Abstract
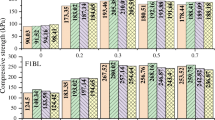
In order to study the influence of organic matter on the mechanical properties of stabilized soil and the effect of XGL2005 on stabilizing organic soil, unconfined compressive strength tests were carried out. Test results indicated that the strength of stabilized soil decreased in the form of a logarithmic function as the organic matter content increased. In contrast, the strength increased in the form of a power function as the content of the stabilization agent increased. The strength of cement stabilized organic soil was reinforced greatly by adding the stabilizer XGL2005. Based on the law obtained from the test, a strength prediction model was established by regression analysis. The model included the influence of the curing time, the content of the cement, the organic matter content and the stabilization agent on the strength of stabilized soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan Zhaoping, Zhu Wei, Zhang Chunlei. Experimental study on influence of organic matter content on solidified dredging. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(8): 1327–1334 (in Chinese)
Chen Su, Song Shaohua, Shen Jianlin, et al. Experimental study on mechanical property of cement-stabilized dark soil in DJM pile. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(3): 302–305 (in Chinese)
Tang Yixin, Liu Hanlong, Zhu Wei. Study on engineering properties of cement-stabilized soil. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2000, 22(5): 549–554 (in Chinese)
Chu Chengfu, Hong Zhenshun, Liu Songyu, et al. Prediction of unconfined compressive strength of cemented soils with quasi-water-cement ratio. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(4): 645–649 (in Chinese)
Horpibulsuk S, Norihiko M, Nagaraj T S. Clay-water/cement ratio identity for cement admixed soft clays. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvionmental Engineering, 2005, 131(2): 187–192
Lee F H, Lee Y, Chew S H. Strength and modulus of marine clay-cement mixes. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvionmental Engineering, 2005, 131(2): 178–186
Bush W H, Keller G H. The physical properties of Peru-Chile continental margin sediments-the influence of coastal upwelling on sediment properties. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1981, 51: 705–719
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2007, 41(1): 109–113 [译自: 浙江 大学学报(工学版)]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, R., Guo, Y. & Liu, Z. Mechanical properties of stabilized artificial organic soil. Front. Archit. Civ. Eng. China 2, 161–165 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-008-0023-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-008-0023-9