Abstract
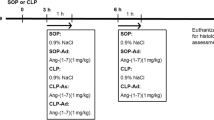
Glucagon-like peptide-2 (GLP-2) has potent anti-inflammatory effects and protects against experimental ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in pulmonary, intestinal, and myocardial tissue. However, its protective abilities against I/R injury in the liver are unknown. We investigated the potential role of GLP-2 pretreatment on hepatic I/R injury in rats. A total of 24 rats were randomly divided into three groups (n = 8). The first group was the control group; the second group was the vehicle-treated hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (HIR, vehicle saline-treated) group; and the third group was the GLP-2 pretreated I/R (GLP2-IR) group. Each rat in the third group was intraperitoneally administered 5 µg GLP-2 for 5 d before the procedure. A portal triad was created to induce ischemia with a vascular atraumatic clamp. After 40 min, the clamp was released to initiate hepatic reperfusion for 6 h. Blood samples and tissue specimens from the liver were obtained. Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and total bilirubin levels significantly increased in the salinetreated HIR group (P < 0.001), whereas GLP-2 pretreatment significantly decreased their levels (P < 0.01). Our data suggested that GLP-2 pretreatment may have a protective effect on liver I/R injury. However, dose-response studies are necessary to determine the most effective dose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Amara M, Yang SY, Tapuria N, Fuller B, Davidson B, Seifalian A. Liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: processes in inflammatory networks—a review. Liver Transpl 2010; 16(9): 1016–1032
Taki-Eldin A, Zhou L, Xie HY, Chen KJ, Yu D, He Y, Zheng SS. Triiodothyronine attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in a partial hepatectomy model through inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, transcription factors, and adhesion molecules. J Surg Res 2012; 178(2): 646–656
Rushing GD, Britt LD. Reperfusion injury after hemorrhage: a collective review. Ann Surg 2008; 247(6): 929–937
Birrer R, Takuda Y, Takara T. Hypoxic hepatopathy: pathophysiology and prognosis. Intern Med 2007; 46(14): 1063–1070
Tapuria N, Kumar Y, Habib MM, Abu Amara M, Seifalian AM, Davidson BR. Remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury—a review. J Surg Res 2008; 150(2): 304–330
Kandilci HB, Gümüsel B. Ischemia-reperfusion injury and ischemic preconditioning in lungs. Hacettepe University Journal of the Faculty of Pharmacy 2005; 25: 35–49 (in Turkish)
Kaplowitz N. Mechanisms of liver cell injury. J Hepatol 2000; 32(1 Suppl): 39–47
Jaeschke H. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2003; 284(1): G15–G26
Teoh NC, Farrell GC. Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: pathogenic mechanisms and basis for hepatoprotection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003; 18(8): 891–902
Guan X, Karpen HE, Stephens J, Bukowski JT, Niu S, Zhang G, Stoll B, Finegold MJ, Holst JJ, Hadsell D, Nichols BL, Burrin DG. GLP-2 receptor localizes to enteric neurons and endocrine cells expressing vasoactive peptides and mediates increased blood flow. Gastroenterology 2006; 130(1): 150–164
Bremholm L, Hornum M, Henriksen BM, Larsen S, Holst JJ. Glucagon-like peptide-2 increases mesenteric blood flow in humans. Scand J Gastroenterol 2009; 44(3): 314–319
Bremholm L, Hornum M, Andersen UB, Hartmann B, Holst JJ, Jeppesen PB. The effect of glucagon-like peptide-2 on mesenteric blood flow and cardiac parameters in end-jejunostomy short bowel patients. Regul Pept 2011; 168(1–3): 32–38
Deniz M, Bozkurt A, Kurtel H. Mediators of glucagon-like peptide 2-induced blood flow: responses in different vascular sites. Regul Pept 2007; 142(1–2): 7–15
Benjamin MA, McKay DM, Yang PC, Cameron H, Perdue MH. Glucagon-like peptide-2 enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function of both transcellular and paracellular pathways in the mouse. Gut 2000; 47(1): 112–119
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van deWiele T, Guiot Y, Everard A, Rottier O, Geurts L, Naslain D, Neyrinck A, Lambert DM, Muccioli GG, Delzenne NM. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 2009; 58(8): 1091–1103
Ivory CP, Wallace LE, McCafferty DM, Sigalet DL. Interleukin-10- independent anti-inflammatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2008; 295(6): G1202–G1210
Sigalet DL, Wallace LE, Holst JJ, Martin GR, Kaji T, Tanaka H, Sharkey KA. Enteric neural pathways mediate the anti-inflammatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2007; 293(1): G211–G221
Munroe DG, Gupta AK, Kooshesh F, Vyas TB, Rizkalla G, Wang H, Demchyshyn L, Yang ZJ, Kamboj RK, Chen H, McCallum K, Sumner-Smith M, Drucker DJ, Crivici A. Prototypic G proteincoupled receptor for the intestinotrophic factor glucagon-like peptide 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96(4): 1569–1573
Thulesen J, Hartmann B, Ørskov C, Jeppesen PB, Holst JJ, Poulsen SS. Potential targets for glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in the rat: distribution and binding of i.v. injected (125)I-GLP-2. Peptides 2000; 21(10): 1511–1517
Chiappa AC, Makuuchi M, Zbar AP, Biella F, Vezzoni A, Torzilli G, Andreoni B. Protective effect of methylprednisolone and of intermittent hepatic pedicle clamping during liver vascular inflow occlusion in the rat. Hepatogastroenterology 2004; 51(59): 1439–1444
Aslan A, Karagüzel G, Celik M, Uysal N, Yücel G, Melikoglu M. Pentoxifylline contributes to the hepatic cytoprotective process in rats undergoing hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury. Eur Surg Res 2001; 33(4): 285–290
Portakal O, Inal-Erden M. Effects of pentoxifylline and coenzyme Q10 in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Clin Biochem 1999; 32(6): 461–466
Vardareli E, Saricam T, Koken T, Degirmenci I, Aral E, Erenoglu E. The effect of alpha-tocopherol and pentoxyfilline on ischemiareperfusion induced liver injury in rats. Hepatogastroenterology 1998; 45(23): 1505–1508
Yildirim S, Tok H, Köksal H, Erdem L, Baykan A. Allopurinol plus pentoxifilline in hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Asian J Surg 2002; 25(2): 149–153
Vaghasiya JD, Sheth NR, Bhalodia YS, Jivani NP. Exaggerated liver injury induced by renal ischemia reperfusion in diabetes: effect of exenatide. Saudi J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(3): 174–180
Ozturk H, Gezici A, Ozturk H. The effect of celecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, on liver ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in rats. Hepatol Res 2006; 34(2): 76–83
Farber JL, Gerson RJ. Mechanism of cell injury with hepatotoxic chemicals. Pharmacol Rew 1984; 36: 715–745
Hearse DJ. Reperfusion of the ischemic myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1977; 9(8): 605–616
Arda-Pirincci P, Bolkent S. The role of glucagon-like peptide-2 on apoptosis, cell proliferation, and oxidant-antioxidant system at a mouse model of intestinal injury induced by tumor necrosis factoralpha/ actinomycin D. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 350(1–2): 13–27
Neuman MG. Apoptosis in diseases of the liver. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2001; 38(2): 109–166
Rüdiger HA, Graf R, Clavien PA. Liver ischemia: apoptosis as a central mechanism of injury. J Invest Surg 2003; 16(3): 149–159
Schmeling DJ, Caty MG, Oldham KT, Guice KS. Cytoprotection by diclofenac sodium after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Pediatr Surg 1994; 29(8): 1044–1048
Tsung A, Kaizu T, Nakao A, Shao L, Bucher B, Fink MP, Murase N, Geller DA. Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by decreasing hepatic necrosis and apoptosis. Transplantation 2005; 79(2): 196–204
Schmeding M, Neumann UP, Boas-Knoop S, Spinelli A, Neuhaus P. Erythropoietin reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat liver. Eur Surg Res 2007; 39(3): 189–197
Erdogan O, Yildiz S, Basaran A, Demirbas A, Yesilkaya A. Effect of intraportal verapamil infusion on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pol J Pharmacol 2001; 53(2): 137–141
Hiranuma S, Ito K, Noda Y, Ozasa H, Koike Y, Horikawa S. Amelioration of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in the remnant liver after partial hepatectomy in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 22(12): 2167–2172
Taylor-Edwards CC, Burrin DG, Kristensen NB, Holst JJ, McLeod KR, Harmon DL. Glucagon-like peptide-2 (GLP-2) increases net amino acid utilization by the portal-drained viscera of ruminating calves. Animal 2012; 6(12): 1985–1997
Guan X, Stoll B, Lu X, Tappenden KA, Holst JJ, Hartmann B, Burrin DG. GLP-2-mediated up-regulation of intestinal blood flow and glucose uptake is nitric oxide-dependent in TPN-fed piglets 1. Gastroenterology 2003; 125(1): 136–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topaloğlu, N., Küçük, A., Yıldırım, Ş. et al. Glucagon-like peptide-2 exhibits protective effect on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Front. Med. 9, 368–373 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-015-0403-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-015-0403-1