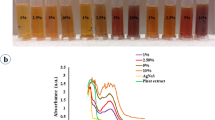
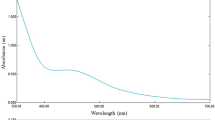
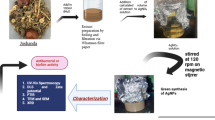
Abstract
Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via green approach holds great potential in diverse fields of biotechnology and medicine with special mention to silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) which undoubtedly display antimicrobial, radical scavenging, and dye degradation properties. Currently, there is a need to explore more cost-effective and efficient methods to synthesize AgNPs. In this study, we have synthesized biogenic AgNPs using an aqueous extract of a flowering plant of the legume family, Fabaceae, subfamily Caesalpiniaceae, Cassia fistula, which is also well known for its medicinal values. Spectroscopically and physicochemically characterized AgNPs were evaluated for their cytocompatibility, antimicrobial effects, antioxidant and catalytic activity to establish their potential for various biomedical applications. DLS studies revealed their size ~ 237 nm with the surface charge of ~ − 30 mV. The results of the zone of inhibition and MIC assays showed the superiority of the activity of these particles over the pod extract. Catalytic reduction of toxic p-nitrophenol to benign p-aminophenol as well as degradation of hazardous industrial dyes (methyl orange and methylene blue) advocated their potential as environmental toxicant eradicators. Besides, these biogenic AgNPs displayed profound antibiofilm effects in static microtiter plates. Altogether, the results of various bioassays using these biogenic nanoparticles demonstrate their immense potential as antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antibiofilm agents.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi E, Milani M, Aval SF, Kouhi M, Akbarzadeh A, Nasrabadi HT, Nikasa P, Joo SW, Hanifehpour Y, Nejati-Koshki K, Samiei M (2016) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis methods, bio-applications and properties. Crit Rev Microbiol 42:173–180. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2014.912200
Agnihotri S, Pathak R, Jha D, Roy I, Gautam HK, Sharma AK, Kumar P (2015) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of aminoglycoside-conjugated silica nanoparticles against clinical and resistant bacteria. New J Chem 39:6746–6755. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nj00007f
Albanese A, Lam AK, Sykes EA, Rocheleau JV, Chan WC (2013) Tumour-on-a-chip provides an optical window into nanoparticle tissue transport. Nat Commun 4:2718. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3718
Al-Marhaby F, Seoudi R (2016) Preparation and characterization of silver nanoparticles and their use in catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. World J Nano Sci Eng 6:29–37. https://doi.org/10.4236/wjnse.2016.61003
Anand U, Jacobo-Herrera N, Altemimi A, Lakhssassi N (2019) A comprehensive review on medicinal plants as antimicrobial therapeutics: potential avenues of biocompatible drug discovery. Metabolites 9:258. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110258
Andrews JM (2001) Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J Antimicrob Chemother 48:5–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/48.suppl_1.5
Bahorun T, Neergheen VS, Aruoma OI (2005) Phytochemical constituents of Cassia fistula. Afr J Biotechnol 4:1530–1540. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajfand.v4i13.71772
Baltazar-Encarnación E, Escárcega-González CE, Vasto-Anzaldo XG, Cantú-Cárdenas ME, Morones-Ramírez JR (2019) Silver nanoparticles synthesized through green methods using Escherichia coli Top 10 (Ec-Ts) growth culture medium exhibit antimicrobial properties against nongrowing bacterial strains. J Nanomater 9:4637325. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4637325
Burdușel AC, Gherasim O, Grumezescu A, Mogoantă L, Ficai A, Andronescu E (2018) Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: an up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 8:681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090681
Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle LK, Hess KL, Jones RL, Schlager JJ (2008) Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B 112:13608–13619. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp712087m
Chang ST, Wu JH, Wang SY, Kang PL, Yang NS, Shyur LF (2001) Antioxidant activity of extracts from Acacia confusa bark and heartwood. J Agric Food Chem 49:3420–3424. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0100907
Chernousova S, Epple M (2013) Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:1636–1653. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201205923
Das RK, Pachapur VL, Lonappan L, Naghdi M, Pulicharla R, Maiti S, Cledon M, Dalila LMA, Sarma SJ, Brar SK (2017) Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: plants, animals and microbial aspects. Nanotechnol Environ Eng 2:18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-017-0029-4
Defoirdt T, Boon N, Bossier P (2010) Can bacteria evolve resistance to quorum sensing disruption? PLoS Pathog 6:e1000989. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000989
Ding MY, Meng DS, Tang YH, Liu CB, Luo SL (2015) One-dimensional porous Ag/AgBr/TiO2 nanofibres with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Chem Pap 69:1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0151
Długosz O, Chwastowski J, Banach M (2020) Hawthorn berries extract for the green synthesis of copper and silver nanoparticles. Chem Pap 74:239–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00873-z
Duan X, Li Y (2013) Physicochemical characteristics of nanoparticles affect circulation, biodistribution, cellular internalization, and trafficking. Small 9:1521–1532. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201201390
Evans BC, Nelson CE, Shann SY, Beavers KR, Kim AJ, Li H, Nelson HM, Duvall GTD (2013) Ex vivo red blood cell hemolysis assay for the evaluation of pH-responsive endosomolytic agents for cytosolic delivery of biomacromolecular drugs. J Vis Exp 73:e50166. https://doi.org/10.3791/50166
Fouad H, Hongjie L, Hosni D, Wei J, Abbas G (2018) Controlling Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens pallens using silver nanoparticles synthesized from aqueous extract of Cassia fistula fruit pulp and its mode of action. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:558–567. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1329739
Gerbig DG Jr, Engohang-Ndong J, Aubihl H (2013) A new twist to the kirby-bauer antibiotic susceptibility test activity—increasing antibiotic sensitivity of pseudomonas fluorescence through thermal stress. J Microbiol Biol Edu 14:269–270. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v14i2.617
Ghadi FE, Ghara AR, Naeimi A (2018) Phytochemical fabrication, characterization, and antioxidant application of copper and cobalt oxides nanoparticles using Sesbania sesban plant. Chem Pap 72:2859–2869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0506-7
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A (2017) Health and environmental impacts of dyes: mini review. Am J Environ Sci Eng 1:64–67. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajese.20170103.11
Iqbal I, Afzal M, Aftab MN, Manzoor F, Kaleem A, Kaleem A (2016) Hepatotoxicity of Cassia fistula extracts in experimental chicks and assessment of clinical parameters. Kuwait J Sci 43:135–141
Jo DH, Kim JH, Lee TG, Kim JH (2015) Size, surface charge, and shape determine therapeutic effects of nanoparticles on brain and retinal diseases. Nanomed-Nanotechnol 11:1603–1611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.04.015
Kästner C, Thünemann AF (2016) Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using silver nanoparticles with adjustable activity. Langmuir 32:7383–7391. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01477
Khandel P, Yadaw RK, Soni DK, Kanwar L, Shahi SK (2018) Biogenesis of metal nanoparticles and their pharmacological applications: present status and application prospects. J Nanostr Chem 8:217–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-018-0267-4
Kumar H, Gaur A, Kumar S, Park JW (2019) Development of silver nanoparticles-loaded CMC hydrogel using bamboo as a raw material for special medical applications. Chem Pap 73:953–964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0650-0
Li G, He D, Qian Y, Guan B, Gao S, Cui Y, Yokoyama K, Wang L (2012) Fungus-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Aspergillus terreus. Int J Mol Sci 13:466–476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13010466
Lopes AP, Galuch MB, Petenuci ME, Oliveira JH, Canesin EA, Schneider VVA, Visentainer JV (2020) Quantification of phenolic compounds in ripe and unripe bitter melons (Momordica charantia) and evaluation of the distribution of phenolic compounds in different parts of the fruit by UPLC–MS/MS. Chem Pap 74:2613–2625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01094-5
Low FCF, Wu TY, Teh CY, Juan JC, Balasubramanian N (2012) Investigation into photocatalytic decolorisation of CI reactive black 5 using titanium dioxide nanopowder. Color Technol 128:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-4408.2011.00326.x
Luximon-Ramma A, Bahorun T, Soobrattee MA, Aruoma OI (2002) Antioxidant activities of phenolic, proanthocyanidin, and flavonoid components in extracts of Cassia fistula. J Agric Food Chem 50:5042–5047. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0201172
Maeda T, García-Contreras R, Pu M, Sheng L, Garcia LR, Tomás M, Wood TK (2012) Quorum quenching quandary: resistance to antivirulence compounds. ISME J 6:493–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.122
Marslin G, Siram K, Maqbool Q, Selvakesavan R, Kruszka D, Kachlicki P, Franklin G (2018) Secondary metabolites in the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Materials 11:940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060940
Mathur P, Jha S, Ramteke S, Jain NK (2018) Pharmaceutical aspects of silver nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1414825
McDonald S, Prenzler PD, Antolovich M, Robards K (2001) Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of olive extracts. Food Chem 73:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00288-0
Mehrabi K, Nowack B, Dasilva YAR, Mitrano DM (2017) Improvements in nanoparticle tracking analysis to measure particle aggregation and mass distribution: a case study on engineered nanomaterial stability in incineration landfill leachates. Environ Sci Technol 51:5611–5621. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00597
Mohanta YK, Panda SK, Biswas K, Tamang A, Bandyopadhyay J, De D, Mohanta D, Bastia AK (2016) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Cassia fistula (Linn.): in vitro assessment of their antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities. IET Nanobiotechnol 10:438–444. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2015.0104
Niknejad F, Nabili M, Ghazvini RD, Moazeni M (2015) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: advantages of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae model. Curr Med Mycol 1:17–24. https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.cmm.1.3.17
Nirmala A, Eliza J, Rajalakshmi M, Priya E, Daisy P (2008) Effect of hexane extract of Cassia fistula barks on blood glucose and lipid profile in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Int J Pharmacol 4:292–296. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijp.2008.292.296
O'Toole GA (2011) Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J Vis Exp 47:e2437. https://doi.org/10.3791/2437
Panda SK, Padhi LP, Mohanty G (2011) Antibacterial activities and phytochemical analysis of Cassia fistula (Linn) leaf. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2:62. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-4040.79814
Phuong DL, Thuy NT, Long PQ, Kuo PC, Thang TD (2019) Composition of fatty acids, tocopherols, sterols, total phenolics, and antioxidant activity of seed oils of Afzelia xylocarpa and Cassia fistula. Chem Nat Compd 55:242–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-019-02659-x
Rao PV, Nallappan D, Madhavi K, Rahman S, Wei LJ, Gan SH (2016) Phytochemicals and biogenic metallic nanoparticles as anticancer agents. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3685671
Ravichandran A, Subramanian P, Manoharan V, Muthu T, Periyannan R, Thangapandi M, Ponnuchamy K, Pandi B, Marimuthu PN (2018) Phyto-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fucoidan isolated from Spatoglossum asperum and assessment of antibacterial activities. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 185:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.05.031
Saha J, Begum A, Mukherjee A, Kumar S (2017) A novel green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic action in reduction of methylene blue dye. Sust Env Res 27:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2017.04.003
Samuel MS, Jose S, Selvarajan E, Mathimani T, Pugazhendhi A (2020) Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens: application for cytotoxicity effect on A549 cell line and photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 202:111642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111642
Singh J, Chang YY, Koduru JR, Yang JK (2018) Potential degradation of methylene blue (MB) by nano-metallic particles: A kinetic study and possible mechanism of MB degradation. Environ Eng Res 23:1–9. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2016.158
Singh N, Rajwade J, Paknikar KM (2019) Transcriptome analysis of silver nanoparticles treated Staphylococcus aureus reveals potential targets for biofilm inhibition. Coll Surf B Biointerfaces 175:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.12.032
Slavin YN, Asnis J, Häfeli UO, Bach H (2017) Metal nanoparticles: understanding the mechanisms behind the antibacterial activity. J Nanobiotechnol 15:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-017-0308-z
Staquicini FI, Ozawa MG, Moya CA, Driessen WH, Barbu EM, Nishimori H, Soghomonyan S, Flores LG, Liang X, Paolillo V, Alauddin MM (2011) Systemic combinatorial peptide selection yields a non-canonical iron-mimicry mechanism for targeting tumors in a mouse model of human glioblastoma. J Clin Invest 121:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI44798
van de Loosdrecht AA, Beelen RHJ, Ossenkoppele G, Broekhoven MG, Langenhuijsen MMAC (1994) A tetrazolium-based colorimetric MTT assay to quantitate human monocyte mediated cytotoxicity against leukemic cells from cell lines and patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Immunol Methods 174:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(94)90034-5
Vidhu VK, Philip D (2014) Catalytic degradation of organic dyes using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Micron 56:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2013.10.006
Yunan Qing LC, Li R, Liu G, Zhang Y, Tang X, Wang J, Liu H, Qin Y (2018) Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int J Nanomed 13:3311. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S165125
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the CSIR project (OLP1144). IS thanks DST for awarding DST-INSPIRE fellowship for carrying out this work. The authors also wish to thank Ms. R. Purohit for her valuable support during experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, I., Gupta, S., Gautam, H.K. et al. Antimicrobial, radical scavenging, and dye degradation potential of nontoxic biogenic silver nanoparticles using Cassia fistula pods. Chem. Pap. 75, 979–991 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01355-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01355-3