Abstract
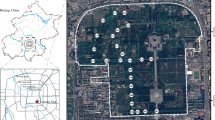
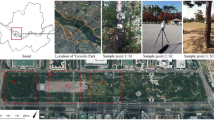
Taking a certain housing in Guangzhou as an example, we conduct the field measurement of the microclimate at fixed points for air temperature, relative humidity, black globe temperature and wind speed, etc. We investigate the effects of manmade lake, shade of trees and ground surface character on outdoor thermal environment, and make a quantitative analysis on the weighting position of the landscape design factors in design behavior. The study intends to explore a method to improve the thermal environment of residential quarters by changing the corresponding factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenberg N J, Blad B L, Verma S B. Microclimate: The Biological Environment. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1983
Zhou Suzhen, Shu Jiong. Urban Meteorology. Beijing: Meteorology Press, 1994 (in Chinese)
Chinese Academic of Building Science. Green Building Evaluation Code GB/T 50378-2006. Beijing: Chinese Building Industry Press, 2006 (in Chinese)
Guangzhou: Urban heat island effects releases. [2004-September-14]. http://info.hvacr.hc360.com/HTML/001/033/002/36844.htm (in Chinese)
US Green Building Council. Leadership on Energy and Environment Design. 2nd version. Beijing: Chinese Building Industry Press, 2000 (in Chinese)
Bonan G B. The microclimates of a suburban Colorado landscape and implications for planning and design. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2000, 49: 97–114
Dong Liang. Researches on the Thermal Environment in Street Canyons. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Architecture and Technology, 1994 (in Chinese)
Lin Borong. Researches of the Vegetation Impacts on Outdoor Thermal Environment. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2004 (in Chinese)
Li Xiaofeng. Researches on Simulation Methods of Microclimate in Residential Communities. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2003 (in Chinese)
Huang Liangmei, Li Jianlong, Zhao Dehua, Zhu Jiyu. A fieldwork study on the diurnal changes of urban microclimate in four types of ground cover and urban heat island of Nanjing, China. Building and Environment, 2008, 43(1): 7–17 (in Chinese)
Weather in Guangzhou. http://www.tqyb.com.cn/index.asp (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Architectural Journal, 2008, (11): 24–27 [译自: 建筑学报]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Zhao, L., Meng, Q. et al. Field measurements on microclimate in residential community in Guangzhou, China. Front. Archit. Civ. Eng. China 3, 462–468 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-009-0066-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-009-0066-6