Abstract
Objective
To observe the clinical efficacy of electroacupuncture (EA) on Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Methods
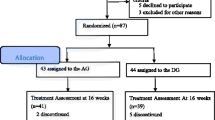
A total of 50 AD patients were randomly allocated into a Western medication (WM) group (n=25) and an acupuncture plus medication (APM) group (n=25). Patients in the WM group took oral huperzine A capsules. In addition to huperzine A capsules, patients in the APM group also received EA at Shenting (GV 24), Baihui (GV 20), Dazhui (GV 14), Fengfu (GV 16), Mingmen (GV 4) and Yongquan (KI 1). The needles on the above points were connected to G6805-II electric stimulator [3 pairs: Shenting (GV 24) and Baihui (GV 20); Dazhui (GV 14) and Fengfu (GV 16); and bilateral Yongquan (KI 1)]. The needles were retained 25 min. The treatment was done once a day, and 10 times made up a course of treatment. The patients received a total of 3 treatment courses. There was a 3-day interval between two courses. The mini-mental state examination (MMSE) and Hasegawa dementia scale revised (HDS-R) were conducted before and after treatment. The clinical efficacies were evaluated when the treatment was completed.
Results
Before treatment, there were no between-group statistical differences in MMSE and HDS-R scores (both P>0.05). After treatment, the MMSE and HDS-R scores in the APM group were significantly higher than those in the WM group (both P<0.05). The total effective rate in the APM group was 88.0%, versus 76.0% in the WM group, showing a statistical difference (P<0.05).
Conclusion
EA is effective for AD and can improve clinical symptoms in AD patients.
摘要
目的
观察电针治疗阿尔茨海默病(AD)的临床疗效, 探讨其临床应用价值。
方法
将50例AD 患者采用随 机数字表分为2组, 每组25例。西药组口服石杉碱甲胶囊; 针药组在口服石杉碱甲胶囊基础上加用电针治疗, 穴位 选神庭、百会、大椎、风府、命门和涌泉, 针刺得气后接G6805-II型电针治疗仪(神庭与百会为一组, 大椎和风 府为一组, 双侧涌泉为一组)。刺激量以患者能够耐受为度。每次留针25 min, 每日1次, 连续10次为1疗程, 两个 疗程间休息3 d, 共治疗3个疗程。治疗前后进行简易精神状态检查量表(MMSE)和修订后的长谷川智能量表(HDS-R) 评分, 并于治疗结束后进行临床疗效评价。
结果
治疗前两组MMSE 及HDS-R 评分均无统计学差异(均P>0.05)。 治疗后针药组MMSE 和HDS-R 评分均明显高于西药组(均P<0.05)。治疗后针药组总有效率为88.0%, 西药组为 76.0%, 针药组的临床疗效优于西药组(P<00.05)。
结论
电针是治疗AD 的有效方法, 能有效改善AD 患者的临床 症状, 提高疗效。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma HJ, Tang N, Li YY, Cao CD, Yi ZX, Zhang WN. Advance in acupuncture treatment for senile dementia. Guangxi Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao, 2012, 15(2): 84–86.
Cardoso SM, Santana I, Swerdlow RH, Oliveira CR. Mitochondria dysfunction of Alzheimer’s disease cybrids enhances Abeta toxicity. J Neurochem, 2004, 89(6): 1417–1426.
Huang HM, Fowler C, Xu H, Zhang H, Gibson GE. Mitochondrial function in fibroblasts with aging in culture and/or Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging, 2005, 26(6): 839–848.
Deng HM, Xiao F, Yang L, Zhu MM, Huang F. Research survey on inflammatory mechanism and related drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. Guangdong Yixue, 2010, 31(16): 2170–2172.
Small GW, Rabins PV, Barry PP, Buckholtz NS, De Kosky ST, Ferris SH, Finkel SI, Gwyther LP, Khachaturian ZS, Lebowitz BD, Mc Rae TD, Morris JC, Oakley F, Schneider LS, Streim JE, Sunderland T, Teri LA, Tune LE. Diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer disease and related disorders. Consensus statement of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the American Geriatrics Society. JAMA, 1997, 278(16): 1363–1371.
Wang P, Yang J, Wang P. Research advance in acupuncture treatment for vascular dementia. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jizheng, 2011, 20(11): 1814–1816.
WHO. ICD-10 1989 Draft of Chapter V: Mental and Behavioural disorder’s (including disorders of psychological development). WHO, 1989: 60-68.
Wei QX, Zhang XM, Yan XY, Yan YJ, Chen SL. Clinical observation on butylphthalide combined acupuncture for Alzheimer’s disease. Xiandai Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2011, 20(3): 291–292.
Zhang MY. Handbook of Psychiatric Rating Scale. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 2003: 154–159.
Tang CM. Neuropsychology. Beijing: People’s Military Medical Press, 2001: 343–344.
Fu RJ. Diagnosis, pattern identification and efficacy evaluation criteria for senile dementia. Zhongyi Zazhi, 1991, 32(2): 56.
Kuang ML, Zhang J. Effects of sargassum fusiforme phlorotanninon on the senile dementia mouse model induced by D-galactose. Guangdong Yixue, 2014, 35(13): 1984–1986.
Tian TT, Zhang YL, Cui YW, Gao C, Han WW, Li Q. A systematic review on acupuncture versus Western medication for senile dementia. Changchun Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2012, 28(1): 48–50.
Zhou CX, Hu YS, Cui X, Ni HH, Wu J, Shi JC. Observation on therapeutic effect of acupuncture combined with herbal medicine and cognitive training on mild cognitive impairment in patients with post-stroke. Zhenjiu Linchuang Zazhi, 2012, 28(8): 1–4.
Sun JP, Zhang XZ, Zhang Y, Xu SS. Progress in the treatment of vascular dementia with acupuncture and moxibustion. Zhonghua Zhenjiu Dianzi Zazhi, 2014, 3(2): 34–36.
Jiang MC, Liang J, Wang JR, Zhang YJ, He XD, Xu JY. Effect of moxibustion on the learning and memory of rat models of Alzheimer’s disease and the expreßsion of hippocampal Aß, IL-1β and IL-2. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2016, 35(7): 870–875.
Liu YM, Zhao BX, Liu JT, Huang C, Han L. Exploration on application of acupuncture and moxibustion in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2016, 35(11): 1375–1377.
Ren XL, Zhang HY, Li YZ. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of huperzine A for mild and moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Zhongguo Yaofang, 2010, 21(10): 909–913.
Peng J, Luo L, Xu L, Chen X. Therapeutic efficacy observation on electroacupuncture for Alzheimer’s disease. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2015, 13(3): 171–174.
Liu P, Liu Z, Wei JR, Xia W. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and learning and memory in rats with vascular dementia. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi, 2013, 28(9): 822–825.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Key Research Project of Science and Technology Bureau of Leshan Town (乐山市 科技局重点研究项目, No. 15ZDYJ0150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, J., Chen, X., Wang, Ap. et al. Efficacy evaluation on electroacupuncture for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 15, 296–299 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1017-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-017-1017-8
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Acupuncture Medication Combined
- Alzheimer Disease
- Dementia
- Rehabilitation
- Mental Status Schedule