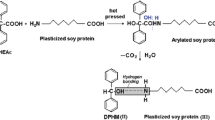
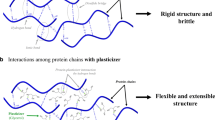
Abstract
There is a rising demand for packaged food in the twenty-first century. Fresh food products are prone to spoilage, moisture loss, physical damage, microbial decay, and biochemical changes. These are the principal reasons for the quality loss and decreased shelf-life, necessitating the usage of packing films. The packaging films are currently made from different synthetic polymers including polypropylene, polyethylene, and other types of artificial polymers. However, it would be better to use soy protein as a justifiable antibacterial film in packaging. Soy Protein Isolate (SPI) is cheap and widely available for different uses in the food industry. Soy-based films made from renewable resources are a better option than synthetic-based films. They have strong mechanical characteristics and they are transparent in the presence of other additions like acids, nanoparticles, and natural substances. Furthermore, the production technique (compression molding and solution casting) for SPI film in the absence or presence of additives is simple and economically beneficial. Chemicals derived from plants such as essential oils and plant extracts are also useful to add antioxidant and antibacterial properties to films and coatings resulting in SPI. This paper was focused on the application of soy protein-based coatings and films, as well as coatings incorporated with nano-materials (nano-bioactive chemicals or essential oils), in food models to extend shelf life, as reported in recent years.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Haosagul, S. Boonyawanich, N. Pisutpaisal, Biomethane production from co-fermentation of agricultural wastes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 44(11), 5355–5364 (2019)
Z.B. Zehi, A. Afshari, S. Noori, B. Jannat, M. Hashemi, The effects of X-ray irradiation on safety and nutritional value of food: a systematic review article. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 21(10), 919–926 (2020)
F. Mohajer, S. Khanzadi, K. Keykhosravy, S.M.A. Noori, M. Azizzadeh, M. Hashemi, Impact of gelatin nanogel coating containing thymol and nisin on the microbial quality of rainbow trout fillets and the inoculated Listeria monocytogenes. Aquac. Res. 52(8), 3958–3965 (2021)
S.M.H. Marashi, M. Hashemi, E. Berizi, M. Raeisi, S.M.A. Noori, Elaboration of whey protein-based Films in Food Products: emphasis on the addition of natural edible bio-nanocomposites with antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. Jundishapur Journal of Natural Pharmaceutical Products 17(2), (2022)
H. Chen, J. Wang, Y. Cheng, C. Wang, H. Liu, H. Bian et al. Application of protein-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Polymers 11(12), 2039. (2019)
S.A. Mohamed, M. El-Sakhawy, M.A.M. El-Sakhawy, Polysaccharides, protein and lipid-based natural edible films in food packaging: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers 238(116178. (2020)
N. Kumar, Polysaccharide-based component and their relevance in edible film/coating: a review. Nutrition & Food Science (2019)
S. Rani, Kumar, R a review on material and antimicrobial properties of soy protein isolate film. J. Polym. Environ. 27(8), 1613–1628 (2019)
J. Małecki, S. Muszyński, B.G. Sołowiej, Proteins in food systems—Bionanomaterials, conventional and unconventional sources, functional properties, and development opportunities. Polymers 13(15), 2506 (2021)
M. Zubair, A. Ullah Recent advances in protein derived bionanocomposites for food packaging applications. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 60(3), 406 – 34. (2020)
H. Tian, G. Guo, X. Fu, Y. Yao, L. Yuan, A. Xiang, Fabrication, properties and applications of soy-protein-based materials: a review. International journal of biological macromolecules 120(475 – 90. (2018)
J.E. Kinsella, Functional properties of soy proteins. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society 56(3Part1), 242 – 58. (1979)
J.G. Endres, Soy Protein Products: Characteristics, Nutritional Aspects, and Utilization (The American Oil Chemists Society, 2001)
G. Zhao, C. Zhou, F. Fan, Preparation and properties of soy protein isolate/cotton-nanocrystalline cellulose films. International Journal of Polymer Science 2021((2021)
S.M. Hossaeini Marashi, M. Hashemi, E. Berizi, M. Raeisi, S.M.A. Noori, Elaboration of whey protein-based Films in Food Products: emphasis on the addition of natural edible bio-nanocomposites with antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. Jundishapur Journal of Natural Pharmaceutical Products 17(1), (2022)
S.A.A.E.-S.M. Mohamed, M.A. El-Sakhawy. Polysaccharides, Protein and lipid -based Natural Edible Films in Food Packaging: a review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Jun 15;238:116178. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116178. Epub 2020 Mar 20. PMID: 32299560
V. Mihalca, A.D. Kerezsi, A. Weber, C. Gruber-Traub, J. Schmucker, D.C. Vodnar et al., Protein-based films and coatings for food industry applications. Polymers 13(5), 769 (2021)
M.H. Moosavi, M.R. Khani, B. Shokri, S.M. Hosseini, S. Shojaee-Aliabadi, L. Mirmoghtadaie, Modifications of protein-based films using cold plasma. International journal of biological macromolecules 142(769 – 77. (2020)
Z. Zareie, F.T. Yazdi, S.A. Mortazavi Development and characterization of antioxidant and antimicrobial edible films based on chitosan and gamma-aminobutyric acid-rich fermented soy protein. Carbohydrate Polymers 244(116491. (2020)
X. Huang, X. Zhou, Q. Dai, Z. Qin, Antibacterial, Antioxidation, UV-Blocking, and biodegradable soy protein isolate Food Packaging Film with Mangosteen Peel Extract and ZnO nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 11(12), 3337 (2021)
F. Li, Q. Ye, Q. Gao, H. Chen, S.Q. Shi, W. Zhou et al., Facile fabrication of self-healable and antibacterial soy protein-based films with high mechanical strength. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(17), 16107–16116 (2019)
F. Xue, Y. Gu, Y. Wang, C. Li, B. Adhikari, Encapsulation of essential oil in emulsion based edible films prepared by soy protein isolate-gum acacia conjugates. Food Hydrocolloids 96(178 – 89. (2019)
M. Raeisi, M.A. Mohammadi, O.E. Coban, S. Ramezani, M. Ghorbani, M. Tabibiazar et al., Physicochemical and antibacterial effect of soy protein Isolate/Gelatin electrospun nanofibres incorporated with Zataria multiflora and cinnamon zeylanicum essential oils. J. Food Meas. Charact. 15(2), 1116–1126 (2021)
J. Wu, Q. Sun, H. Huang, Y. Duan, G. Xiao, T. Le, Enhanced physico-mechanical, barrier and antifungal properties of soy protein isolate film by incorporating both plant-sourced cinnamaldehyde and facile synthesized zinc oxide nanosheets. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 180(31 – 8. (2019)
Y. Xiao, Y. Liu, S. Kang, K. Wang, H. Xu Development and evaluation of soy protein isolate-based antibacterial nanocomposite films containing cellulose nanocrystals and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Food Hydrocolloids 106(105898. (2020)
R. Tao, J. Sedman, A. Ismail, Characterization and in vitro antimicrobial study of soy protein isolate films incorporating carvacrol. Food Hydrocoll. 122, 107091 (2022)
Z. Zhang, X. Zhou, C. Fang, D. Wang, Characterization of the Antimicrobial Edible Film based on Grasshopper Protein/Soy protein Isolate/Cinnamaldehyde blend crosslinked with xylose. Frontiers in Nutrition 9((2022)
A.J. Pellissery, P.G. Vinayamohan, M.A.R. Amalaradjou, K. Venkitanarayanan, Spoilage bacteria and meat Quality (Elsevier, Meat quality analysis, 2020), pp. 307–334
J. Tkaczewska, Peptides and protein hydrolysates as food preservatives and bioactive components of edible films and coatings-A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 106, 298–311 (2020)
C.G. Otoni, R.J. Avena-Bustillos, C.W. Olsen, C. Bilbao-Sáinz, T.H. McHugh, Mechanical and water barrier properties of isolated soy protein composite edible films as affected by carvacrol and cinnamaldehyde micro and nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocolloids 57(72 – 9. (2016)
Z. Karimian, A. Tabatabaee Bafroee, A. Sharifan, Physico-mechanical and antimicrobial properties of isolated soy protein film incorporated with peppermint essential oil on raw hamburger. J. Agricultural Sci. Technol. 21(5), 1145–1159 (2019)
I. Echeverría, M.E. López-Caballero, M.C. Gómez-Guillén, A.N. Mauri, Montero MP active nanocomposite films based on soy proteins-montmorillonite-clove essential oil for the preservation of refrigerated bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) fillets. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 266, 142–149 (2018)
J. Xu, H. Ji, H. Dong, S. Duan, H. Chen, D. Zhang et al., A promising natural purple batter system with antioxidant activity for vacuum fried breaded shrimp. Food Science and Technology 42((2021)
L. Di Giorgio, P.R. Salgado, Mauri AN flavored oven bags for cooking meat based on proteins. Lwt 101(374 – 81. (2019)
D. Wulandari, Y. Erwanto, Y. Pranoto, R. Rusman, S. Sugiyanto, Quality of chicken sausage coated by transglutaminase-crosslinked bovine split hide gelatin and soy protein isolate edible film during chilled storage. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Hasil Ternak (JITEK) 15(3), 142 – 51. (2020)
L. Xu, W. Cao, R. Li, H. Zhang, N. Xia, T. Li et al., Properties of soy protein isolate/nano-silica films and their applications in the preservation of Flammulina velutipes. J. Food Process. Preserv. 43(11), e14177 (2019)
A.R. Yousef, E.A. Abd El-Moniem, T.S.M. Mahmoud, EDIBLE COATING OF SOY PROTEIN OR, GELATIN AS A CARRIER OF THYME OIL FOR MAINTAINING QUALITY OF ‘BARHEE’DATES FRUITS DURING COLD STORAGE, Plant. Archives 20(2), 9311–9322 (2020)
B. Yousuf, A.K. Srivastava Impact of honey treatments and soy protein isolate-based coating on fresh-cut pineapple during storage at 4 C. Food Packaging and Shelf Life 21(100361. (2019)
B. Yousuf, A.K. Srivastava, S. Ahmad, Application of natural fruit extract and hydrocolloid-based coating to retain quality of fresh-cut melon. J. Food Sci. Technol. 57(10), 3647–3658 (2020)
R.R. Koshy, A. Reghunadhan, S.K. Mary, K. Thomas, K. Ajish, S. Thomas et al., Intelligent pH-sensitive films from whole arrowroot powder and soy protein isolate incorporating red cabbage anthocyanin: monitoring freshness of shrimps and ammonia in fish farming ponds. New J. Chem. 46(19), 9036–9047 (2022)
H. Li, X. Zhang, S. Tan, G. Tan, H. Zhang, N. Xia et al. Intelligent colorimetric soy protein isolate-based films incorporated with curcumin through an organic solvent-free pH-driven method: Properties, molecular interactions, and application. Food Hydrocolloids 133(107904. (2022)
H. Wu, J. Lu, D. Xiao, Z. Yan, S. Li, T. Li et al. Development and characterization of antimicrobial protein films based on soybean protein isolate incorporating diatomite/thymol complex. Food Hydrocolloids 110(106138. (2021)
D.E. Azab, Y.A. Heikal, T.A. Salaheldin, A.A. Hassan, F.M. Abu-Salem, Nano formulated soy proteins for improvement of Beef Burgers Quality. Egypt. J. Chem. 62(7), 1167–1184 (2019)
J. Li, Q. Sun, Y. Sun, B. Chen, X. Wu, T. Le Improvement of banana postharvest quality using a novel soybean protein isolate/cinnamaldehyde/zinc oxide bionanocomposite coating strategy. Scientia Horticulturae 258(108786. (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akrami, S., Saki, M., Marashi Hossaeini, S. et al. Application of soy protein-based films and coatings on the shelf life of food products: a mini-review of recent publications with emphasis on nanotechnology. Food Measure 17, 1393–1401 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01708-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01708-4