Abstract
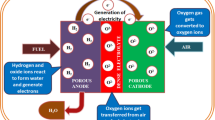
A positive-electrolyte-negative (PEN) assembly solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) with a thin electrolyte film for intermediate temperature operation was fabricated. Instead of the traditional screen-printing method, both anode and cathode catalysts were pressed simultaneously and formed with the fabrication of nano-composite electrolyte by press method. This design offered some advantageous configurations that diminished ohmic resistance between electrolyte and electrodes. It also increased the proton-conducting rate and improved the performance of SOFCs due to the reduction of membrane thickness and good contact between electrolyte and electrodes. The fabricated PEN cell generated electricity between 600°C and 680°C using H2S as fuel feed and air as oxidant. Maximum power densities 40 mW·cm−2 and 130 mW·cm−2 for the PEN configuration with a Mo-Ni-S-based composite anode, nano-composite electrolyte (Li2SO4+Al2O3) film and a NiO-based composite cathode were achieved at 600°C and 680°C, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pujare N U, Semkow K W, Sammells A F. A direct H2S/air solid oxide fuel cell. J Electrochem Soc, 1987, 134(10): 2639–2640
Tao S W, Irvine J T S. Investigation of the mixed conducting oxide ScYZT as a potential SOFC anode material. J Electrochem Soc, 2004, 151(4): A497–A503
Zhu B, Liu X G, Schober T. Novel hybrid conductors based on doped ceria and BCY20 for ITSOFC applications. Electrochem Commun, 2004, 6: 378–383
Zhong L, Chen J J, Wei G L, Luo J L, Chuang K. Hydrogen sulfides solid oxide fuel cell using proton-conducting electrolytes. J Chem Ind Eng, 2004, 55(10): 1732–1735
Zhong L, Liu M, Wei G L, Luo J L, Chuang K. Influence of metal sulfides as anode catalysts on performance of H2S SOFC. Chin J Chem Eng, 2003, 11(3): 245–248
Bockris J O M, Srinivasan S. Fuel Cells: Their Electrochemistry. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc Press, 1969
Gopalan P, Bhandari S, Kulkarni A R, Palkar V R. Effect of preparative parameters on electrical conductivity of Li2SO4-Al2O3 components. Mater Res Bull, 2003, 37: 2043–2053
Wei G L, Luo J L, Sanger A R, Chuang K. High-performance anode for H2S-air SOFC. J Electrochem Soc, 2004, 151(2): A232–A237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, L., Luo, J. & Karl, C. Fabrication and performance of PEN SOFCs with proton-conducting electrolyte. Front. Chem. Eng. China 1, 40–44 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-007-0008-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-007-0008-6