Abstract
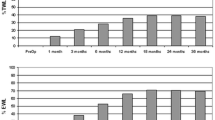
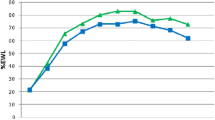
Different hormones and peptides involved in inflammation have been studied in and related to obesity. The aim of our work is to assess the variations of different molecules related to inflammation in obese patients during the first year following sleeve gastrectomy. This was a prospective study on patients who underwent sleeve gastrectomy. The variations in different clinical, anthropometric, and analytical parameters related to inflammation were determined and analysed in all patients at the preoperative visit and at the first and fifth days, first and sixth months, and 1 year following surgery. We enrolled 20 patients to the study. The median body mass index (BMI) before intervention was 48.5 kg/m2. With respect to comorbidities, 70 % of the patients had obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome (OSA), 65 % high blood pressure, 45 % dyslipidaemia, and 40 % diabetes mellitus (DM). The median percentage of BMI lost (%BMIL) 1 year after the intervention was 71 %. The dyslipidaemia healing or improvement rate was 100 %, whereas it was 87.5 % for diabetes, 84.6 % for hypertension, and 57.1 % for OSA. During the 1-year postintervention period, the average levels of adiponectin increased, although not significantly, whereas those of leptin significantly decreased. In addition, the blood levels of MCP-1, IL-6, CRP, ferritin, and PAI-1 significantly decreased in that period. Sleeve gastrectomy is a surgical technique that is associated with improvements in body weight and comorbid conditions from the first postoperative months, which lead to significant variations in the levels of different inflammation-related parameters and a decrease in the levels of leptin, IL-6, CRP, MCP-1, ferritin, and serpin (PAI-1).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg. 2013;23:427–36.
Rubino F, Gagner M, Gentileschi P, Kini S, Fukuyama S, Feng J, et al. The early effect of the Rou-en-Y gastric bypass on hormones involved in body weight regulation and glucose metabolism. Ann Surg. 2004;240:236–42.
Pickup JC, Crook MA. Is type II diabetes mellitus a disease of the innate immune system? Diabetologia. 1998;41:1241–8.
Brethauer SA, Heneghan HM, Eldar S, Gatmaitan P, Huang H, Kashyap S, et al. Early effects of gastric bypass on endothelial function, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk in obese patients. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:2650–9.
Marti A, Marcos A, Martinez JA. Obesity and immune function relationships. Rev Obes Rev. 2001;2:131–40.
Wärnberg J, Moreno LA, Mesana MI, Marcos A, AVENA group. Inflammatory mediators in overweight and obese Spanish adolescents. The AVENA Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28:S59–63.
Wu DM, Chu NF, Shen MH, Chang JB. Plasma C-reactive protein levels and their relationship to anthropometric and lipid characteristics among children. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56:94–100.
Bockelbrink A, Stöber Y, Roll S, Vauth C, Willich SN, von der Schulenburg JM. Evaluation of medical and health economic effectiveness of bariatric surgery (obesity surgery) versus conservative strategies in adult patients with morbid obesity. GMS Health Technol Assess. 2008;4:Doc06.
Williams IL, Chowienczyk PJ, Wheatcroft SB, Patel AG, Sherwood RA, Momin A, et al. Endothelial function and weight loss in obese humans. Obes Surg. 2005;15:1055–60.
Gokce N, Vita JA, McDonnell M, Forse AR, Istfan N, Stoeckl M, et al. Effect of medical and surgical weight loss on endothelial vasomotor function in obese patients. Am J Cardiol. 2005;95:266–8.
Ryan AS, Nicklas BJ. Reductions in plasma cytokine levels with weight loss improve insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese postmenopausal women. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1699–705.
Bastard JP, Jardel C, Bruckert E, Blondy P, Capeau J, Laville M, et al. Elevated levels of interleukin 6 are reduced in serum and subcutaneous adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:3338–42.
Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:448–54.
Havel PJ. Update on adipocyte hormones. Regulation of energy balance and carbohydrate/lipid metabolism. Diabetes. 2004;53:S143–51.
Tschritter O, Fritsche A, Thamer C, Haap M, Shirkavand F, Rahe S, et al. Plasma adiponectin concentrations predict insulin sensitivity of both glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes. 2003;52:239–43.
Lichtash CT, Cui J, Guo X, Xen YD, Hsueh WA, Rotter JI, et al. Body adiposity index versus body mass index and other anthropometric traits as correlates of cardiometabolic risk factors. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e65954.
Chen SC, Huang YF, Wang JD. Hyperferritinemia and hyperuricemia may be associated with liver function abnormality in obese adolescents. PLoS One. 2012;7:e48645.
Cancello R, Henegar C, Viguerie N, Taleb S, Poitou C, Rouault C, et al. Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes. 2005;54:2277–86.
Christiansen T, Richelsen B, Bruun JM. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is produced in isolated adipocytes, associated with adiposity and reduced after weight loss in morbid obese subjects. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005;29:146–50.
Oreopoulos A, Ezekowitz JA, McAlister FA, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Fonarow GC, et al. Association between direct measures of body composition and prognostic factors in chronic heart failure. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:609–17.
Marzullo P, Minocci A, Giarda P, Marconi C, Tagliaferri A. Walker GE, et al. Endocrine: Lymphocytes and immunoglobulin patterns across the threshold of severe obesity; 2013. doi:10.1007/s12020-013-0006-z.
Woelnerhanssen B, Peterli R, Steinert RE, Peters T, Borbély Y, Beglinger C. Effects of postbariatric surgery weight loss on adipokines and metabolic parameters: comparison of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy—a prospective randomized trial. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7:561–8.
Conflict of interest
All authors (Verónica Gumbau, Marcos Bruna, Enrique Canelles, Marcos Guaita, Claudia Mulas, Carla Basés, Isabel Celma, Jose Puche, Goitzane Marcaida, Miguel Oviedo, Antonio Vázquez) declare that they have no conflict of interests in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gumbau, V., Bruna, M., Canelles, E. et al. A Prospective Study on Inflammatory Parameters in Obese Patients After Sleeve Gastrectomy. OBES SURG 24, 903–908 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-014-1186-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-014-1186-1