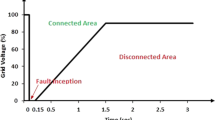
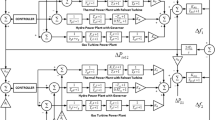
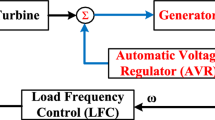
Abstract
This paper presents an adaptive neuro fuzzy interference system (ANFIS) based approach to tune the parameters of the static synchronous compensator (STATCOM) with frequent disturbances in load model and power input of a wind-diesel based isolated hybrid power system (IHPS). In literature, proportional integral (PI) based controller constants are optimized for voltage stability in hybrid systems due to the interaction of load disturbances and input power disturbances. These conventional controlling techniques use the integral square error (ISE) criterion with an open loop load model. An ANFIS tuned constants of a STATCOM controller for controlling the reactive power requirement to stabilize the voltage variation is proposed in the paper. Moreover, the interaction between the load and the isolated power system is developed in terms of closed loop load interaction with the system. Furthermore, a comparison of transient responses of IHPS is also presented when the system has only the STATCOM and the static compensation requirement of the induction generator is fulfilled by the fixed capacitor, dynamic compensation requirement, meanwhile, is ful-filled by STATCOM. The model is tested for a 1% step increase in reactive power load demand at t = 0 s and then a sudden change of 3% from the 1% at t = 0.01 s for a 1% step increase in power input at variable wind speed model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murthy S S, Malik O P, Tandon A K. Analysis of self-excited induction generator. IEE Proceedings, 1982, 129(6): 261–266
Bansal R C, Bhatti T S, Kothari D P. Bibliography on the application of induction generators in nonconventional energy systems. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2003, 18(3): 433–439
Bansal R C. Three phase self-excited induction generators: an overview. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2005, 20(2): 292–299
Singh G K. Self-excited induction generator research—a survey. Electric Power Systems Research, 2004, 69(2–3): 107–114
Sharma P, Kumar Saxena N, Ramakrishna K S S, Bhatti T S. Reactive power compensation of isolated wind-diesel hybrid power systems with STATCOM and SVC. International Journal on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 2010, 2(3): 192–203
Suresh Babu A, Saibabu C. Simulation studies on automatic generation control in deregulated environment without considering GRC. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2012, 4(3): 912–921 (IJEST)
Muyeen S M, Ali M H, Takahashi R, Murata T, Tamura J. Stabilization of wind farms connected with multi machine power system by using STATCOM. In: Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Power Technology. Lausanne, Switzerland, 2007, 1–5
Singh B, Murthy S S, Gupta S. Analysis and design of STATCOM based voltage regulator for self-excited induction generators. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2004, 19(4): 783–790
Craven R H, Michael M R. Load representations in the dynamic solution of the Queensland power system. Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, 1983, 3(1): 1–7
Saxena N, Kumar A. Load modeling interaction on hybrid power system using STATCOM. In: Proceedings of 2010 Annual IEEE India Conference, Kolkata, India, 2010
Kassem A M, Yousef A M. Robust control of an isolated hybrid wind-diesel power system using Linear Quadratic Gaussian approach. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2011, 33(4): 1092–1100
Bansal R C. Automatic reactive power control of autonomous hybrid power system. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Centre for Energy Studies, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, India, 2002
Sharma P, Saxena N K, Bhatti T S. Study of autonomous hybrid power system using SVC and STATCOM. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Power Systems. Kharagpur, India, 2009, 1–5
Bansal R C, Bhatti T S, Kumar V. Reactive power control of autonomous wind diesel hybrid power systems using ANN. In: Proceedings of the International Power Engineering Conference 2007. Singapore, 2007, 982–987
Leidhold R, Garcia G, Valla M I. Induction generator controller based on the instantaneous reactive power theory. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2002, 17(3): 368–373
Milanovic J V, Hiskens I A. Effect of load dynamics on power system damping. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 1995, 10 (2): 1022–1028
Hiskens I A, Milanovic J V. Load modeling in studies of power system damping. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 1995, 10(4): 1781–1788
Fraile-Ardanuy J, Zufiria P J. Adaptive power system stabilizer using ANFIS and genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference. Seville, Spain, 2005, 8028–8033
Dastranj M R, Ebrahimi E, Changizi N, Sameni E. Control DC motor speed with adaptive neuro fuzzy control (ANFIS). Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 2011, 5(10): 1499–1504
Kusagur A, Kodad S F, Sankar Ram B V. Modeling, design & simulation of an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) for speed control of induction motor. International Journal of Computers and Applications, 2010, 6(12): 29–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, N., Kumar, A. Reactive power compensation of an isolated hybrid power system with load interaction using ANFIS tuned STATCOM. Front. Energy 8, 261–268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-014-0298-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-014-0298-6