Abstract
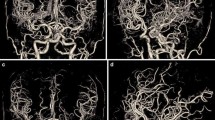
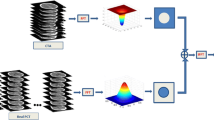
We implemented a new protocol—multiphase dynamic helical scan to acquire CT angiography (CTA) and whole brain CT perfusion (CTP) images simultaneously with single scan on 16 multidetector CT (MDCT). A total of 90 patients who were randomly assigned into 3 groups were included in our study. Each group underwent CT scan by using the new protocol, traditional CTA and CTP protocol, respectively. The image quality of CTA, the CTP parameter values and the X-ray doses were measured and compared between the new protocol and the traditional protocols. There was no statistically significant difference in the CTA image quality between the above methods (P = 0.55). For CTP parameters, the new protocol tended to overestimate the blood volume (BV) and blood flow (BF) value, and to underestimate the mean transit time (MTT) value compared with the traditional method. However, there was no statistically significant difference in BV, BF, and MTT value between the two methods except permeability surface (PS) (P>0.05). The volume CT dose index (CTDIvol) and dose length product (DLP) of our protocol were lower than the traditional one. The new protocol can obtain valuable diagnostic information in a shorter time without significant compromise in image quality. In addition, it reduces the radiation dose as well as contrast medium usage on the patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue J, Gao P, Wang X, Liao X, Wang Y, Wang Y. Ischemic lesion typing on computed tomography perfusion and computed tomography angiography in hyperacute ischemic stroke: a preliminary study. Neurol Res, 2008, 30(4): 337–340
Parsons M W. Perfusion CT: is it clinically useful? Int J Stroke, 2008, 3(1): 41–50
Scaroni R, Tambasco N, Cardaioli G, Parnetti L, Paloni F, Boranga B, Pelliccioli G P. Multimodal use of computed tomography in early acute stroke, part 2. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2006, 28(3,4): 427–431
Murphy B D, Fox A J, Lee D H, Sahlas D J, Black S E, Hogan M J, Coutts S B, Demchuk A M, Goyal M, Aviv R I, Symons S, Gulka I B, Beletsky V, Pelz D, Hachinski V, Chan R, Lee T Y. Identification of penumbra and infarct in acute ischemic stroke using computed tomography perfusion-derived blood flow and blood volume measurements. Stroke, 2006, 37(7): 1771–1777
Zhang Q B, Feng X Y, He H J, Jiang B D. Multi-slice helical CT perfusion imaging in evaluating intracranial neoplasms and tumor-like lesions. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2007, 29(2): 131–135 (in Chinese)
Cianfoni A, Colosimo C, Basile M, Wintermark M, Bonomo L. Brain perfusion CT: principles, technique and clinical applications. Radiol Med, 2007, 112(8): 1225–1243
Schramm P. High-concentration contrast media in neurological multidetector-row CT applications: implications for improved patient management in neurology and neurosurgery. Neuroradiology, 2007, 49(Suppl1): S35–45
Eastwood J D, Lev M H, Azhari T, Lee T Y, Barboriak D P, Delong D M, Fitzek C, Herzau M, Wintermark M, Meuli R, Brazier D, Provenzale J M. CT perfusion scanning with deconvolution analysis: pilot study in patients with acute middle cerebral artery stroke. Radiology, 2002, 222(1): 227–236
Scharf J, Brockmann M A, Daffertshofer M, Diepers M, Neumaier-Probst E, Weiss C, Paschke T, Groden C. Improvement of sensitivity and inter-rater reliability to detect acute stroke by dynamic perfusion computed tomography and computed tomography angiography. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2006, 30(1): 105–110
Rydberg J, Buckwalter K A, Caldemeyer K S, Phillips M D, Conces D JJr, Aisen A M, Persohn S A, Kopecky K K. Multisection CT: Scanning Techniques and Clinical Applications. Radiographics, 2000, 20(6): 1787–1806
Wintermark M, Fischbein N J, Smith WS, Ko N U, Quist M, Dillon W P. Accuracy of dynamic perfusion CT with deconvolution in detecting acute hemispheric stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2005, 26(1): 104–112
Schramm P, Schellinger P D, Klotz E, Kallenberg K, Fiebach J B, Külkens S, Heiland S, Knauth M, Sartor K. Comparison of perfusion computed tomography and computed tomography angiography source images with perfusion-weighted imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with acute stroke of less than 6 hours’ duration. Stroke, 2004, 35(7): 1652–1658
Youn S W, Kim J H, Weon Y C, Kim S H, Han M K, Bae H J. Perfusion CT of the brain using 40-mm-wide detector and toggling table technique for initial imaging of acute stroke. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2008, 191(3): W120–126
Laghi A. Multidetector CT (64 Slices) of the liver: examination techniques. Eur Radiol, 2007, 17(3): 675–683
Eastwood J D, Lev M H, Provenzale J M. Perfusion CT with iodinated contrast material. Am J Roentgenol, 2003, 180(1): 3–12
Ezzeddine M A, Lev M H, McDonald C T, Rordorf G, Oliveira-Filho J, Aksoy F G, Farkas J, Segal A Z, Schwamm L H, Gonzalez R G, Koroshetz W J. CT angiography with whole brain perfused blood volume imaging: added clinical value in the assessment of acute stroke. Stroke, 2002, 33(4): 959–966
Lev M H, Segal A Z, Farkas J, Hossain S T, Putman C, Hunter G J, Budzik R, Harris G J, Buonanno F S, Ezzeddine M A, Chang Y, Koroshetz W J, Gonzalez R G, Schwamm L H. Utility of perfusion-weighted CT imaging in acute middle cerebral artery stroke treated with intra-arterial thrombolysis: prediction of final infarct volume and clinical outcome. Stroke, 2001, 32(9): 2021–2028
Dittrich R, Akdeniz S, Kloska S P, Fischer T, Ritter M A, Seidensticker P, Heindel W, Ringelstein E B, Nabavi D G. Low rate of contrast-induced nephropathy after CT perfusion and CT angiography in acute stroke patients. J Neurol, 2007, 254(11): 1491–1497
Roberts H C, Roberts T P, SmithWS, Lee T J, Fischbein N J, Dillon W P. Multisection dynamic CT perfusion for acute cerebral ischemia: the “toggling-table” technique. Am J Neuroradiol, 2001, 22(6): 1077–1080
Wintermark M, SmithWS, Ko N U, Quist M, Schnyder P, Dillon W P. Dynamic perfusion CT: optimizing the temporal resolution and contrast volume for calculation of perfusion CT parameters in stroke patients. Am J Neuroradiol, 2004, 25(5): 720–729
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Qi, J., Zhu, W. et al. Simultaneous acquisition of CT angiography and whole brain CT perfusion images by using multiphase dynamic helical scan on 16 MDCT. Front. Med. China 3, 230–235 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-009-0023-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-009-0023-8