Abstract
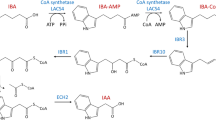
Stable lines of hairy roots were established from leaf explants of Bacopa monnieri using different strains (A4, R1000, SA79, MTCC 532 and MTCC 2364) of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. The efficiency of hairy roots induction of these strains varied significantly and the maximum transformation frequency (75 %) was observed in case of strain SA79 using leaf explants followed by internode (55 %) in the presence of acetosyringone. Different parameters such as cell density of Agrobacterium suspension, co-cultivation period and infection time influenced the root induction frequency. Maximum frequency of root induction was obtained with bacterial density of 0.6 OD600, 2 days of co-cultivation period and 10 min of infection time. Integration of T-DNA in the genome of hairy roots was confirmed by PCR amplification of rolB gene. Elimination of Agrobacterium from the established root cultures was ascertained by amplifying the DNA fragment specific to 16S rDNA and virD gene. All lines of hairy roots except strain A4 induced showed higher growth rate and accumulated higher levels of ‘bacoside A’ than the untransformed roots. Maximum biomass accumulation (6.8 g l−1) and ‘bacoside A’ content (10.02 mg g−1 DW) were recorded in case of the hairy root line induced by strain MTCC 2364.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal D, Jaiswal N, Kumar A, Reddy MS (2013) Factors affecting genetic transformation and shoot organogenesis of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 22:382–391
Alpizar E, Dechamp E, Espeout S, Royer M, Lecouls AC, Nicole M, Bertrand B, Lashermes P, Etienne H (2006) Efficient production of Agrobacterium rhizogenes-transformed roots and composite plants for studying gene expression in coffee roots. Plant Cell Rep 25:959–967
Anonymous (1988) Wealth of India, raw materials. Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi
Bansal M, Kumar A, Reddy MS (2014) Diversity among wild accessions of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. and their morphogenetic potential. Acta Physiol. doi:10.1007/s11738-014-1493-0
Barik DP, Mohapatra U, Chand PK (2005) Transgenic grasspea (Lathyrus sativus L.): factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and regeneration. Plant Cell Rep 24:523–531
Bulgakov VP (2008) Functions of rol genes in plant secondary metabolism. Biotechnol Adv 26:318–324
Chatterji N, Rastogi RP, Dhar ML (1965) Chemical examination of Bacopa monnieri Wettst.: parti-isolation of chemical constituents. Indian J Chem 3:24–29
Cho HJ, Widholm JM, Tanaka N, Nakanishi Y, Murooka Y (1998) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation and regeneration of the legume Astragalus sinicus (Chinese milk vetch). Plant Sci 138:53–65
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissues. Focus 12:13–15
Flores HE, Vivanco JM, Loyola-Vargas VM (1999) Radicle biochemistry: the biology of root-specific metabolism. Trends Plant Sci 4:220–226
Giri A, Narasu ML (2000) Transgenic hairy roots: recent trends and applications. Biotechnol Adv 18:1–22
Giri A, Ravindra ST, Dhingra V, Narasu ML (2001) Influence of different strains of Agrobacterium rhizogenes on induction of hairy roots and artemisinin production in Artemisia annua. Curr Sci 81:378–382
Holmes DS, Quigley M (1981) A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem 114:193–197
Jian B, Hou W, Wu C, Liu B, Liu W, Song S, Bi Y, Han T (2009) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of Superroot-derived Lotus corniculatus plants: a valuable tool for functional genomics. BMC Plant Biol 9:78
Jun YX, Qing Y, Qin J, Ming LY, Feng ZY, Ke G, Zhan WD (2007) Optimization of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation parameters for sweet potato embryogenic callus using beta -glucuronidase (GUS) as a reporter. Afr J Biotechnol 6:2578–2584
Kang HJ, Anbazhagan VR, You XL, Moon HK, Yi JS, Choi YE (2006) Production of transgenic Aralia elata regenerated from Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformed roots. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 85:187–196
Karthikeyan AS, Sarma KS, Veluthambi K (1996) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper. Plant Cell Rep 15:328–331
Lemcke K, Schmulling T (1998) A putative rol B gene homologue of Agrobacterium rhizogenes TL-DNA has different morphogenetic activity in tobacco than rolB. Plant Mol Biol 15:423–434
Majumdar S, Garai S, Jha S (2011) Genetic transformation of Bacopa monnieri by wild type strains of Agrobacterium rhizogenes stimulates production of bacopa saponins in transformed calli and plants. Plant Cell Rep 30:941–954
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Ooi CT, Syahida A, Stanslas J, Maziah M (2013) Efficiency of different Agrobacterium rhizogenes strains on hairy roots induction in Solanum mammosum. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:421–430
Pase MP, Kean J, Sarris J, Neale C, Scholey AB, Stough C (2012) The cognitive-enhancing effects of Bacopa monnieri: a systematic review of randomized, controlled human clinical trials. J Altern Complem Med 18:647–652
Porter RR (1991) Host range and implication of plant infection by Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Crit Rev Plant Sci 10:387–421
Potrykus I (1990) Gene transfer to plants: assessment and perspectives. Physiol Plant 79:125–134
Rahman LU, Verma PC, Singh D, Gupta MM, Banerjee S (2002) Bacoside production by suspension cultures of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell. Biotechnol Lett 24:1427–1429
Rajani M (2008) Bacopa monnieri, a nootropic drug. In: Ramawat KG, Merillon JM (eds) Bioactive molecules and medicinal plants. pp 175–195
Rastogi RP (1990) Compendium of Indian medicinal plants, vol 1. CSIR, New Delhi, pp 118–122
Russo A, Borrelli F (2005) Bacopa monniera, a reputed nootropic plant: an overview. Phytomedicine 12:305–317
Sevon N, Oksman-Caldentey KM (2002) Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated transformation: root cultures as a source of alkaloids. Planta Med 68:859–868
Sharma N, Satsangi R, Pandey R, Singh R, Kaushik N, Tyagi RK (2012) In vitro conservation of Bacopa monnieri (L.) using mineral oil. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 111:291–301
Shkryl YN, Veremeichik GN, Bulgakov VP, Tchernoded GK, Mischenko NP, Fedoreyev SA, Zhuravlev YN (2008) Individual and combined effect of the rol A, B and C genes on anthraquinone production in Rubia cordifolia transformed calli. Biotechnol Bioeng 100:118–125
Sonia Saini R, Singh RP, Jaiswal PK (2007) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transfer of Phaseolus vulgaris a-amylase inhibitor-1 gene into mungbean: Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek using bar as selectable marker. Plant Cell Rep 26:187–198
Srivastava S, Srivastava AK (2007) Hairy root culture for mass-production of high-value secondary metabolites. Crit Rev Biotechnol 27:29–43
Sujatha G, Zdravkovic-Korac S, alic DC, Flaminic G, Ranjitha Kumaria BD (2013) High-efficiency Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated genetic transformation in Artemisia vulgaris: Hairy root production and essential oil analysis. Ind Crop Prod 44:643–652
Tao J, Li L (2006) Genetic transformation of Torenia fournieri L. mediated by Agrobacterium rhizogenes. South Afr J Bot 72:211–216
Thimmaraju R, Venkatachalam L, Bhagyalakshmi N (2008) Morphometric and biochemical characterization of red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) hairy roots obtained after single and double transformations. Plant Cell Rep 27:1039–1052
Tiwari V, Singh BD, Tiwari NK (1998) Shoot regeneration and somatic embryogenesis from different explants of Brahmi Bacopa monniera (L.) Wettst. Plant Cell Rep 17:538–543
Tiwari RK, Trivedi M, Guang ZC, Guo GQ, Zheng GC (2007) Genetic transformation of Gentiana macrophylla with Agrobacterium rhizogenes: growth and production of secoiridoid glucoside gentiopicroside in transformed hairy root cultures. Plant Cell Rep 26:199–210
Tripathi N, Chouhan DS, Saini N, Tiwari S (2012) Assessment of genetic variations among highly endangered medicinal plant Bacopa monnieri (L.) from Central India using RAPD and ISSR analysis. 3. Biotech 2:327–336
Weisburg WA, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S rDNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Zehra M, Banerjee S, Sharma S, Kumar S (1999) Influence of Agrobacterium rhizogenes strains on biomass and alkaloid productivity in hairy root lines of Hyoscyamus muticus and H. albus. Planta Med 65:60–63
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to University Grant Commission (UGC), Govt. of India, New Delhi for the financial assistance. Professor A. K. Srivastava, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi is thanked for providing some of the strains of Agrobacterium rhizogenes and Professor Desh Bir Sharma is thanked for editing the English of the ms. Thanks are also due to TIFAC-CORE, Thapar University Patiala for the facilities to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K.-Y. Paek.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, M., Kumar, A. & Sudhakara Reddy, M. Influence of Agrobacterium rhizogenes strains on hairy root induction and ‘bacoside A’ production from Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst.. Acta Physiol Plant 36, 2793–2801 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1650-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1650-5