Abstract
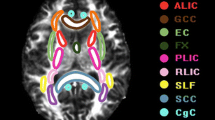
Vascular cognitive impairment, no dementia (VCIND) refers to cognitive deficits associated with underlying vascular causes that are insufficient to confirm a diagnosis of dementia. The default mode network (DMN) is a large-scale brain network of interacting brain regions involved in attention, working memory and executive function. The role of DMN white matter integrity in cognitive deficits of VCIND patients is unclear. Using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), this study was carried out to investigate white matter microstructural changes in the DMN in VCIND patients and their contributions to cognitive deficits. Thirty-one patients with subcortical VCIND and twenty-two healthy elderly subjects were recruited. All patients underwent neuropsychological assessments and DTI examination. Voxel-based analyses were performed to extract fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) measures in the DMN. Compared with the healthy elderly subjects, patients diagnosed with subcortical VCIND presented with abnormal white matter integrity in several key hubs of the DMN. The severity of damage in the white matter microstructure in the DMN significantly correlated with cognitive dysfunction. Mediation analyses demonstrated that DTI values could account for attention, executive and language impairments, and partly mediated global cognitive dysfunction in the subcortical VCIND patients. DMN integrity is significantly impaired in subcortical VCIND patients. The disrupted DMN connectivity could explain the attention, language and executive dysfunction, which indicates that the white matter integrity of the DMN may be a neuroimaging marker for VCIND.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agosta, F., Caso, F., & Filippi, M. (2013). Dementia and neuroimaging. Journal of Neurology, 260(2), 685–691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6778-x.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173–1182. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3806354.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain's default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124, 1–38. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1440.011.
Chen, S. Q., Cai, Q., Shen, Y. Y., Xu, C. X., Zhou, H., & Zhao, Z. (2016). Hydrogen proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in multidomain amnestic mild cognitive impairment and vascular Cognitive impairment without dementia. American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Other Dementias, 31(5), 422–429. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533317515628052.
Chen, H. J., Gao, Y. Q., Che, C. H., Lin, H., & Ruan, X. L. (2018). Diffusion tensor imaging with tract-based spatial statistics reveals white matter abnormalities in patients with vascular cognitive impairment. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 12, 53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00053.
Chua, T. C., Wen, W., Slavin, M. J., & Sachdev, P. S. (2008). Diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Current Opinion in Neurology, 21(1), 83–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e3282f4594b.
Corbetta, M., & Shulman, G. L. (2002). Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 3(3), 201–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn755.
de Vocht, F. (2007). [Health complaints and cognitive effects caused by exposure to MRI scanner magnetic fields]. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd, 132(2), 46–47. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17334150.
Debette, S., Bombois, S., Bruandet, A., Delbeuck, X., Lepoittevin, S., Delmaire, C., Leys, D., & Pasquier, F. (2007). Subcortical hyperintensities are associated with cognitive decline in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Stroke, 38(11), 2924–2930. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.488403.
Della Nave, R., Foresti, S., Pratesi, A., Ginestroni, A., Inzitari, M., Salvadori, E., Giannelli, M., Diciotti, S., Inzitari, D., & Mascalchi, M. (2007). Whole-brain histogram and voxel-based analyses of diffusion tensor imaging in patients with leukoaraiosis: correlation with motor and cognitive impairment. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 28(7), 1313–1319. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0555.
Fan, L., Li, H., Zhuo, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Chen, L., Yang, Z., Chu, C., Xie, S., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. T., Eickhoff, S. B., Yu, C., & Jiang, T. (2016). The human brainnetome atlas: a new brain atlas based on connectional architecture. Cerebral Cortex, 26(8), 3508–3526. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw157.
Fazekas, F., Chawluk, J. B., Alavi, A., Hurtig, H. I., & Zimmerman, R. A. (1987). MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology, 149(2), 351–356. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.149.2.351.
Fazekas, F., Kleinert, R., Offenbacher, H., Schmidt, R., Kleinert, G., Payer, F., et al. (1993). Pathologic correlates of incidental MRI white matter signal hyperintensities. Neurology, 43(9), 1683–1689 Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8414012.
Fazekas, F., Kapeller, P., Schmidt, R., Offenbacher, H., Payer, F., & Fazekas, G. (1996). The relation of cerebral magnetic resonance signal hyperintensities to Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neurological Science, 142(1-2), 121-125. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8902731.
Filippi, M., van den Heuvel, M. P., Fornito, A., He, Y., Hulshoff Pol, H. E., Agosta, F., et al. (2013). Assessment of system dysfunction in the brain through MRI-based connectomics. Lancet Neurology, 12(12), 1189–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70144-3.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189-198. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1202204.
Hachinski, V., Iadecola, C., Petersen, R. C., Breteler, M. M., Nyenhuis, D. L., Black, S. E., Powers, W. J., DeCarli, C., Merino, J. G., Kalaria, R. N., Vinters, H. V., Holtzman, D. M., Rosenberg, G. A., Wallin, A., Dichgans, M., Marler, J. R., & Leblanc, G. G. (2006). National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Canadian stroke network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards. Stroke, 37(9), 2220–2241. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000237236.88823.47.
Hansen, N. L., Lauritzen, M., Mortensen, E. L., Osler, M., Avlund, K., Fagerlund, B., & Rostrup, E. (2014). Subclinical cognitive decline in middle-age is associated with reduced task-induced deactivation of the brain's default mode network. Human Brain Mapping, 35(9), 4488–4498. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22489.
Hughes, C. P., Berg, L., Danziger, W. L., Coben, L. A., & Martin, R. L. (1982). A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 140, 566-572. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7104545.
Jia, J., Zhou, A., Wei, C., Jia, X., Wang, F., Li, F., Wu, X., Mok, V., Gauthier, S., Tang, M., Chu, L., Zhou, Y., Zhou, C., Cui, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, W., Yin, P., Hu, N., Zuo, X., Song, H., Qin, W., Wu, L., Li, D., Jia, L., Song, J., Han, Y., Xing, Y., Yang, P., Li, Y., Qiao, Y., Tang, Y., Lv, J., & Dong, X. (2014). The prevalence of mild cognitive impairment and its etiological subtypes in elderly Chinese. Alzheimers Dement, 10(4), 439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2013.09.008.
Kim, S. H., Park, J. S., Ahn, H. J., Seo, S. W., Lee, J. M., Kim, S. T., Han, S. H., & Na, D. L. (2011). Voxel-based analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in patients with subcortical vascular cognitive impairment: correlates with cognitive and motor deficits. Journal of Neuroimaging, 21(4), 317–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2010.00527.x.
Leech, R., Kamourieh, S., Beckmann, C. F., & Sharp, D. J. (2011). Fractionating the default mode network: distinct contributions of the ventral and dorsal posterior cingulate cortex to cognitive control. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(9), 3217–3224. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5626-10.2011.
Li, J. C., Jin, D., Li, A., Liu, B., Song, C. Y., Wang, P., et al. (2019). ASAF: altered spontaneous activity fingerprinting in Alzheimer’s disease based on multisite fMRI. Science Bulletin, 64(14), 998–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.04.034.
Lin, L., Xue, Y., Duan, Q., Sun, B., Lin, H., Chen, X., Luo, L., Wei, X., & Zhang, Z. (2015). Microstructural white matter abnormalities and cognitive dysfunction in subcortical ischemic vascular disease: an atlas-based diffusion tensor analysis study. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 56(2), 363–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0550-5.
Liu, Q., Zhu, Z., Teipel, S. J., Yang, J., Xing, Y., Tang, Y., & Jia, J. (2017). White matter damage in the cholinergic system contributes to cognitive impairment in subcortical vascular cognitive impairment, no dementia. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00047.
Lopez-Oloriz, J., Lopez-Cancio, E., Arenillas, J. F., Hernandez, M., Dorado, L., Dacosta-Aguayo, R., et al. (2014). Diffusion tensor imaging, intracranial vascular resistance and cognition in middle-aged asymptomatic subjects. Cerebrovascular Diseases, 38(1), 24–30. https://doi.org/10.1159/000363620.
Mansfield, A., Inness, E. L., & McIlroy, W. E. (2018). Stroke. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 159, 205–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63916-5.00013-6.
Mintun, M. A., Larossa, G. N., Sheline, Y. I., Dence, C. S., Lee, S. Y., Mach, R. H., Klunk, W. E., Mathis, C. A., DeKosky, S., & Morris, J. C. (2006). [11C]PIB in a nondemented population: potential antecedent marker of Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 67(3), 446–452. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000228230.26044.a4.
Mirsen, T. R., Lee, D. H., Wong, C. J., Diaz, J. F., Fox, A. J., Hachinski, V. C., & Merskey, H. (1991). Clinical correlates of white-matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging scans of the brain. Archives of Neurology, 48(10), 1015–1021. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1929891.
Nitkunan, A., McIntyre, D. J., Barrick, T. R., O'Sullivan, M., Shen, Y., Clark, C. A., et al. (2006). Correlations between MRS and DTI in cerebral small vessel disease. NMR in Biomedicine, 19(5), 610–616. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1052.
O'Sullivan, M., Morris, R. G., Huckstep, B., Jones, D. K., Williams, S. C., & Markus, H. S. (2004). Diffusion tensor MRI correlates with executive dysfunction in patients with ischaemic leukoaraiosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 75(3), 441–447. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14966162.
Pinto, T. C. C., Machado, L., Bulgacov, T. M., Rodrigues-Junior, A. L., Costa, M. L. G., Ximenes, R. C. C., & Sougey, E. B. (2018). Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) screening superior to the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) in the detection of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in the elderly? International Psychogeriatrics, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610218001370.
Qiu, A., Fennema-Notestine, C., Dale, A. M., Miller, M. I., & Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging, I. (2009). Regional shape abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage, 45(3), 656–661. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19280688.
Raichle, M. E., MacLeod, A. M., Snyder, A. Z., Powers, W. J., Gusnard, D. A., & Shulman, G. L. (2001). A default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(2), 676–682. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.98.2.676.
Robinson, J. L., Baxi, M., Katz, J. S., Waggoner, P., Beyers, R., Morrison, E., Salibi, N., Denney, T. S., Vodyanoy, V., & Deshpande, G. (2016). Characterization of structural connectivity of the default mode network in dogs using diffusion tensor imaging. Scientific Reports, 6, 36851. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36851.
Rockwood, K., Wentzel, C., Hachinski, V., Hogan, D. B., MacKnight, C., & McDowell, I. (2000). Prevalence and outcomes of vascular cognitive impairment. Vascular Cognitive impairment investigators of the Canadian Study of Health and Aging. Neurology, 54(2), 447–451. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10668712.
Rosazza, C., & Minati, L. (2011). Resting-state brain networks: literature review and clinical applications. Neurological Sciences, 32(5), 773–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0636-y.
Sachdev, P., Kalaria, R., O'Brien, J., Skoog, I., Alladi, S., Black, S. E., et al. (2014). Diagnostic criteria for vascular cognitive disorders: a VASCOG statement. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 28(3), 206–218. https://doi.org/10.1097/WAD.0000000000000034.
Scheltens, P., Leys, D., Barkhof, F., Huglo, D., Weinstein, H. C., Vermersch, P., ... Valk, J. (1992). Atrophy of medial temporal lobes on MRI in “probable” Alzheimer's disease and normal ageing: diagnostic value and neuropsychological correlates. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 55(10), 967-972. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1431963.
Seo, S. W., Ahn, J., Yoon, U., Im, K., Lee, J. M., Tae Kim, S., Ahn, H. J., Chin, J., Jeong, Y., & Na, D. L. (2010). Cortical thinning in vascular mild cognitive impairment and vascular dementia of subcortical type. Journal of Neuroimaging, 20(1), 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2008.00293.x.
Seo, S. W., Lee, J. M., Im, K., Park, J. S., Kim, S. H., Kim, S. T., Ahn, H. J., Chin, J., Cheong, H. K., Weiner, M. W., & Na, D. L. (2012). Cortical thinning related to periventricular and deep white matter hyperintensities. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(7), 1156–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.12.003.
Skrobot, O. A., Black, S. E., Chen, C., DeCarli, C., Erkinjuntti, T., Ford, G. A., et al. (2018). Progress toward standardized diagnosis of vascular cognitive impairment: guidelines from the vascular impairment of cognition classification consensus study. Alzheimers Dement, 14(3), 280–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.09.007.
Stephan, B. C., Matthews, F. E., Khaw, K. T., Dufouil, C., & Brayne, C. (2009). Beyond mild cognitive impairment: vascular cognitive impairment, no dementia (VCIND). Alzheimer's Research & Therapy, 1(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt4.
Sun, Y. W., Qin, L. D., Zhou, Y., Xu, Q., Qian, L. J., Tao, J., & Xu, J. R. (2011). Abnormal functional connectivity in patients with vascular cognitive impairment, no dementia: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Behavioural Brain Research, 223(2), 388–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.05.006.
Tao, Y., Liu, B., Zhang, X., Li, J., Qin, W., Yu, C., & Jiang, T. (2015). The structural connectivity pattern of the default mode network and its association with memory and anxiety. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 9, 152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00152.
Thong, J. Y., Du, J., Ratnarajah, N., Dong, Y., Soon, H. W., Saini, M., et al. (2014). Abnormalities of cortical thickness, subcortical shapes, and white matter integrity in subcortical vascular cognitive impairment. Human Brain Mapping, 35(5), 2320–2332. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22330.
van de Pol, L. A., Korf, E. S., van der Flier, W. M., Brashear, H. R., Fox, N. C., Barkhof, F., & Scheltens, P. (2007). Magnetic resonance imaging predictors of cognition in mild cognitive impairment. Archives of Neurology, 64(7), 1023–1028. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.64.7.1023.
van Straaten, E. C., Fazekas, F., Rostrup, E., Scheltens, P., Schmidt, R., Pantoni, L., et al. (2006). Impact of white matter hyperintensities scoring method on correlations with clinical data: the LADIS study. Stroke, 37(3), 836–840. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000202585.26325.74.
Weiler, M., de Campos, B. M., Nogueira, M. H., Pereira Damasceno, B., Cendes, F., & Balthazar, M. L. (2014). Structural connectivity of the default mode network and cognition in Alzheimers disease. Psychiatry Research, 223(1), 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.04.008.
Winblad, B., Palmer, K., Kivipelto, M., Jelic, V., Fratiglioni, L., Wahlund, L. O., Nordberg, A., Bäckman, L., Albert, M., Almkvist, O., Arai, H., Basun, H., Blennow, K., de Leon, M., DeCarli, C., Erkinjuntti, T., Giacobini, E., Graff, C., Hardy, J., Jack, C., Jorm, A., Ritchie, K., van Duijn, C., Visser, P., & Petersen, R. C. (2004). Mild cognitive impairment--beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Journal of Internal Medicine, 256(3), 240–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01380.x.
Xie, S., Chen, L., Zuo, N., & Jiang, T. (2016). DiffusionKit: A light one-stop solution for diffusion MRI data analysis. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 273, 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.08.011.
Xu, Q., Zhou, Y., Li, Y. S., Cao, W. W., Lin, Y., Pan, Y. M., & Chen, S. D. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging changes correlate with cognition better than conventional MRI findings in patients with subcortical ischemic vascular disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 30(4), 317–326. https://doi.org/10.1159/000320491.
Zarei, M., Damoiseaux, J. S., Morgese, C., Beckmann, C. F., Smith, S. M., Matthews, P. M., Scheltens, P., Rombouts, S. A., & Barkhof, F. (2009). Regional white matter integrity differentiates between vascular dementia and Alzheimer disease. Stroke, 40(3), 773–779. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.530832.
Zhan, Y. F., Yao, H. X., Wang, P., Zhou, B., Zhang, Z. Q., Guo, Y. E., et al. (2016). Network-based statistic show aberrant functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Ieee Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 10(7), 1182–1188. https://doi.org/10.1109/Jstsp.2016.2600298.
Zhang, M. Y., Katzman, R., Salmon, D., Jin, H., Cai, G. J., Wang, Z. Y., et al. (1990). The prevalence of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in Shanghai, China: Impact of age, gender, and education. Annals of Neurology, 27(4), 428–437. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410270412.
Zhou, Y., Lin, F. C., Zhu, J., Zhuang, Z. G., Li, Y. S., Tao, J., Qian, L. J., Xu, J. R., & Lei, H. (2008). Whole brain diffusion tensor imaging histogram analysis in vascular cognitive impairment. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 268(1–2), 60–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2007.11.005.
Zhou, Y., Qun, X., Qin, L. D., Qian, L. J., Cao, W. W., & Xu, J. R. (2011). A primary study of diffusion tensor imaging-based histogram analysis in vascular cognitive impairment with no dementia. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 113(2), 92–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2010.09.007.
Funding
This work was partially supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (JQ19024), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671040, 81970996), Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (Z191100006619046, Z171100000117001) and the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB32020200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 202 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Q., Tang, Y., Dou, X. et al. Default mode network integrity changes contribute to cognitive deficits in subcortical vascular cognitive impairment, no dementia. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 255–265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00252-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00252-y