Abstract
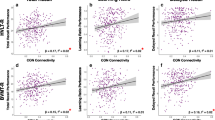
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease remains a challenge, and the development and validation of novel cognitive markers of Alzheimer’s disease is critical to earlier disease detection. The goal of the present study is to examine brain-behavior relationships of translational cognitive paradigms dependent on the medial temporal lobes and prefrontal cortices, regions that are first to undergo Alzheimer’s-associated changes. We employed multi-modal structural and functional MRI to examine brain-behavior relationships in a healthy, middle-aged sample (N = 133; 40–60 years). Participants completed two medial temporal lobe-dependent tasks (virtual Morris Water Task and Transverse Patterning Discriminations Task), and a prefrontal cortex-dependent task (Reversal Learning Task). No associations were found between various MRI measures of brain integrity and the Transverse Patterning or Reversal Learning tasks (p’s > .05). We report associations between virtual Morris Water Task performance and medial temporal lobe volume, hippocampal microstructural organization, fornix integrity, and functional connectivity within the executive control and frontoparietal control resting state networks (all p’s < 0.05; did not survive correction for multiple comparisons). This study suggests that virtual Morris Water Task performance is associated with medial temporal lobe integrity in middle age, a critical window for detection and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease, and may be useful as an early cognitive marker of Alzheimer’s disease risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Cabronero, J., & Nestor, P. J. (2014). Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer's disease: Insights into the limbic-diencephalic network and methodological considerations. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 6, 266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00266
Amlien, I. K., & Fjell, A. M. (2014). Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.017
Andersson, J. L., & Sotiropoulos, S. N. (2016). An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage, 125, 1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.019
Antonova, E., Parslow, D., Brammer, M., Dawson, G. R., Jackson, S. H., & Morris, R. G. (2009). Age-related neural activity during allocentric spatial memory. Memory, 17(2), 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658210802077348
Astur, R. S., Ortiz, M. L., & Sutherland, R. J. (1998). A characterization of performance by men and women in a virtual Morris water task: A large and reliable sex difference. Behavioural Brain Research, 93(1–2), 185–190.
Barnes, J., Bartlett, J. W., van de Pol, L. A., Loy, C. T., Scahill, R. I., Frost, C., ... Fox, N. C. (2009). A meta-analysis of hippocampal atrophy rates in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 30(11), 1711–1723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.01.010.
Beckmann, C. F., DeLuca, M., Devlin, J. T., & Smith, S. M. (2005). Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 360(1457), 1001–1013. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1634
Behrens, T. E., Woolrich, M. W., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Nunes, R. G., Clare, S., ... Smith, S. M. (2003). Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 50(5), 1077–1088. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.10609.
Behrens, T. E., Berg, H. J., Jbabdi, S., Rushworth, M. F., & Woolrich, M. W. (2007). Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: What can we gain? Neuroimage, 34(1), 144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.018
Bohbot, V. D., Lerch, J., Thorndycraft, B., Iaria, G., & Zijdenbos, A. P. (2007). Gray matter differences correlate with spontaneous strategies in a human virtual navigation task. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(38), 10078–10083. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1763-07.2007
Bondi, M. W., Edmonds, E. C., Jak, A. J., Clark, L. R., Delano-Wood, L., McDonald, C. R., ... Salmon, D. P. (2014). Neuropsychological criteria for mild cognitive impairment improves diagnostic precision, biomarker associations, and progression rates. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 42(1), 275–289. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-140276.
Cornwell, B. R., Johnson, L. L., Holroyd, T., Carver, F. W., & Grillon, C. (2008). Human hippocampal and parahippocampal theta during goal-directed spatial navigation predicts performance on a virtual Morris water maze. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(23), 5983–5990. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5001-07.2008
Cox, R. W. (1996). AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Computers and Biomedical Research, 29(3), 162–173.
Dahmani, L., & Bohbot, V. D. (2015). Dissociable contributions of the prefrontal cortex to hippocampus- and caudate nucleus-dependent virtual navigation strategies. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 117, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2014.07.002
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage, 9(2), 179–194. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0395
Dixon, R. M., Bradley, K. M., Budge, M. M., Styles, P., & Smith, A. D. (2002). Longitudinal quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease. Brain, 125(Pt 10), 2332–2341.
Driscoll, I., Hamilton, D. A., Petropoulos, H., Yeo, R. A., Brooks, W. M., Baumgartner, R. N., & Sutherland, R. J. (2003). The aging hippocampus: Cognitive, biochemical and structural findings. Cerebral Cortex, 13(12), 1344–1351.
Driscoll, I., Hamilton, D. A., Yeo, R. A., Brooks, W. M., & Sutherland, R. J. (2005). Virtual navigation in humans: The impact of age, sex, and hormones on place learning. Hormones and Behavior, 47(3), 326–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2004.11.013
Fellows, L. K., & Farah, M. J. (2003). Ventromedial frontal cortex mediates affective shifting in humans: Evidence from a reversal learning paradigm. Brain, 126(Pt 8), 1830–1837. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awg180
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., ... Dale, A. M. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Fischl, B., van der Kouwe, A., Destrieux, C., Halgren, E., Ségonne, F., Salat, D. H., ... Dale, A. M. (2004). Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 14(1), 11–22.
Florian, C., & Roullet, P. (2004). Hippocampal CA3-region is crucial for acquisition and memory consolidation in Morris water maze task in mice. Behavioural Brain Research, 154(2), 365–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2004.03.003
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). Mini-mental state: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189–198.
Greenwood, P. M., Lambert, C., Sunderland, T., & Parasuraman, R. (2005). Effects of apolipoprotein E genotype on spatial attention, working memory, and their interaction in healthy, middle-aged adults: Results from the National Institute of Mental Health's BIOCARD study. Neuropsychology, 19(2), 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1037/0894-4105.19.2.199
Greicius, M. D., Flores, B. H., Menon, V., Glover, G. H., Solvason, H. B., Kenna, H., ... Schatzberg, A. F. (2007). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biological Psychiatry, 62(5), 429–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.09.020.
Heise, V., Filippini, N., Trachtenberg, A. J., Suri, S., Ebmeier, K. P., & Mackay, C. E. (2014). Apolipoprotein E genotype, gender and age modulate connectivity of the hippocampus in healthy adults. Neuroimage, 98, 23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.081
Jack, C. R., Wiste, H. J., Weigand, S. D., Knopman, D. S., Vemuri, P., Mielke, M. M., ... Petersen, R. C. (2015). Age, sex, and APOE ε4 effects on memory, brain structure, and β-Amyloid across the adult life span. JAMA Neurology, 72(5), 511–519. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.4821.
Jack, C. R., Bennett, D. A., Blennow, K., Carrillo, M. C., Feldman, H. H., Frisoni, G. B., ... Dubois, B. (2016). A/T/N: An unbiased descriptive classification scheme for Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Neurology, 87(5), 539–547. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002923.
Kesner, R. P., & Churchwell, J. C. (2011). An analysis of rat prefrontal cortex in mediating executive function. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 96(3), 417–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2011.07.002
Kiuchi, K., Morikawa, M., Taoka, T., Nagashima, T., Yamauchi, T., Makinodan, M., ... Kishimoto, T. (2009). Abnormalities of the uncinate fasciculus and posterior cingulate fasciculus in mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer's disease: a diffusion tensor tractography study. Brain Research, 1287, 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.06.052.
Kok, E., Haikonen, S., Luoto, T., Huhtala, H., Goebeler, S., Haapasalo, H., & Karhunen, P. J. (2009). Apolipoprotein E-dependent accumulation of Alzheimer disease-related lesions begins in middle age. Annals of Neurology, 65(6), 650–657. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21696
Korthauer, L. E., Nowak, N. T., Moffat, S. D., An, Y., Rowland, L. M., Barker, P. B., ... Driscoll, I. (2016). Correlates of virtual navigation performance in older adults. Neurobiology of Aging, 39, 118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.12.003.
Korthauer, L. E., Awe, E., Frahmand, M., & Driscoll, I. (2018). Genetic risk for age-related cognitive impairment does not predict cognitive performance in middle age. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 64(2), 459–471. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-171043
Laczó, J., Vlcek, K., Vyhnálek, M., Vajnerová, O., Ort, M., Holmerová, I., ... Hort, J. (2009). Spatial navigation testing discriminates two types of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Behavioural Brain Research, 202(2), 252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.03.041.
Laczó, J., Andel, R., Vyhnalek, M., Vlcek, K., Magerova, H., Varjassyova, A., ... Hort, J. (2010). Human analogue of the morris water maze for testing subjects at risk of Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegenerative Diseases, 7(1–3), 148–152. https://doi.org/10.1159/000289226.
Mattis, S. (1988). Dementia rating scale (DRS). Psychological Assessment Resources.
Metzler-Baddeley, C., Baddeley, R. J., Jones, D. K., Aggleton, J. P., & O'Sullivan, M. J. (2013). Individual differences in fornix microstructure and body mass index. PLoS One, 8(3), e59849. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059849
Moffat, S. D., Kennedy, K. M., Rodrigue, K. M., & Raz, N. (2007). Extrahippocampal contributions to age differences in human spatial navigation. Cerebral Cortex, 17(6), 1274–1282. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhl036
Morris, R. G., Garrud, P., Rawlins, J. N., & O'Keefe, J. (1982). Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature, 297(5868), 681–683.
Morris, J. C., Roe, C. M., Xiong, C., Fagan, A. M., Goate, A. M., Holtzman, D. M., & Mintun, M. A. (2010). APOE predicts amyloid-beta but not tau Alzheimer pathology in cognitively normal aging. Annals of Neurology, 67(1), 122–131. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21843
Nickerson, L. D., Smith, S. M., Öngür, D., & Beckmann, C. F. (2017). Using dual regression to investigate network shape and amplitude in functional connectivity analyses. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 11, 115. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00115
Olsen, R. K., Moses, S. N., Riggs, L., & Ryan, J. D. (2012). The hippocampus supports multiple cognitive processes through relational binding and comparison. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 146. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00146
Ostreicher, M. L., Moses, S. N., Rosenbaum, R. S., & Ryan, J. D. (2010). Prior experience supports new learning of relations in aging. The Journals of Gerontology. Series B, Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 65B(1), 32–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbp081
Parnetti, L., Lowenthal, D. T., Presciutti, O., Pelliccioli, G. P., Palumbo, R., Gobbi, G., ... Senin, U. (1996). 1H-MRS, MRI-based hippocampal volumetry, and 99mTc-HMPAO-SPECT in normal aging, age-associated memory impairment, and probable Alzheimer's disease. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 44(2), 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb02428.x.
Provencher, S. W. (2001). Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo 1H spectra with LCModel. NMR in Biomedicine, 14(4), 260–264.
Redish, A. D., & Touretzky, D. S. (1998). The role of the hippocampus in solving the Morris water maze. Neural Computation, 10(1), 73–111.
Rickard, T. C., & Grafman, J. (1998). Losing their configural mind. Amnesic patients fail on transverse patterning. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 10(4), 509–524.
Smith, S. M. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17(3), 143–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.10062
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., ... Matthews, P. M. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage, 23(Suppl 1), S208–S219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051.
Smith, S. M., Beckmann, C. F., Andersson, J., Auerbach, E. J., Bijsterbosch, J., Douaud, G., ... Consortium, W.-M.H. (2013). Resting-state fMRI in the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage, 80, 144–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.039.
Strange, B. A., Witter, M. P., Lein, E. S., & Moser, E. I. (2014). Functional organization of the hippocampal longitudinal axis. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 15(10), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3785
Wang, L., Zang, Y., He, Y., Liang, M., Zhang, X., Tian, L., ... Li, K. (2006). Changes in hippocampal connectivity in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease: evidence from resting state fMRI. Neuroimage, 31(2), 496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.12.033.
Wang, K., Liang, M., Wang, L., Tian, L., Zhang, X., Li, K., & Jiang, T. (2007). Altered functional connectivity in early Alzheimer's disease: A resting-state fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 28(10), 967–978. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20324
Winkler, A. M., Ridgway, G. R., Webster, M. A., Smith, S. M., & Nichols, T. E. (2014). Permutation inference for the general linear model. Neuroimage, 92, 381–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.01.060
Zarei, M., Beckmann, C. F., Binnewijzend, M. A., Schoonheim, M. M., Oghabian, M. A., Sanz-Arigita, E. J., ... Barkhof, F. (2013). Functional segmentation of the hippocampus in the healthy human brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage, 66, 28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.10.071.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institute on Aging (NIA) R00-AG032361 (Driscoll) and F31-AG050407 (Korthauer).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions included conception and study design (ID), data collection and acquisition (LEK, EA, MF, RP, ID), statistical analysis (LEK, JKB), interpretation of results (LEK, JKB, ID), drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content (LEK, JKB, ID), and approval of the final version to be published and agreement to be accountable for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work (all authors).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All participants provided written informed consent in accordance with guidelines set by the institutional review boards at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee and Medical College of Wisconsin.
Conflict of interest/Disclosure statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korthauer, L.E., Blujus, J.K., Awe, E. et al. Brain-behavior investigation of potential cognitive markers of Alzheimer’s disease in middle age: a multi-modal imaging study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 1098–1105 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00573-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00573-x