Abstract
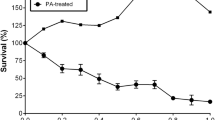
Elevated plasma levels of free fatty acids (FFAs) may contribute to insulin resistance (IR) that is characteristic of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this study, we investigated the effects of two fatty acids, palmitate (PA) and arachidonic acid (AA) on glycogenesis under insulin signaling in HepG2cells, a transformed hepatic carcinoma cell line. In the presence of 200 μmol of palmitate, insulin (10−7 mol/L) stimulation of glycogenesis was inhibited, as evidenced by increased glucose in the medium and decreased intracellular glycogen. Wortmannin (WM), a specific inhibitor of PI3K, dramatically decreased the amount of intracellular glycogen in cells without PA incubation. However, glycogen in PA treated cells was not significantly changed by WM, indicating that PA may also act on PI3K. Interestingly, AA restored the effects of WM inhibition on glycogenesis in PA cells. Western blot analysis demonstrated that PA in the absence of WM increased phosphorylated glycogen synthase (inactive form of GS) and decreased phosphorylated protein kinase B (active form of PKB), causing a reduction of intracellular glycogen. AA, however, reversed the effects of PA on GS and PKB. Furthermore, inhibition of protein kinase C (PKC) by a specific inhibitor chelerythrine chloride (CC) abolished the inhibitory effect of PA on glycogen synthesis by decreasing phosphorylated GS and increasing phosphorylated PKB. However, the effect of CC in the presence of PA disappeared when AA was also present.
Our results suggest that there is a disruption of the insulin signaling pathway between PKB and GS when the cells were exposed to PA, contributing to IR. PA may also interrupt the PKC signaling pathway. In contrast, AA could rescue glycogenesis impaired by PA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu R, Chandramouli V, Dicke B, Landau B, Rizza R. Obesity and type 2 diabetes impair insulin-induced suppression of glycogenolysis as well as gluconeogenesis. Diabetes, 2005, 54(7): 1942–1948
Bastard J P, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim M J, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw, 2006, 17(1): 4–12
Raubenheimer P J, Nyirenda M J, Walker B R. A choline-deficient diet exacerbates fatty liver but attenuates insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes, 2006, 55(7): 2015–2020
Armoni M, Harel C, Bar-Yoseph F, Milo S, Karnieli E. Free fatty acids repress the GLUT4 gene expression in cardiac muscle via novel response elements. J Biol Chem, 2005, 14,280(41): 34786–34795
Koo S H, Montminy M. Fatty acids and insulin resistance: A perfect storm. Mol Cell, 2006, 21(4): 449–450
Takahashi A, Shimano H, Nakagawa Y, Yamamoto T, Motomura K, Matsuzaka T, Sone H, Suzuki H, Toyoshima H, Yamada N. Transgenic mice overexpressing SREBP-1a under the control of the PEPCK promoter exhibit insulin resistance, but not diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2005, 1740(3): 427–433
Bell JA, Volpi E, Fujita S, Cadenas JG, Rasmussen BB. Dysregulation of muscle fatty acid metabolism in type 2 diabetes is independent of malonyl-CoA. Diabetologia, 2006, 49(9): 2144–2152
Storgaard H, Jensen C B, Bjornholm M, Song X M, Madsbad S, Zierath J R, Vaag A A. Dissociation between fat-induced in vivo insulin resistance and proximal insulin signaling in skeletal muscle in men at risk for type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004, 89(3): 1301–1311
Chavez J A, Holland W L, Bar J, Sandhoff K, Summers S A. Acid ceramidase overexpression prevents the inhibitory effects of saturated fatty acids on insulin signaling. J Biol Chem, 2005, 20,280(20): 20148–20153
Ginsberg H N, Zhang Y L, Hernandez-Ono A. Regulation of plasma triglycerides in insulin resistance and diabetes. Arch Med Res, 2005, 36(3): 232–240
Rask-Madsen C, King G L. Proatherosclerotic mechanisms involving protein kinase C in diabetes and insulin resistance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2005, 25(3): 487–496
Klover P J, Mooney R A. Hepatocytes: Critical for glucose homeostasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2004, 36(5): 753–758
Taniguchi C M, Ueki K, Kahn R. Complementary roles of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in the hepatic regulation of metabolism. J Clin Invest, 2005, 115(3): 718–727
Gual P, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti J F. Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling through IRS-1 phosphorylation. Biochimie, 2005, 87(1): 99–109
Feldstein A E, Werneburg N W, Canbay A, Guicciardi M E, Bronk S F, Rydzewski R, Burgart L J, Gores G J. Free fatty acids promote hepatic lipotoxicity by stimulating TNF-alpha expression via a lysosomal pathway. Hepatology, 2004, 40(1): 185–194
Yun M R, Lee J Y, Park H S, Heo H J, Park J Y, Bae S S, Hong K W, Sung S M, Kim C D. Oleic acid enhances vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res, 2006, 54(2): 97–102
Wang X L, Zhang L, Youker K, Zhang M X, Wang J, LeMaire S A, Coselli J S, Shen Y H. Free fatty acids inhibit insulin signaling-stimulated endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation through upregulating PTEN or inhibiting Akt kinase. Diabetes, 2006, 55(8): 2301–2310
Mook S, Halkes Cj C, Bilecen S, Cabezas M C. In vivo regulation of plasma free fatty acids in insulin resistance. Metabolism, 2004, 53(9): 1197–1201
Tiikkainen M, Hakkinen A M, Korsheninnikova E, Nyman T, Makimattila S, Yki-Jarvinen H. Effects of rosiglitazone and metformin on liver fat content, hepatic insulin resistance, insulin clearance, and gene expression in adipose tissue in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, 2004, 53(8): 2169–2176
Powell D J, Turban S, Gray A, Hajduch E, Hundal H S. Intracellular ceramide synthesis and protein kinase Czeta activation play an essential role in palmitate-induced insulin resistance in rat L6 skeletal muscle cells. Biochem J, 2004, 382(Pt 2): 619–629
Gupta D, Khandelwal R L. Modulation of insulin effects on phosphorylation of protein kinase B and glycogen synthesis by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in HepG2 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2004, 1671(1–3): 51–58
Jessen N, Djurhuus C B, Jorgensen J O, Jensen L S, Moller N, Lund S, Schmitz O. Evidence against a role for insulin-signaling proteins PI 3-kinase and Akt in insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle induced by short-term GH infusion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2005, 288(1): E194–E199
Au C S, Wagner A, Chong T, Qiu W, Sparks J D, Adeli K. Insulin regulates hepatic apolipoprotein B production independent of the mass or activity of Akt1/PKBalpha. Metabolism, 2004, 53(2):228–35
Gaster M, Beck-Nielsen H. Triacylglycerol accumulation is not primarily affected in myotubes established from type 2 diabetic subjects. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2006, 1761(1): 100–110
Bailey C J. Treating insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes with metformin and thiazolidinediones. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2005, 7(6): 675–691
Bajotto G, Murakami T, Nagasaki M, Qin B, Matsuo Y, Maeda K, Ohashi M, Oshida Y, Sato Y, Shimomura Y. Increased expression of hepatic pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases 2 and 4 in young and middle-aged Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats: Induction by elevated levels of free fatty acids. Metabolism, 2006, 55(3):317–323
Du K, Herzig S, Kulkarni R N, Montminy M. TRB3: A tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by insulin in liver. Science, 2003, 300: 1574–1577
Roden M. Mechanisms of Disease: hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes — pathogenesis and clinical relevance. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab, 2006, 2(6): 335–348
Kim J K, Fillmore J J, Sunshine M J, Albrecht B, Higashimori T, Kim D W, Liu Z X, Soos T J, Cline G W, O’Brien W R, Littman D R, Shulman G I. PKC-theta knockout mice are protected from fat-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest, 2004, 114(6):823–827
Cool B, Zinker B, Chiou W, Kifle L, Cao N, Perham M, Dickinson R, Adler A, Gagne G, Iyengar R, Zhao G, Marsh K, Kym P, Jung P, Camp H S, Frevert E. Identification and characterization of a small molecule AMPK activator that treats key components of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab, 2006, 3(6): 403–416
Louet J F, LeMay C, Mauvais-Jarvis F. Anti-diabetic actions of estrogen: Insight from human and genetic mouse models. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2004, 6(3): 180–185
Min Y, Lowy C, Ghebremeskel K, Thomas B, Offley-Shore B, Crawford M. Unfavorable effect of type 1 and type 2 diabetes on maternal and fetal essential fatty acid status: A potential marker of fetal insulin resistance. Am J Clin Nutr, 2005, 82(6): 1162–1168
Delarue J, LeFoll C, Corporeau C, Lucas D. N-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids: A nutritional tool to prevent insulin resistance associated to type 2 diabetes and obesity? Reprod Nutr Dev, 2004, 44(3): 289–299
Verlengia R, Gorjao R, Kanunfre C C, Bordin S, de Lima T M, Curi R. Effect of arachidonic acid on proliferation, cytokines production and pleiotropic genes expression in Jurkat cells—A comparison with oleic acid. Life Sciences, 2003, 73(23):2939–2951
Song M K, Hwang I K, Rosenthal M J, Harris D M, Yamaguchi D T, Yip I, Go V L. Antidiabetic action of arachidonic acid and zinc in genetically diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats. Metabolism, 2003, 52(1): 7–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Y., Wan, X., Duan, Q. et al. Inhibition of protein kinase B by palmitate in the insulin signaling of HepG2 cells and the preventive effect of arachidonic acid on insulin resistance. Front. Med. China 1, 200–206 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0038-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-007-0038-y