Abstract
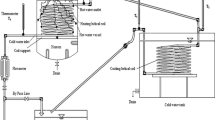
Forced convection heat transfer of single-phase water in helical coils was experimentally studied. The testing section was constructed from a stainless steel round tube with an inner diameter of 10 mm, coil diameter of 300 mm, and pitch of 50 mm. The experiments were conducted over a wide Reynolds number range of 40000 to 500000. Both constant-property flows at normal pressure and variable-property flows at supercritical pressure were investigated. The contribution of secondary flow in the helical coil to heat transfer was gradually suppressed with increasing Reynolds number. Hence, heat transfer coefficients of the helical tube were close to those of the straight tube under the same flow conditions when the Reynolds number is large enough. Based on the experimental data, heat transfer correlations for both incompressible flows and supercritical fluid flows through helical coils were proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merkel F. Die Grundlagen der Warmeubertragung. Berlin: Springer Publishing Company, 1927
Seban R A, Mclanghlin E F. Heat transfer in tube coils with laminar and turbulent flow. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1963, 6(5): 387–395
Rogers G F C, Mayhew Y R. Heat transfer and pressure loss in helically coiled tubes with turbulent flow. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1964, 7(11): 1207–1216
Mori Y, Nakayama W. Study on forced convection heat transfer in curved pipes (2nd report, turbulent region). International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1967, 10(1): 37–59
Guo L J, Chen X J, Feng Z P, Bai B F. Transient convective heat transfer in a helical coiled tube with pulsatile fully developed turbulent flow. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1998, 41(19): 2867–2875
Pioro I L, Duffey R B. Experimental heat transfer in supercritical water flowing inside channels (survey). Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2005, 235(22): 2407–2430
Taler J, Zima W. Solution of inverse heat conduction problems using control volume approach. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1999, 42(6): 1123–1140
Wagner W, Pruß A. The IAPWS formulation 1995 for the thermodynamic properties of ordinary water substance for general and scientific use. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 2002, 31: 387–535
Yamagata K, Nishikawa K, Hasegawa S, Fujii T, Yoshida S. Forced convective heat transfer to supercritical water flowing in tubes. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1972, 15(12): 2575–2593
Xu F. Study of water flow and heat transfer characteristics through pipes under supercritical pressure. Dissertation for the Master’s Degree. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2004, 40–42 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Y., Guo, L., Bai, B. et al. Convective heat transfer in helical coils for constant-property and variable-property flows with high Reynolds numbers. Front. Energy Power Eng. China 4, 546–552 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-010-0116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-010-0116-8