Abstract
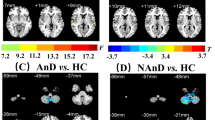
The current study aimed to characterize the regional homogeneity (ReHo) or fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuations (fALFF) alterations in first-episode drug-naïve schizophrenia comorbid with depression. Sixty-nine first-episode drug-naïve schizophrenia patients and 34 healthy controls (HC) were included in the final analysis. Schizophrenia patients were divided into depressive patients (DP) and non-depressive patients (NDP), with 35 and 34 patients respectively, using the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression -17(HRSD-17). All participants underwent resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI), the fALFF (slow-4 and slow-5 bands) and ReHo were used to process the data. The results revealed eleven brain regions with altered slow-5 fALFF, eleven brain regions with altered slow-4 fALFF and ten brain regions with altered ReHo among DP, NDP and HC groups. Compared to NDP, the DP group had increased slow-5 fALFF in the Right Inferior Temporal Gyrus, increased ReHo in the Right Superior and Inferior Frontal Gyrus. The altered slow-5 fALFF in the Right Inferior Temporal Gyrus, altered ReHo in the Right Inferior Frontal Gyrus and Superior Frontal Gyrus were all positively correlated with the depressive symptoms in patients. However, there were no significant differences in slow-4 fALFF between DP and NDP groups. Our results indicate that the increased slow-5 fALFF in the Right Inferior Temporal Gyrus, increased ReHo in the Right Superior and Inferior Frontal Gyrus were associated with depressive symptoms in schizophrenia, which may provide preliminary evidence in better understanding the neural mechanisms underlying depressive symptoms in schizophrenia.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 October 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00586-6
References
Anderson, G., Maes, M., & Berk, M. (2013). Schizophrenia is primed for an increased expression of depression through activation of immuno-inflammatory, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and tryptophan catabolite pathways. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry., 42, 101–114.
Biswal, B., Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine., 34(4), 537–541.
Chang, W. C., Cheung, R., Hui, C. L., Lin, J., Chan, S. K., Lee, E. H., et al. (2015). Rate and risk factors of depressive symptoms in Chinese patients presenting with first-episode non-affective psychosis in Hong Kong. Schizophrenia Research, 168(1–2), 99–105.
Chen, J. D., Liu, F., Xun, G. L., Chen, H. F., Hu, M. R., Guo, X. F., Xiao, C. Q., Wooderson, S. C., Guo, W. B., & Zhao, J. P. (2012). Early and late onset, first-episode, treatment-naive depression: Same clinical symptoms, different regional neural activities. Journal of Affective Disorders, 143(1–3), 56–63.
Chen, S., Xia, H. S., Zhu, F., Yin, G. Z., Qian, Z. K., Jiang, C. X., Gu, X. C., Yin, X. Y., Tang, W. J., Zhang, T. H., Wang, J. J., Jia, Q. F., & Hui, L. (2018). Association between decreased serum albumin levels and depressive symptoms in patients with schizophrenia in a Chinese Han population: A pilot study. Psychiatry Research, 270, 438–442.
Conley, R. R., Ascher-Svanum, H., Zhu, B., Faries, D. E., & Kinon, B. J. (2007). The burden of depressive symptoms in the long-term treatment of patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia research., 90(1–3), 186–197.
Cooper, C. M., Chin Fatt, C. R., Jha, M., Fonzo, G. A., Grannemann, B. D., Carmody, T., Ali, A., Aslan, S., Almeida, J. R. C., Deckersbach, T., Fava, M., Kurian, B. T., McGrath, P. J., McInnis, M., Parsey, R. V., Weissman, M., Phillips, M. L., Lu, H., Etkin, A., & Trivedi, M. H. (2019). Cerebral blood perfusion predicts response to sertraline versus placebo for major depressive disorder in the EMBARC trial. EClinicalMedicine., 10, 32–41.
Crespo-Facorro, B., Ortiz-García de la Foz, V., Mata, I., Ayesa-Arriola, R., Suarez-Pinilla, P., Valdizan, E. M., Vázquez-Barquero, J. L., & Pérez-Iglesias, R. (2013). Aripiprazole, Ziprasidone and Quetiapine in the treatment of first-episode nonaffective psychosis: A 12-week randomized, flexible-dose, open-label trial. Schizophrenia research., 147(2–3), 375–382.
Dai, J., Du, X., Yin, G., Zhang, Y., Xia, H., Li, X., et al. (2018). Prevalence, demographic and clinical features of comorbid depressive symptoms in drug naive patients with schizophrenia presenting with first episode psychosis. Schizophrenia Research, 193, 182–187.
Dai, L., Zhou, H., Xu, X., & Zuo, Z. (2019). Brain structural and functional changes in patients with major depressive disorder: A literature review. PeerJ., 7, e8170–e8170.
DeWitt, S. J., Bradley, K. A., Lin, N., Yu, C., & Gabbay, V. (2018). A pilot resting-state functional connectivity study of the kynurenine pathway in adolescents with depression and healthy controls. Journal of affective disorders., 227, 752–758.
Fang, X., Chen, L., Wang, D., Yu, L., Wang, Y., Chen, Y., Ren, J., Tang, W., & Zhang, C. (2019a). Metabolic profiling identifies TC and LDL as potential serum biomarkers for depressive symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 281, 112522–112522.
Fang, X., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Ren, J., & Zhang, C. (2019b). Depressive symptoms in schizophrenia patients: A possible relationship between SIRT1 and BDNF. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 95, 109673.
Gao, B., Wang, Y., Liu, W., Chen, Z., Zhou, H., Yang, J., Cohen, Z., Zhu, Y., & Zang, Y. (2015). Spontaneous activity associated with delusions of schizophrenia in the left medial superior frontal Gyrus: A resting-state fMRI study. PLoS One, 10(7), e0133766.
Guo, W.-B., Liu, F., Xun, G.-L., Hu, M.-R., Guo, X.-F., Xiao, C.-Q., et al. (2013). Reversal alterations of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in early and late onset, first-episode, drug-naive depression. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry., 40, 153–159.
Hare, S. M., Law, A. S., Ford, J. M., Mathalon, D. H., Ahmadi, A., Damaraju, E., Bustillo, J., Belger, A., Lee, H. J., Mueller, B. A., Lim, K. O., Brown, G. G., Preda, A., van Erp, T. G. M., Potkin, S. G., Calhoun, V. D., & Turner, J. A. (2018). Disrupted network cross talk, hippocampal dysfunction and hallucinations in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia research., 199, 226–234.
Herniman, S. E., Allott, K., Phillips, L. J., Wood, S. J., Uren, J., Mallawaarachchi, S. R., & Cotton, S. M. (2019). Depressive psychopathology in first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Psychological Medicine, 49(15), 2463–2474.
Huang, M., Lu, S., Yu, L., Li, L., Zhang, P., Hu, J., Zhou, W., Hu, S., Wei, N., Huang, J., Weng, J., & Xu, Y. (2017). Altered fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuation associated with cognitive dysfunction in first-episode drug-naïve major depressive disorder patients. BMC Psychiatry, 17(1), 11–11.
Huang, J., Zhu, Q., Hao, X., Shi, X., Gao, S., Xu, X., & Zhang, D. (2019). Identifying resting-state multifrequency biomarkers via tree-guided group sparse learning for schizophrenia classification. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 23(1), 342–350.
Lai, C. H., & Wu, Y. T. (2012). Frontal regional homogeneity increased and temporal regional homogeneity decreased after remission of first-episode drug-naïve major depressive disorder with panic disorder patients under duloxetine therapy for 6 weeks. Journal of Affective Disorders, 136(3), 453–458.
Lai, C. H., Wu, Y. T., Chen, C. Y., & Hou, Y. C. (2016). Gray matter increases in fronto-parietal regions of depression patients with aripiprazole monotherapy: An exploratory study. Medicine., 95(34), e4654–e4654.
Liang, Y., Shao, R., Zhang, Z., Li, X., Zhou, L., & Guo, S. (2019). Amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in childhood-onset schizophrenia with or without obsessive-compulsive symptoms: A resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Archives of Medical Science, 15(1), 126–133.
Little, J. T., Ketter, T. A., Kimbrell, T. A., Dunn, R. T., Benson, B. E., Willis, M. W., Luckenbaugh, D. A., & Post, R. M. (2005). Bupropion and venlafaxine responders differ in pretreatment regional cerebral metabolism in unipolar depression. Biological Psychiatry, 57(3), 220–228.
Meda, S. A., Wang, Z., Ivleva, E. I., Poudyal, G., Keshavan, M. S., Tamminga, C. A., Sweeney, J. A., Clementz, B. A., Schretlen, D. J., Calhoun, V. D., Lui, S., Damaraju, E., & Pearlson, G. D. (2015). Frequency-specific neural signatures of spontaneous low-frequency resting state fluctuations in psychosis: Evidence from bipolar-schizophrenia network on intermediate phenotypes (B-SNIP) consortium. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 41(6), 1336–1348.
Oldfield, R. C. (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia., 9(1), 97–113.
Park, S. C., Kim, J. M., Jun, T. Y., Lee, M. S., Kim, J. B., Yim, H. W., & Park, Y. C. (2017). How many different symptom combinations fulfil the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder? Results from the CRESCEND study. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 71(3), 217–222.
Peitl, V., Vidrih, B., Karlovic, Z., Getaldic, B., Peitl, M., & Karlovic, D. (2016). Platelet serotonin concentration and depressive symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 239, 105–110.
Peng, D.-H., Jiang, K.-D., Fang, Y.-R., Xu, Y.-F., Shen, T., Long, X.-Y., et al. (2011). Decreased regional homogeneity in major depression as revealed by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Chinese medical journal., 124(3), 369–373.
Rajkumar, R. P. (2015). Depressive symptoms during an acute schizophrenic episode: Frequency and clinical correlates. Depression Research and Treatment, 2015, 674641.
Rocca, P., Giugiario, M., Montemagni, C., Rigazzi, C., Rocca, G., & Bogetto, F. (2009). Quality of life and psychopathology during the course of schizophrenia. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 50(6), 542–548.
Tandon, R., Nasrallah, H. A., & Keshavan, M. S. (2009). Schizophrenia, “just the facts” 4. Clinical features and conceptualization. Schizophrenia Research, 110(1–3), 1–23.
Tang, S., Lu, L., Zhang, L., Hu, X., Bu, X., Li, H., Hu, X., Gao, Y., Zeng, Z., Gong, Q., & Huang, X. (2018). Abnormal amygdala resting-state functional connectivity in adults and adolescents with major depressive disorder: A comparative meta-analysis. EBioMedicine., 36, 436–445.
Turner, J. A., Damaraju, E., van Erp, T. G., Mathalon, D. H., Ford, J. M., Voyvodic, J., et al. (2013). A multi-site resting state fMRI study on the amplitude of low frequency fluctuations in schizophrenia. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7, 137.
Upthegrove, R., Ross, K., Brunet, K., McCollum, R., & Jones, L. (2014). Depression in first episode psychosis: The role of subordination and shame. Psychiatry Research, 217(3), 177–184.
Upthegrove, R., Marwaha, S., & Birchwood, M. (2017). Depression and schizophrenia: Cause, consequence, or trans-diagnostic issue? Schizophrenia bulletin., 43(2), 240–244.
Wang, L., Kong, Q., Li, K., Su, Y., Zeng, Y., Zhang, Q., Dai, W., Xia, M., Wang, G., Jin, Z., Yu, X., & Si, T. (2016). Frequency-dependent changes in amplitude of low-frequency oscillations in depression: A resting-state fMRI study. Neuroscience Letters, 614, 105–111.
Wang, P., Yang, J., Yin, Z., Duan, J., Zhang, R., Sun, J., Xu, Y., Liu, L., Chen, X., Li, H., Kang, J., Zhu, Y., Deng, X., Chang, M., Wei, S., Zhou, Y., Jiang, X., Wang, F., & Tang, Y. (2019). Amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) may be associated with cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: A correlation study. BMC Psychiatry, 19(1), 30–30.
Xu, Y., Zhuo, C., Qin, W., Zhu, J., & Yu, C. (2015). Altered spontaneous brain activity in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis and a large-sample study. BioMed Research International, 2015, 204628.
Yang, L., Yan, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, X., Lu, J., Chan, P., Yan, T., & Han, Y. (2018). Gradual disturbances of the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) and fractional ALFF in Alzheimer Spectrum. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12, 975–975.
Yu, R., Chien, Y. L., Wang, H. L., Liu, C. M., Liu, C. C., Hwang, T. J., et al. (2014). Frequency-specific alternations in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in schizophrenia. Human Brain Mapping, 35(2), 627–637.
Yu, Y., Li, Z., Lin, Y., Yu, J., Peng, G., Zhang, K., Jia, X., & Luo, B. (2019). Depression affects intrinsic brain activity in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13, 1333.
Zhang, N., Ji, L., Chen, Z., An, L., Ren, D., Bi, Y., Guo, Z., Yuan, R., Yuan, F., Dong, Z., Yin, L., Sun, X., Yang, F., Li, X., Yu, T., He, L., Shi, L., & He, G. (2020). No association between CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism with treatment remission to antidepressant venlafaxine in Han Chinese population. Psychiatric genetics., 30(1), 30–33.
Zhao, C., Zhu, J., Liu, X., Pu, C., Lai, Y., Chen, L., Yu, X., & Hong, N. (2018). Structural and functional brain abnormalities in schizophrenia: A cross-sectional study at different stages of the disease. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry., 83, 27–32.
Zhou, C., Tang, X., You, W., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., & Yu, M. (2019). Altered patterns of the fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation and functional connectivity between deficit and non-deficit schizophrenia. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10, 680–680.
Acknowledgments
We are deeply grateful to all participants who made contributions to our study for their generous participation, and psychiatrists for their help in the recruitment and diagnosis of schizophrenia patients.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1306800, 2018YFC1314300 and 2016YFC1307002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81971255 and 81571314), the medical key talent projects in Jiangsu Province (ZDRCA2016075), the Jiangsu Municipal Commission of Heath and Family Planning (H2017051), the Nanjing Municipal Commission of Heath and Family Planning (ZKX15033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XF, XZ and SX conceptualized and designed the study. RZ, CB, MZ, WY, SL and SX recruited the participants and completed the screening assessments. XF, RZ and CB performed the MRI manipulation. XF, RZ, CB, XZ and SX analyzed the data and performed the statistical analysis. XF, RZ, CB, XZ and SX wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All procedures for this study were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the Nanjing Brain Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant before the commencement of this study.
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xinyu Fang, Rongrong Zhang and Chenxi Bao contributed to this work equally. They should be regarded as Joint First Author.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 40 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, X., Zhang, R., Bao, C. et al. Abnormal regional homogeneity (ReHo) and fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuations (fALFF) in first-episode drug-naïve schizophrenia patients comorbid with depression. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 2627–2636 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00465-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00465-0