Abstract
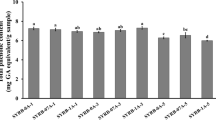
Rice bran protein concentrate (RBPC) was digested using four commercial enzymes, Alcalase, Trypsin, Protamex, and Flavourzyme at a various digestion time (2, 4, and 6 h), in order to produce antioxidant active peptides. The degree of hydrolysis (DH), total phenolic content (TPC), and antioxidant activity, including DPPH, ABTS, and metal chelating assays were examined. The obtained results indicated that DH varied with the type of enzyme used, Protamex > Trypsin > Alcalase > Flavourzyme, respectively. The optimum conditions of hydrolysis was 2 h using Flavourzyme, which gives protein content of 62.90 ± 0.77 mg/100 g, TPC of 893.75 ± 0.57 mg GAE/100 g, DPPH of 83.68 ± 0.97%, ABTS of 35.11 ± 0.66%, and a metal chelating activity of 53.90 ± 0.13%. These results indicate that the hydrolysate produced by digesting RBPC using Flavourzyme may contain bioactive components useful as natural food antioxidants. That can increase their potentials as natural food additives which could be useful in the food industry sector.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Guo, J. Zhang, Y. Ma, S. Tian, J. Food Process. Pres. 37, 245–253 (2013)
X. Wang, H. Chen, X. Fu, S. Li, J. Wei, LWT-Food. Sci. Technol. 75, 93–99 (2017)
S. Phongthai, S.T. Lim, S. Rawdkuen, J. Cereal Sci. 70, 146–154 (2016)
A.P. Adebiyi, A.O. Adebiyi, J. Yamashita, T. Ogawa, K. Muramoto, Eur. Food Res. Technol. 228, 553–563 (2009)
D. Teng, Y. Fang, X. Song, Y. Gao, Food Bioprod. Process. 89, 202–208 (2011)
S.J. Lee, S.H. Cheong, Y.S. Kim, J.W. Hwang, H.J. Kwon, S.H. Kang, S.H. Moon, B.T. Jeon, P.J. Park, Food Chem. Toxicol. 62, 276–280 (2013)
P. Puchalska, M.L. Marina, M.C. Garcia, Food Chem. 148, 147–154 (2014)
L. Amagliani, J. O’Regan, A.L. Kelly, J.A. O’Mahony, J. Food Compos. Anal. 59, 18–26 (2017)
M. Wang, N.S. Hettiarachchy, M. Qi, W. Burks, T. Siebenmorgen, J. Agric. Food Chem. 47, 411–416 (1999)
AOAC, Official Methods of Analysis, 20th edn. (AOAC 54 International, Gaithersburg, MA, 2016)
J.S. Hamada, J. Food Sci. 65, 305–310 (2000)
J. Adler-Nissen, Enzymic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins (Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, New York, 1986)
O.H. Lowry, N.J. Rosebrough, A.L. Farr, R.J. Randall, J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
S.Y. El-Faham, M.M.S. Ashour, A.M. Sharaf, A.A. Zaky, Curr. Sci. Int. 05(04), 529–542 (2016)
J. Oh, H. Jo, A.R. Cho, S.J. Kim, J. Han, Food Control 31, 403–409 (2013)
U.K. Laemmli, Nature 227, 680–685 (1970)
K. Elavarasan, K.V. Naveen, B.A. Shamasundar, J. Food Process. Pres. 38, 1207–1214 (2014)
P. Thamnarathip, J. Kamolwan, J. Anuvat, N. Sunee, T. Sukuntaros, V. Bongkosh, Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 194–202 (2016)
H.J. Zhang, J. Wang, B.H. Zhang, H. Zhang, Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 49, 1330–1336 (2014)
W. Chanput, C. Theerakulkait, S. Nakai, J. Cereal Sci. 49, 422–428 (2009)
L. Wattanasiritham, C. Theerakulkait, S. Wickramasekara, C.S. Maier, J.F. Stevens, Food Chem. 192, 156–162 (2016)
P. Thamnarathip, K. Jangchud, S. Nitisinprasert, B. Vardhanabhuti, J. Cereal Sci. 69, 329–335 (2016)
L.Y. Aydemir, A. Yemenicioglu, Physiology 1, 1–3 (2013)
S. Phongthai, S. D'Amico, R. Schoenlechner, W. Homthawornchoo, S. Rawdkuen, Food Chem. 240, 156–164 (2018)
L. Zhu, J. Chen, X. Tang, L.Y. Xiong, J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 2714–2721 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31771951 and 31801510).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaky, A.A., Chen, Z., Liu, Y. et al. Preparation and assessment of bioactive extracts having antioxidant activity from rice bran protein hydrolysates. Food Measure 13, 2542–2548 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00174-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00174-9