Abstract
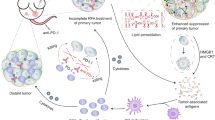
Nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF) is a novel, nonthermal, and minimally invasive modality that can ablate solid tumors by inducing apoptosis. Recent animal experiments show that nsPEF can induce the immunogenic cell death of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and stimulate the host’s immune response to kill residual tumor cells and decrease distant metastatic tumors. nsPEF-induced immunity is of great clinical importance because the nonthermal ablation may enhance the immune memory, which can prevent HCC recurrence and metastasis. This review summarized the most advanced research on the effect of nsPEF. The possible mechanisms of how locoregional nsPEF ablation enhances the systemic anticancer immune responses were illustrated. nsPEF stimulates the host immune system to boost stimulation and prevail suppression. Also, nsPEF increases the dendritic cell loading and inhibits the regulatory responses, thereby improving immune stimulation and limiting immunosuppression in HCC-bearing hosts. Therefore, nsPEF has excellent potential for HCC treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65(2): 87–108
Fitzmorris P, Shoreibah M, Anand BS, Singal AK. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2015; 141(5): 861–876
Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R, Andreola S, Pulvirenti A, Bozzetti F, Montalto F, Ammatuna M, Morabito A, Gennari L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 1996; 334(11): 693–699
Nault JC, Sutter O, Nahon P, Ganne-Carrié N, Séror O. Percutaneous treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: state of the art and innovations. J Hepatol 2018; 68(4): 783–797
Wu F, Wang ZB, Chen WZ, Wang W, Gui Y, Zhang M, Zheng G, Zhou Y, Xu G, Li M, Zhang C, Ye H, Feng R. Extracorporeal high intensity focused ultrasound ablation in the treatment of 1038 patients with solid carcinomas in China: an overview. Ultrason Sonochem 2004; 11(3–4): 149–154
Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y, Guo RP, Liang HH, Zhang YQ, Lin XJ, Lau WY. A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 2006; 243(3): 321–328
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, Rossi S. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology 2008; 47(1): 82–89
Künzli BM, Abitabile P, Maurer CA. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: actual limitations and potential solutions in the future. World J Hepatol 2011; 3(1): 8–14
Pliquett U, Nuccitelli R. Measurement and simulation of Joule heating during treatment of B-16 melanoma tumors in mice with nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Bioelectrochemistry 2014; 100: 62–68
Beebe SJ, Sain NM, Ren W. Induction of cell death mechanisms and apoptosis by nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs). Cells 2013; 2(1): 136–162
Nuccitelli R, McDaniel A, Anand S, Cha J, Mallon Z, Berridge JC, Uecker D. Nano-pulse stimulation is a physical modality that can trigger immunogenic tumor cell death. J Immunother Cancer 2017; 5(1): 32
Nuccitelli R, Lui K, Kreis M, Athos B, Nuccitelli P. Nanosecond pulsed electric field stimulation of reactive oxygen species in human pancreatic cancer cells is Ca2+-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 435(4): 580–585
He L, Xiao D, Feng J, Yao C, Tang L. Induction of apoptosis of liver cancer cells by nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs). Med Oncol 2017; 34(2): 24
Chen X, Yin S, Hu C, Chen X, Jiang K, Ye S, Feng X, Fan S, Xie H, Zhou L, Zheng S. Comparative study of nanosecond electric fields in vitro and in vivo on hepatocellular carcinoma indicate macrophage infiltration contribute to tumor ablation in vivo. PLoS One 2014; 9(1): e86421
Chen R, Sain NM, Harlow KT, Chen YJ, Shires PK, Heller R, Beebe SJ. A protective effect after clearance of orthotopic rat hepatocellular carcinoma by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Eur J Cancer 2014; 50(15): 2705–2713
Nuccitelli R, Tran K, Lui K, Huynh J, Athos B, Kreis M, Nuccitelli P, De Fabo EC. Non-thermal nanoelectroablation of UV-induced murine melanomas stimulates an immune response. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2012; 25(5): 618–629
Guo S, Burcus NI, Hornef J, Jing Y, Jiang C, Heller R, Beebe SJ. Nano-pulse stimulation for the treatment of pancreatic cancer and the changes in immune profile. Cancers (Basel) 2018; 10(7): 217
Guo S, Jing Y, Burcus NI, Lassiter BP, Tanaz R, Heller R, Beebe SJ. Nano-pulse stimulation induces potent immune responses, eradicating local breast cancer while reducing distant metastases. Int J Cancer 2018; 142(3): 629–640
Nuccitelli R, Wood R, Kreis M, Athos B, Huynh J, Lui K, Nuccitelli P, Epstein EH Jr. First-in-human trial of nanoelectroablation therapy for basal cell carcinoma: proof of method. Exp Dermatol 2014; 23(2): 135–137
Chen X, Chen Y, Jiang J, Wu L, Yin S, Miao X, Swanson RJ, Zheng S. Nano-pulse stimulation (NPS) ablate tumors and inhibit lung metastasis on both canine spontaneous osteosarcoma and murine transplanted hepatocellular carcinoma with high metastatic potential. Oncotarget 2017; 8(27): 44032–44039
Yin S, Chen X, Hu C, Zhang X, Hu Z, Yu J, Feng X, Jiang K, Ye S, Shen K, Xie H, Zhou L, James Swanson R, Zheng S. Nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF) treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: a novel locoregional ablation decreasing lung metastasis. Cancer Lett 2014; 346(2): 285–291
Chen X, Zhuang J, Kolb JF, Schoenbach KH, Beebe SJ. Long term survival of mice with hepatocellular carcinoma after pulse power ablation with nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2012; 11(1): 83–93
Schoenbach KH, Joshi R, Kolb J, Buescher S, Beebe S. Subcellular effects of nanosecond electrical pulses. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2004; 7: 5447–5450
Nuccitelli R, Pliquett U, Chen X, Ford W, James Swanson R, Beebe SJ, Kolb JF, Schoenbach KH. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields cause melanomas to self-destruct. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 343(2): 351–360
Nuccitelli R, Chen X, Pakhomov AG, Baldwin WH, Sheikh S, Pomicter JL, Ren W, Osgood C, Swanson RJ, Kolb JF, Beebe SJ, Schoenbach KH. A new pulsed electric field therapy for melanoma disrupts the tumor’s blood supply and causes complete remission without recurrence. Int J Cancer 2009; 125(2): 438–445
Nuccitelli R, Tran K, Sheikh S, Athos B, Kreis M, Nuccitelli P. Optimized nanosecond pulsed electric field therapy can cause murine malignant melanomas to self-destruct with a single treatment. Int J Cancer 2010; 127(7): 1727–1736
Vernier PT, Sun Y, Marcu L, Salemi S, Craft CM, Gundersen MA. Calcium bursts induced by nanosecond electric pulses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 310(2): 286–295
Pakhomova ON, Khorokhorina VA, Bowman AM, Rodaité-Riševičiene R, Saulis G, Xiao S, Pakhomov AG. Oxidative effects of nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure in cells and cell-free media. Arch Biochem Biophys 2012; 527(1): 55–64
Adkins I, Fucikova J, Garg AD, Agostinis P, Špíšek R. Physical modalities inducing immunogenic tumor cell death for cancer immunotherapy. OncoImmunology 2015; 3(12): e968434
Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12(12): 860–875
Mbeunkui F, Johann DJ Jr. Cancer and the tumor microenvironment: a review of an essential relationship. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2009; 63(4): 571–582
Leonardi GC, Candido S, Cervello M, Nicolosi D, Raiti F, Travali S, Spandidos DA, Libra M. The tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol 2012; 40(6): 1733–1747
Baglieri J, Brenner DA, Kisseleva T. The role of fibrosis and liver-associated fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20(7): 1723
Critelli R, Milosa F, Faillaci F, Condello R, Turola E, Marzi L, Lei B, Dituri F, Andreani S. Microenvironment inflammatory infiltrate drives growth speed and outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective clinical study. Cell Death Dis 2017; 8(8): e3017
Wang Y, Takeishi K, Li Z, Cervantes-Alvarez E, Collin de l’Hortet A, Guzman-Lepe J, Cui X, Zhu J. Microenvironment of a tumor-organoid system enhances hepatocellular carcinoma malignancy-related hallmarks. Organogenesis 2017; 13(3): 83–94
Smyth MJ, Ngiow SF, Ribas A, Teng MW. Combination cancer immunotherapies tailored to the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2016; 13(3): 143–158
Gao C, Zhang X, Chen J, Zhao J, Liu Y, Zhang J, Wang J. Utilizing the nanosecond pulse technique to improve antigen intracellular delivery and presentation to treat tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2018; 23(3): e344–e350
Skeate JG, Da Silva DM, Chavez-Juan E, Anand S, Nuccitelli R, Kast WM. Nano-pulse stimulation induces immunogenic cell death in human papillomavirus-transformed tumors and initiates an adaptive immune response. PLoS One 2018; 13(1): e0191311
Lassiter BP, Guo S, Beebe SJ. Nano-pulse stimulation ablates orthotopic rat hepatocellular carcinoma and induces innate and adaptive memory immune mechanisms that prevent recurrence. Cancers (Basel) 2018; 10(3): 69
Nuccitelli R, Berridge JC, Mallon Z, Kreis M, Athos B, Nuccitelli P. Nanoelectroablation of murine tumors triggers a CD8-dependent inhibition of secondary tumor growth. PLoS One 2015; 10(7): e0134364
Blachère NE, Darnell RB, Albert ML. Apoptotic cells deliver processed antigen to dendritic cells for cross-presentation. PLoS Biol 2005; 3(6): e185
Dromi SA, Walsh MP, Herby S, Traughber B, Xie J, Sharma KV, Sekhar KP, Luk A, Liewehr DJ, Dreher MR, Fry TJ, Wood BJ. Radiofrequency ablation induces antigen-presenting cell infiltration and amplification of weak tumor-induced immunity. Radiology 2009; 251(1): 58–66
Mizukoshi E, Yamashita T, Arai K, Sunagozaka H, Ueda T, Arihara F, Kagaya T, Yamashita T, Fushimi K, Kaneko S. Enhancement of tumor-associated antigen-specific T cell responses by radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013; 57(4): 1448–1457
Ahmad F, Gravante G, Bhardwaj N, Strickland A, Basit R, West K, Sorge R, Dennison AR, Lloyd DM. Changes in interleukin-1β and 6 after hepatic microwave tissue ablation compared with radio-frequency, cryotherapy and surgical resections. Am J Surg 2010; 200(4): 500–506
Sabel MS. Cryo-immunology: a review of the literature and proposed mechanisms for stimulatory versus suppressive immune responses. Cryobiology 2009; 58(1): 1–11
Slovak R, Ludwig JM, Gettinger SN, Herbst RS, Kim HS. Immuno-thermal ablations — boosting the anticancer immune response. J Immunother Cancer 2017; 5(1): 78
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National S&T Major Project (No. 2018ZX10301201) and Innovative Research Groups of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81721091). The authors thank Dr. Lin Zhou, Dr. Haiyang Xie, Danjing Guo, and Liangjie Hong from Key Laboratory of Combined Multi-organ Transplantation, Ministry of Public Health for their comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Jianpeng Liu, Xinhua Chen, and Shusen Zheng declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest. This manuscript is a review article and does not involve a research protocol requiring approval by the relevant institutional review board or ethics committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Chen, X. & Zheng, S. Immune response triggered by the ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma with nanosecond pulsed electric field. Front. Med. 15, 170–177 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-020-0747-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-020-0747-z