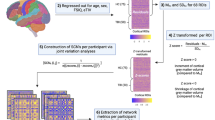
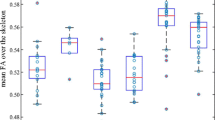
Abstract
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the main cause of disability in people younger than 35 in the United States. The mechanisms of TBI are complex resulting in both focal and diffuse brain damage. Fractal dimension (FD) is a measure that can characterize morphometric complexity and variability of brain structure especially white matter (WM) structure and may provide novel insights into the injuries evident following TBI. FD-based brain morphometry may provide information on WM structural changes after TBI that is more sensitive to subtle structural changes post injury compared to conventional MRI measurements. Anatomical and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) data were obtained using a 3 T MRI scanner in subjects with moderate to severe TBI and in healthy controls (HC). Whole brain WM volume, grey matter volume, cortical thickness, cortical area, FD and DTI metrics were evaluated globally and for the left and right hemispheres separately. A neuropsychological test battery sensitive to cognitive impairment associated with traumatic brain injury was performed. TBI group showed lower structural complexity (FD) bilaterally (p < 0.05). No significant difference in either grey matter volume, cortical thickness or cortical area was observed in any of the brain regions between TBI and healthy controls. No significant differences in whole brain WM volume or DTI metrics between TBI and HC groups were observed. Behavioral data analysis revealed that WM FD accounted for a significant amount of variance in executive functioning and processing speed beyond demographic and DTI variables. FD therefore, may serve as a sensitive marker of injury and may play a role in outcome prediction in TBI.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 November 2020
The original published version of this article contained mistakes. The author noticed that figure captions/legends got mismatched with the figures.
Abbreviations
- BET:
-
Brain Extraction Tool
- DTI:
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging
- FAST:
-
FMRIB’s Automated Segmentation Tool
- FD:
-
Fractal Dimension
- FLIRT:
-
FMRIB’s Linear Image Registration Tool
- FMRIB:
-
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Brain
- FNIRT:
-
FMRIB’s Nonlinear Image Registration Tool
- FSL:
-
Functional MRI of the brain Software Libraries
- FWER:
-
Family-Wise Error Rate
- FWHM:
-
Full-Width Half-Maximum
- GLM:
-
general linear model
- GM:
-
grey matter
- MPRAGE:
-
magnetization prepared rapid gradient echo
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- SPM:
-
statistical parametric mapping
- TBI:
-
Traumatic Brain Injury
- VBM:
-
voxel based morphometry
- WM:
-
white matter
References
Adams, J. H., Doyle, D., Ford, I., Gennarelli, T. A., Graham, D. I., & McLellan, D. R. (1989). Diffuse axonal injury in head injury: Definition, diagnosis and grading. [comparative study]. Histopathology, 15(1), 49–59.
Bazarian, J. J., Veazie, P., Mookerjee, S., & Lerner, E. B. (2006). Accuracy of mild traumatic brain injury case ascertainment using ICD-9 codes. [Comparative Study Evaluation Studies Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural. Validation Studies]. Academic emergency medicine : official journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, 13(1), 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1197/j.aem.2005.07.038.
Bigler, E. D. (2004). Neuropsychological results and neuropathological findings at autopsy in a case of mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 10(5), 794–806. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617704105146.
Bigler, E. D. (2015). Structural image analysis of the brain in neuropsychology using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques. Neuropsychology Review, 25(3), 224–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-015-9290-0.
Bolzenius, J. D., B, W., Velez, C. S., Drennon, A. M., Cooper, D. B., Kennedy, J. E., Reid, M. W., Bowles, A. O., Thompson, P. M., Gutman, B., Lewis, J. D., Ritter, J. L., York, G. E., Bigler, E. D., & Tate, D. F. (2018). Relationships between subcortical shape measures and subjective symptom reporting in US Service members with mild traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil, Mar/Apr, 33(2), 113–122.
Bullmore, E., Brammer, M., Harvey, I., Persaud, R., Murray, R., & Ron, M. (1994). Fractal analysis of the boundary between white matter and cerebral cortex in magnetic resonance images: A controlled study of schizophrenic and manic-depressive patients. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. Psychological Medicine, 24(3), 771–781.
Chelly, H., Chaari, A., Daoud, E., Dammak, H., Medhioub, F., Mnif, J., et al. (2011). Diffuse axonal injury in patients with head injuries: An epidemiologic and prognosis study of 124 cases. The Journal of Trauma, 71(4), 838–846. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3182127baa.
Cloots, R. J., Gervaise, H. M., van Dommelen, J. A., & Geers, M. G. (2008). Biomechanics of traumatic brain injury: Influences of the morphologic heterogeneities of the cerebral cortex. [research support, non-U.S. Gov't]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 36(7), 1203–1215, doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-008-9510-3.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage, 9(2), 179–194. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0395.
Delis, D. C., Kaplan, E., & Kramer, J. H. (2001). Delis-Kaplan executive function system (D-KEFS). San Antonio: Psychological Corporation.
Desikan, R. S., Segonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., et al. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021.
Douglas, D. B., Iv, M., Douglas, P. K., Anderson, A., Vos, S. B., Bammer, R., et al. (2015). Diffusion tensor imaging of TBI: Potentials and challenges. Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 24(5), 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1097/RMR.0000000000000062.
Esteban, F. J., Sepulcre, J., de Mendizabal, N. V., Goni, J., Navas, J., de Miras, J. R., et al. (2007). Fractal dimension and white matter changes in multiple sclerosis. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. NeuroImage, 36(3), 543–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.03.057.
Faul, M., Xu, L., Wald, M. M., & Coronado, V. G. (2010). Traumatic brain injury in the United States. Emergency department visits, hospitalizations and deaths 2002–2006. Atlanta, GA.: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Feng, Y., Abney, T. M., Okamoto, R. J., Pless, R. B., Genin, G. M., & Bayly, P. V. (2010). Relative brain displacement and deformation during constrained mild frontal head impact. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface / the Royal Society, 7(53), 1677–1688. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2010.0210.
Finkelstein, E., Corso, P., & Miller, T. (2006). The incidence and economic burden of injuries in the United States. New York: Oxford University Press.
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. [Research Support, U.S. Gov't, P.H.S.]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11050–11055. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.200033797.
Fischl, B., Liu, A., & Dale, A. M. (2001). Automated manifold surgery: Constructing geometrically accurate and topologically correct models of the human cerebral cortex. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 20(1), 70–80. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.906426.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., van der Kouwe, A. J., Makris, N., Segonne, F., Quinn, B. T., et al. (2004). Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage, 23(Suppl 1), S69–S84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.016.
Gennarelli, T. A., Thibault, L. E., Adams, J. H., Graham, D. I., Thompson, C. J., & Marcincin, R. P. (1982). Diffuse axonal injury and traumatic coma in the primate. [Research Support, U.S. Gov't, P.H.S.]. Annals of Neurology, 12(6), 564–574. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410120611.
Ghosh, A., Wilde, E. A., Hunter, J. V., Bigler, E. D., Chu, Z., Li, X., et al. (2009). The relation between Glasgow Coma Scale score and later cerebral atrophy in paediatric traumatic brain injury. [Multicenter Study Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. Brain injury : [BI], 23(3), 228–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699050802672789.
Graham DI, G. T. (2000). Pathology of brain damage after head injury. In G. J. Cooper PR (Ed.), Head Injury (pp. 133–153). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Huang, M. X., Theilmann, R. J., Robb, A., Angeles, A., Nichols, S., Drake, A., et al. (2009). Integrated imaging approach with MEG and DTI to detect mild traumatic brain injury in military and civilian patients. [Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S.]. Journal of Neurotrauma, 26(8), 1213–1226. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2008.0672.
Johnston, K. M., Ptito, A., Chankowsky, J., & Chen, J. K. (2001). New frontiers in diagnostic imaging in concussive head injury. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't Review]. Clinical journal of sport medicine : official journal of the Canadian Academy of Sport Medicine, 11(3), 166–175.
Jovicich, J., Czanner, S., Han, X., Salat, D., van der Kouwe, A., Quinn, B., et al. (2009). MRI-derived measurements of human subcortical, ventricular and intracranial brain volumes: Reliability effects of scan sessions, acquisition sequences, data analyses, scanner upgrade, scanner vendors and field strengths. NeuroImage, 46(1), 177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.010.
Kinnunen, K. M., Greenwood, R., Powell, J. H., Leech, R., Hawkins, P. C., Bonnelle, V., et al. (2011). White matter damage and cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. Brain : a Journal of Neurology, 134(Pt 2), 449–463. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq347.
Kirkwood, M. W., Yeates, K. O., & Wilson, P. E. (2006). Pediatric sport-related concussion: A review of the clinical management of an oft-neglected population. [review]. Pediatrics, 117(4), 1359–1371. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2005-0994.
Kraus, M. F., Susmaras, T., Caughlin, B. P., Walker, C. J., Sweeney, J. A., & Little, D. M. (2007). White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: A diffusion tensor imaging study. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural]. Brain : a journal of neurology, 130(Pt 10), 2508–2519. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm216.
Maas, A. I., Stocchetti, N., & Bullock, R. (2008). Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S. Review]. Lancet Neurology, 7(8), 728–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70164-9.
Maas, A. I., Roozenbeek, B., & Manley, G. T. (2010). Clinical trials in traumatic brain injury: Past experience and current developments. [Review]. Neurotherapeutics : the journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics, 7(1), 115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2009.10.022.
Mandelbrot, B. B. (1982). The fractal geometry of nature. New York, NY: Freeman.
Medina, D., DeToledo-Morrell, L., Urresta, F., Gabrieli, J. D., Moseley, M., Fleischman, D., et al. (2006). White matter changes in mild cognitive impairment and AD: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurobiology of Aging, 27(5), 663–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.03.026.
Mustafa, N., Ahearn, T. S., Waiter, G. D., Murray, A. D., Whalley, L. J., & Staff, R. T. (2012). Brain structural complexity and life course cognitive change. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. NeuroImage, 61(3), 694–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.088.
Powell, J. M., Ferraro, J. V., Dikmen, S. S., Temkin, N. R., & Bell, K. R. (2008). Accuracy of mild traumatic brain injury diagnosis. [research support, U.S. Gov't, P.H.S.]. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 89(8), 1550–1555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2007.12.035.
Rabinowitz, A. R., Hart, T., Whyte, J., & Kim, J. (2018). Neuropsychological recovery trajectories in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury: Influence of patient characteristics and diffuse axonal injury. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 24(3), 237–246. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617717000996.
Rajagopalan, V., Liu, Z., Allexandre, D., Zhang, L., Wang, X. F., Pioro, E. P., et al. (2013). Brain white matter shape changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): A fractal dimension study. PLoS One, 8(9), e73614. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073614.
Scheid, R., Walther, K., Guthke, T., Preul, C., & von Cramon, D. Y. (2006). Cognitive sequelae of diffuse axonal injury. Archives of Neurology, 63(3), 418–424. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.63.3.418.
Scolding, N. J. (1999). Greenfield's neuropathology. Sixth edition. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 66(5), 696.
Segonne, F., Pacheco, J., & Fischl, B. (2007). Geometrically accurate topology-correction of cortical surfaces using nonseparating loops. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 26(4), 518–529. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2006.887364.
Skandsen, T., Kvistad, K. A., Solheim, O., Strand, I. H., Folvik, M., & Vik, A. (2010). Prevalence and impact of diffuse axonal injury in patients with moderate and severe head injury: A cohort study of early magnetic resonance imaging findings and 1-year outcome. Journal of Neurosurgery, 113(3), 556–563. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.9.JNS09626.
Sled, J. G., Zijdenbos, A. P., & Evans, A. C. (1998). A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 17(1), 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.668698.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage, 23(Suppl 1), S208–S219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051.
Tate, D. F., Wade, B. S., Velez, C. S., Drennon, A. M., Bolzenius, J., Gutman, B. A., et al. (2016). Volumetric and shape analyses of subcortical structures in United States service members with mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurology, 263(10), 2065–2079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8236-7.
Teasdale, G., & Jennett, B. (1976). Assessment and prognosis of coma after head injury. [Research Support, U.S. Gov't, P.H.S.]. Acta Neurochirurgica, 34(1–4), 45–55.
Wen, W., & Sachdev, P. S. (2004). Extent and distribution of white matter hyperintensities in stroke patients: The Sydney stroke study. Stroke, 35(12), 2813–2819. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000147034.25760.3d.
Wilson, J. T., Pettigrew, L. E., & Teasdale, G. M. (1998). Structured interviews for the Glasgow outcome scale and the extended Glasgow outcome scale: Guidelines for their use. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. Journal of Neurotrauma, 15(8), 573–585.
Yue, J. K., Vassar, M. J., Lingsma, H., Cooper, S. R., Yuh, E. L., Mukherjee, P., et al. (2013). Transforming research and clinical knowledge in traumatic brain injury (TRACK-TBI) pilot: Multicenter implementation of the common data elements for traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2013.2970.
Zhang, Y., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2001). Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. [research support, non-U.S. Gov't]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 20(1), 45–57. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.906424.
Zhang, L., Liu, J. Z., Dean, D., Sahgal, V., & Yue, G. H. (2006). A three-dimensional fractal analysis method for quantifying white matter structure in human brain. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S.]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 150(2), 242–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.06.021.
Zhang, L., Dean, D., Liu, J. Z., Sahgal, V., Wang, X., & Yue, G. H. (2007). Quantifying degeneration of white matter in normal aging using fractal dimension. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't. Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S.]. Neurobiology of Aging, 28(10), 1543–1555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.06.020.
Zhang, L., Butler, A. J., Sun, C. K., Sahgal, V., Wittenberg, G. F., & Yue, G. H. (2008). Fractal dimension assessment of brain white matter structural complexity post stroke in relation to upper-extremity motor function. [Multicenter Study Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural]. Brain Research, 1228, 229–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.008.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by a grant of New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research (CBIR15MIG004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajagopalan, V., Das, A., Zhang, L. et al. Fractal dimension brain morphometry: a novel approach to quantify white matter in traumatic brain injury. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 914–924 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9892-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9892-2