją asymilatów a tolerancją roślin na niekorzystne warunki środowiska. Postępy Nauk Rolniczych. nr 3, 19–35.
Starck Z., Niemyska B., Chołuj D. 1996. Post-effect to chilling stress on competitive ability of sinks in tomato plants. Acta Physiol. Planta. 18: 75–83.
Stitt M., Quick W.P. 1989. Photosynthetic carbon partitioning: its regulation and possibilities for manipulation. Physiol. Plant. 77: 633–641.
Sung F.J.M., Krieg D.R. 1979. Relative snsitivity of photosinthetic assimilation and translocation of 14C carbon to water stress. Plant Phisiol. 64: 852–856.
Thornley J.H.M. 1995. Shoot:root allocation with respect to C, N and P: an investigation and comparision of resistance and teleonomic models. Ann. Bot.. 75:391–405.
Thorpe M.R., Minchin P.E.H., Dye E.A. 1979. Oxygen effects on phloem loading. Plant Sci.Let.. 15: 345–350.
Thorpe M.R., Minchin P.E.H. 1987. Effects of anoxia on phloem loading in C3 and C4 species. J.Exp. Bot. 38: 221–232.
Toth F.K., Qi Wang, Sjölund R.D. 1994. Monoclonal antibodies against phloem P-protein from plant tissue cultures. I. Microscopy and biochemical analysis. Am. J. Bot. 81: 1370–1377.
Toth K.F., Sjölund R.D. 1994. Monoclonal antibodies against phloem P-protein from plant tissue cultures. II. Taxonomic distribution of cross-reactivity. Am. J. Bot. 81: 1378–1383.
Troughton J.H., Currie B.G. 1977. Relations between light level, sucrose concetration, and translocation of carbon 11 in Zea mays leaves. Plant Physiol. 59: 808–820.
Turgeon R. 1991. Symplastic phloem loading and the sink — source transition in leaves: a model. In: “Recent advances in phloem transport and assimilate compartmentation”. Eds. J.L. Bonnemain, S. Delrot, W.J. Lucas, J. Dainty. Quest Editions, Nates, pp. 18–22
Turgeon R. 1996. Phloem loading and plasmodesmata. Trends in plant science. 1: 418–423.
Van Bel A.J.L. 1987. The apoplast concept of phloem loading has no universal validity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 25: 677–686.
Van Bel A.J.L. 1992. Different phloem-loading machineries correlated with the climate. Acta Bot. Neerl. 41:121–141.
Van Bel A.J.E., Van Rijen H.V.M. 1994. Microelectrode-recorded development of the symplasmic autonomy of the sieve element/companion cell complex in the stem phloem of Lupinus luteus L. Planta 192: 165–175
Van Bel A.J.E., Hendriks J.H.M., Boon E.J.M.C., Gamalei Y.V., van Merwe A.Ph. 1996. Different ratios of sucrose/raffinose-induced membrane depolarizations in the mesophyll of species with symplasmic (Catharanthus roseus, Ocimum basilicum) or apoplasmic (Impatiens walleriana, Vicia faba) minor-vein configurations. Planta. 199: 185–192.
Van Oene M.A., Kolloffel C., Wolswinkel P. 1992. Sink-source interactions: accumulation of sucrose in the apoplast and symplast of the source leaves as a result of sink strength reduction in Pisum sativum L. Acta Bot. Neerl. 41: 143–149.
Verhey S.D., Lomax T.L. 1993. Signal tranduction in vascular plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 12: 179–195.
Vreugdenhil D. 1985. Source-to-sink gradient of potassium in the phloem. Planta. 163: 238–240.
Vreugdenhil D., Kerckhoffs L.H.J. 1992. Abscisic acid stimulates sucrose uptake into tobacco leaf discs. Acta Bot. Neerl. 41: 161–65.
Wang N., Fisher D.B. 1994. The use of fluorescent tracers to characterize the post-phloem transport pathway in maternal tissues of developing wheat grains. Plant Physiol. 104: 17–27.
Wang N., Nobel P.S. 1995. Phloem exudate collected via scale insect stylets for the CAM species Opuntia ficus-indica under current and doubled CO2 concetrations. Ann. Bot. 75: 525–532.
Wang Q., Monroe J., Sjölund R.D. 1995. Identification and characterization of a phloem- specific B-amylase. Plant Physiol. 109: 743–750.
Weatherley P.E., Johnson R.P.C. 1968. The form and function of the sieve tube: a problem in reconciliation. Int. Rev. Cytol. 24: 149–92.
Wong S.-C. 1990. Elevated atmospheric partial pressure of CO2 and plant growth II. Non-structural carbohydrate content in cotton plants and its effects on growth parameters. Photos. Res. 23: 171–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sowiński, P. Transport of photoassimilates in plants under unfavourable environmental conditions. Acta Physiol Plant 21, 75–85 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-999-0030-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-999-0030-z