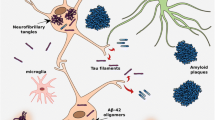
Abstract
The two neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are amyloid-\(\beta\) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles of tau protein. Fifteen years ago, Positron Emission Tomography (PET) with Pittsburgh Compound B (11C-PiB) enabled selective in-vivo visualization of amyloid-\(\beta\) plaque deposits and has since provided valuable information about the role of amyloid-\(\beta\) deposition in AD. The progression of tau deposition has been shown to be highly associated with neuronal loss, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline. Until recently it was not possible to visualize tau deposition in-vivo, but several tau PET tracers are now available in different stages of clinical development. To date, no tau tracer has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the evaluation of AD or other tauopathies, despite very active research efforts. In this paper we review the recent developments in tau PET imaging with a focus on in-vivo findings in AD and discuss the challenges associated with tau tracer development, the status of development and validation of different tau tracers, and the clinical information these provide.


Courtesy of Cristian Salinas, Biogen
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi, H., Williams, L., Beaton, D., Posamentier, M., Harris, T., Krishnan, A., et al. (2012). Analysis of regional cerebral blood flow data to discriminate among Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, and elderly controls: a multi-block barycentric discriminant analysis (MUBADA) methodology. Journal Alzheimers Diseases, 31(S3), S189-201.
Alzforum networking for a cure, News April 2017. (http://www.alzforum.org/news/conference-coverage/next-generation-tau-pet-tracers-strut-their-stuff).
Alzheimer’s Association. (2015). Changing the Trajectory of Alzheimer’s Disease: How a Treatment by 2025 Saves Lives and Dollars, Alzheimer’s Association report. http://www.alz.org/documents custom/trajectory.pdf.
Alzheimer’s Association. (2016). 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 12(4), 459–509.
Arriagada, P. V., Growdon, J. H., Hedley-Whyte, E. T., & Hyman, B. T. (1992). Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 42(3), 631–631.
Baker, S. L., Lockhart, S. N., Price, J. C., He, M., Huesman, R. H., Schonhaut, D., et al. (2016). Reference tissue–based kinetic evaluation of 18 F-AV-1451 for tau imaging. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(2), 332–338.
Barret, O., Alagille, D., Sanabria, S., Comley, R. A., Weimer, R. M., Borroni, E., et al. (2016). Kinetic modeling of the tau PET tracer 18F- AV-1451 in human healthy volunteers and alzheimer’s disease subjects. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(7), 1124–1131.
Barret, O., Seibly, J., Stephens, A., Madonia, J., Alagille, D., Mueller, A., et al. (2017). Initial clinical PET studies with the novel tau agent 18-F PI-2620 in Alzheimer’s disease and controls. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(Suppl 1), 630.
Becker, J. A., Cosio, D., Lee, C., Andrea, N., Sperling, R., & Johnson, K. (2017). A cortical cluster-based measure of change in longitudinal 18F-T807 FTP PET. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Betthauser, T. J., Lao, P. J., Murali, D., Barnhart, T. E., et al. (2017). In vivo comparison of tau radioligands 18F-THK-5351 and 18F-THK-5317. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(6), 996–1002.
Betthauser, T. J., Murali, D., Barnhart, T., Stone, C., et al. (2018). In vivo observations and quantification of tau with [F-18]MK-6240 PET from young controls to Alzheimer’s disease. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Bierer, L. M., Hof, P. R., Purohit, D. P., Carlin, L., Schmeidler, J., Davis, K. L., et al. (1995). Neocortical neurofibrillary tangles correlate with dementia severity in alzheimer’s disease. Archives of Neurology, 52(1), 81–88.
Braak, H., & Braak, E. (1991). Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathologica, 82(4), 239–259.
Braak, H., & Braak, E. (1999). Temporal sequence of Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology. In A. Peters, J. H. Morrison (Eds.), Cerebral Cortex (vol 14 pp. 475–512). Boston: Springer.
Braak, H., Thal, D. R., Ghebremedhin, E., & Del Tredici, K. (2011). Stages of the pathologic process in alzheimer disease: age categories from 1 to 100 Years. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology, 70(11), 960–969.
Carson, R. E., Channing, M. A., Blasberg, R. G., Dunn, B. B., Cohen, R. M., Rice, K. C., & Herscovitch, P. (1993). Comparison of bolus and infusion methods for receptor quantitation: application to 18F-cyclofoxy and positron emission tomography. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 13, 24–42.
Chien, D., Bahri, S., Szardenings, A., Walsh, J., Mu, F., Su, M., et al. (2013). Early clinical PET imaging results with the novel PHF-tau radioligand [F-18]-T807. Journal of Alzheimers Disease, 34, 457–68.
Chien, D., Szardenings, A., Bahri, S., Walsh, J., Mu, F., Xia, C., et al. (2014). Early clinical PET imaging results with the novel PHF-tau radioligand [F18]-T808. Journal of Alzheimers Disease, 38, 171–84.
Chiotis, K., Stenkrona, P., Almkvist, O., Arakawa, R., Takano, A., Stepanov, V., et al. (2017). Head-to-head comparison of tau-specific tracers in Alzheimer’s disease: [11C]THK5351 vs [11C]PBB3 PET imaging. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Cho, H., Choi, J. Y., Hwang, M. S., Kim, Y. J., Lee, H. M., Lee, H. S., Lee, J. H., Ryu, Y. H., Lee, M. S., & Lyoo, C. H. (2016). In vivo cortical spreading pattern of tau and amyloid in the Alzheimer disease spectrum. Annals of Neurology, 80(2), 247–258.
Crary, J., Trojanowski, J., Schneider, J., Abisambra, J., Abner, E., Alafuzoff, I., et al. (2014). Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): a common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathologica, 128, 755–66.
Dani, M., Brooks, D., & Edison, P. (2016). Tau imaging in neurodegener- ative diseases. European Journal Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 43, 1139–1150.
Delacourte, A., David, J. P., Sergeant, N., Buee, L., Wattez, A., Vermersch, P., et al. (1999). The biochemical pathway of neurofibrillary degeneration in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 52(6), 1158–1158.
Devous, M. D., Joshi, A. D., Navitsky, M., Kennedy, I., Lu, M., Pontecorvo, M. J., et al. (2015). Understanding the topology of 18F-AV-1451 (also known as T807) PET tau images in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 11(7), 283–284.
Donohue, M. C., Sperling, R. A., Petersen, R., Sun, C.-K., Weiner, M. W., & and, P. S. A (2017). Association Between Elevated Brain Amyloid and Subsequent Cognitive Decline Among Cognitively Normal Persons. JAMA, 317(22), 2305.
Drachman, D. A. (2014). The amyloid hypothesis time to move on: Amyloid is the downstream result, not cause, of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 10(3), 372–380.
Duyckaerts, C., Braak, H., Brion, J., Buee, L., Del, T. K., Goedert, M., et al. (2015). PART is part of Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathologica, 129, 749–56.
EXPEDITION 3 -Progress of Mild Alzheimer’s Disease in Participants on Solanezumab Versus Placebo. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01900665.
Fessel, J. (2018) Amyloid is essential but insufficient for Alzheimer causation: addition of subcellular cofactors is required for dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 33, 14–21.
Fodero-Tavoletti, M. T., Okamura, N., Mulligan, R., Furumoto, S., Connor, A. R., Kudo, Y., et al. (2010). Characterisation of [18F]-THK523 a novel in vivo tau imaging ligand. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 6(4), S432.
Giacobini, E., & Gold, G. (2013). Alzheimer disease therapy: moving from amyloid-β to tau. Nature Reviews Neurology, 9(12), 677–686.
Goate, A., Chartier-Harlin, M., Mullan, M., Brown, J., Crawford, F., Fidani, L., et al. (1991). Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature, 349, 704–706.
Gunn, R. N., Slifstein, M., Searle, G. E., & Price, J. C. (2015). Quantitative imaging of protein targets in the human brain with PET. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 60(22), R363–R411.
Hahn, A., Schain, M., Erlandsson, M., Sjolin, P., James, G., Strandberg, O., et al. (2017). Modeling strategies for quantification of in vivo 18F- AV1451 binding in patients with tau pathology. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(4), 623–631.
Hanseeuw, B. J., Betensky, R. A., Schultz, A. P., Papp, K. V., Mormino, E. C., Sepulcre, J., et al. (2017). Fluorodeoxyglucose metabolism associated with tau-amyloid interaction predicts memory decline. Annals of Neurology, 81(4), 583–596.
Hansen, A. K., Brooks, D. J., & Borghammer, P. (2017). MAO-B Inhibitors do not block. in vivo Flortaucipir([18F]-AV-1451) binding. Molecular Imaging Biology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-017-1143-1.
Harada, R., Ishiki, A., Kai, H., Sato, N., Furukawa, K., Furumoto, S., Tago, T., et al. (2017). Correlations of 18F-THK5351 PET with post-mortem burden of tau and astrogliosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.117.197426.
Harada, R., Okamura, N., Furumoto, S., Furukawa, K., Ishiki, A., Tomita, N., et al. (2015). 18F-THK5351: a novel PET radiotracer for imaging neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer disease. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 57(2), 208–214.
Harada, R., Okamura, N., Furumoto, S., Tago, T., Yanai, K., Arai, H., et al. (2016). Characteristics of Tau and Its Ligands in PET Imaging. Biomolecules, 6(1), 7.
Hardy, J. (2002). The amyloid hypothesis of alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science, 297(5580), 353–356.
Harrison, J., & Owen, M. (2016). Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid hypothesis on trial. British Journal Psychiatry, 208, 1–3.
Heneka, M., Carson, M., El, K. J., Landreth, G., Brosseron, F., Feinstein, D., et al. (2015). Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurology, 14, 388–405.
Herrup, K. (2015). The case for rejecting the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Nature Neuroscience, 18(6), 794–799.
Honer, M., Gobbi, L., Knust, H., Kuwabara, H., Muri, D., et al. (2017). Preclinical evaluation of (18)F-RO6958948, (11)C-RO6931643 and (11)C-RO6924963 as novel radiotracers for imaging aggregated tau in AD with positron emission tomography. Journal Nuclear Medicine. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.117.196741.
Hostetler, E., Walji, A., Zeng, Z., Miller, P., Bennacef, I., Salinas, C., et al. (2016). Preclinical characterization of 18F-MK-6240, a promising PET tracer for in vivo quantification of human neurofibrillary tangles. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 57(10), 1599–1606.
Hyman, B. T., Phelps, C. H., Beach, T. G., Bigio, E. H., Cairns, N. J., Carrillo, M. C., et al. (2012). National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 8(1), 1–13.
Ikonomovic, M. D., Abrahamson, E. E., Price, J. C., Mathis, C. A., & Klunk, W. E. (2016). [F-18]AV-1451 PET retention in the choroid plexus: more than “off-target” binding. Annals of Neurology, 80(2), 307–308.
Jang, Y., Lyoo, C. H., Park, S., et al. (2017). Head to head comparison of [18F] AV-1451 and [18F] THK5351 for tau imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. European Journal Nuclear Medicine Molecular Imaging (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3876-0.
Johnson, K. A., Schultz, A., Betensky, R. A., Becker, J. A., Sepulcre, J., Rentz, D., et al. (2016). Tau positron emission tomographic imaging in aging and early Alzheimer disease. Annals of Neurology, 79(1), 110–119.
Jonsson, T., Atwal, J., Steinberg, S., Snaedal, J., Jonsson, P., Bjornsson, S., et al. (2012). A mutation in APP protects against Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline. Nature, 488, 96 – 9.
Kimura, Y., Ichise, M., Ito, H., Shimada, H., Ikoma, Y., Seki, C., et al. (2015). PET Quantification of Tau Pathology in Human Brain with 11C- PBB3. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 56(9), 1359–1365.
Klunk, W. E., Engler, H., Nordberg, A., Wang, Y., Blomqvist, G., Holt, D. P., Bergström, M., et al. (2004). Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease using the novel PET tracer, PIB. Annals of Neurology, 55, 306–319.
Landau, S. (2016). The clinical significance of increasing amyloid in cognitively normal, amyloid negative individuals. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Lee, C., Marquie, M., Andrea, N., LaPoint, M., Jin, D., Jacobs, H., et al. (2017). 18F Flortaucipir binding in choroid plexus: association with race and hippocampus binding. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Lemoine, L., Gillberg, P., Svedberg, M., Stepanov, V., Jia, Z., Huang, J., Nag, S., Tian, H., et al. (2017). Comparative binding properties of the tau PET tracers THK5117, THK5351, PBB3, and T807 in postmortem Alzheimer brains. Alzheimers Research & Theraphy, 9(1), 96.
Liu, F., & Gong, C. X. (2008). Tau exon 10 alternative splicing and tauopathies. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 3(1), 8.
Lockhart, S. N., Baker, S., Okamura, N., Furukawa, K., Ishiki, A., Furumoto, S., et al. (2016). Dynamic PET measures of tau accumulation in cognitively normal older adults and Alzheimer’s disease patients measured using [18F] THK-5351. PLoS ONE, 11(6), e0158460.
Lopresti, B. J., Klunk, W. E., Mathis, C. A., Hoge, J. A., Ziolko, S. K., Lu, X., Meltzer, C. C., et al.. Schimmel, K., Tsopelas, N. D., DeKosky, S. T., Price, J. C. (2005). Simplified quantification of Pittsburgh Compound B amyloid imaging PET studies: a comparative analysis. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 46(12), 1959–1972.
Lowe, V., Curran, G., Fang, P., Liesinger, A., Josephs, K., Parisi, J., et al. (2016). An autoradiographic evaluation of AV-1451 Tau PET in dementia. Acta Neuropathologica Communications, 4, 58.
Lowe, V., Murray, M., Sarma, V., Curran, G., Fang, P., Pandey, M., et al. (2017). An autoradiographic evaluation of THK-5351 compared to AV-1451. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Maass, A., Landau, S., Baker, S. L., Horng, A., Lockhart, S. N., La Joie, R., et al. (2017). Comparison of multiple tau-PET measures as biomarkers in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage, 157, 448–463.
Marik, J., Tinianow, J., Ogasawara, A., Liu, N., Williams, S., Lyssikatos, J., Barret, O., et al. (2016). [18F]GTP1 – A tau specific tracer for imaging tau-pathology in AD. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Maruyama, M., Shimada, H., Suhara, T., Shinotoh, H., Ji, B., et al. (2013). Imaging of tau pathology in a tauopathy mouse model and in Alzheimer patients compared to normal controls. Neuron, 79(6), 1094-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.037.
Marquie, M., Aguero, C., Siao Tick Chong, M., Ramanan, P., Saez-Calveras, N., et al. (2018). F-18]-AV-1451 binding profile in Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy: a postmortem case series. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Marquie, M., Normandin, M. D., Meltzer, A. C., Chong, M. S. T., Andrea, N. V., Anton-Fernandez, A., et al. (2017). Pathological correlations of [F-18]-AV-1451 imaging in non-alzheimer tauopathies. Annals of Neurology, 81(1), 117–128.
Marquie, M., Normandin, M. D., Vanderburg, C. R., Costantino, I. M., Bien, E. A., Rycyna, L. G., et al. (2015). Validating novel tau positron emission tomography tracer [F-18]-AV-1451 (T807) on postmortem brain tissue. Annals of Neurology, 78(5), 787–800.
Mathis, C. A., Klunk, W. E., Price, J. C., & DeKosky, S. T. (2005). Amyloid imaging with Pittsburgh Compound B. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 1(1), S6–S7.
Mintun, M. A., Larossa, G. N., Sheline, Y. I., Dence, C. S., Lee, S. Y., Mach, et al. (2006). [11C]PIB in a nondemented population: potential antecedent marker of Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 67, 446–452.
Mormino, E., Schultz, A., Papp, K., LaPoint, M., Hanseeuw, B., Hedden, T., et al. (2017). Neocortical Tau and hippocampus volume reflect distinct processes in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 13(7), S5–S6.
Mueller, A., Kroth, H., Berndt, M., Capotosti, F., Molette, J., Schieferstein, H., et al. (2017). Characterization of the novel PET tracer PI-2620 for the assessment of Tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(Suppl.1), 847.
Ng, K. P., Pascoal, T. A., Mathotaarachchi, S., Therriault, J., Kang, M. S., Shin, M., et al. (2017). Monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, selegiline reduces 18F-THK5351 uptake in the human brain. Alzheimers Res Ther, 9(1), 25.
Okamura, N., Furumoto, S., Fodero-Tavoletti, M. T., Mulligan, R. S., Harada, R., Yates, P., et al. (2014). Non-invasive assessment of Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary pathology using 18F-THK5105 PET. Brain, 137 (6), 1762–1771.
Okamura, N., Furumoto, S., Harada, R., Tago, T., Yoshikawa, T., Fodero- Tavoletti, M., et al. (2013). Novel 18F-labeled arylquinoline derivatives for noninvasive imaging of tau pathology in Alzheimer disease. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 54(8), 1420–1427.
Okamura, N., & Yanai, K. (2017). Brain imaging: applications of tau PET imaging. Nature Reviews Neurology, 13, 197–198.
Olson, M. I., & Shaw, C. M. (1969). Presenile dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in mongolism. Brain, 92(1), 147–156.
Ono, M., Kitamura, S., Shimada, H., Sahara, N., Takuwa, H., Yoshiyama, Y., et al. (2017a). Development of novel tau PET tracers, [18F]AM-PBB3 and [18F]PM-PBB3. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Ono, M., Sahara, N., Kumata, K., Ji, B., Ni, R., Koga, S., et al. (2017b). Distinct binding of PET ligands PBB3 and AV-1451 to tau fibril strains in neurodegenerative tauopathies. Brain, 140(3), 764–780.
Ossenkoppele, R., Schonhaut, D. R., Schöll, M., Lockhart, S. N., Ayakta, N., Baker, S. L., et al. (2016). Tau PET patterns mirror clinical and neuroanatomical variability in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain, 139(5), 1551–1567.
Price, J. C., Klunk, W. E., Lopresti, B. J., Lu, X., Hoge, J. A., Ziolko, S. K., Holt, D. P., et al. (2005). Kinetic modeling of amyloid binding in humans using PET imaging and Pittsburgh Compound-B. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 25, 1528–1547.
Saint-Aubert, L., Lemoine, L., Chiotis, K., Leuzy, A., Rodriguez-Vieitez, E., & Nordberg, A. (2017). Tau PET imaging: present and future directions. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 12, 19.
Salinas, C., Chiao, P., Purohit, A., Schmidt, K., Beaver, J., Sur, C., et al. (2017). Quantitative analysis and correlation with clinical endpoints of [18F]MK6240 targeting neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in healthy volunteers and subjects with Alzheimer’s disease. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Sanabria-Bohorquez, S., Barret, O., Tamagnan, G., Alagille, D., Marik, J., Ayalon, G., et al. (2016). Evaluation of Tau burden in a cross-sectional cohort of Alzheimer’s disease subjects usign [18F]GTP1 (Genentech Tau Probe 1). Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 12(7), P1172.
Sanabria-Bohorquez, S., Bentsson, T., Barret, O., Tamagnan, G., Alagille, D., de Crespigny, A., et al. (2017). Kinetics of [18F]GTP1 (Genentech tau probe 1) in the basal ganglia of Alzheimer’s patients and healthy controls. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Scholl, M., Lockhart, S., Schonhaut, D., O’Neil, J., Janabi, M., Ossenkoppele, R., et al. (2016). PET Imaging of tau deposition in the aging human brain. Neuron, 89, 971 – 82.
Schwarz, A. J., Yu, P., Miller, B. B., Shcherbinin, S., Dickson, J., Navitsky, M., et al. (2016). Regional profiles of the candidate tau PET ligand18F-AV-1451 recapitulate key features of Braak histopathological stages. Brain, 139(5), 1539–1550.
Selkoe, D., & Hardy, J. (2016). The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 8, 595–608.
Shcherbinin, S., Schwarz, A. J., Joshi, A. D., Navitsky, M., Flitter, M., Shankle, W. M., Devous, M. D., & Mintun, M. A. (2016). Kinetics of the tau PET tracer 18F-AV-1451 (T807) in subjects with normal cognitive function, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer disease. Journal Nuclear Medicine, 57(10), 1535–1542.
Shoghi-Jadid, K., Small, G. W., Agdeppa, E. D., Kepe, V., Ercoli, L. M., Siddarth, P., et al. (2002). Localization of neurofibrillary tangles and beta-amyloid plaques in the brains of living patients with alzheimer disease. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 10(1), 24–35.
Slifstein, M. (2008). Revisiting an Old Issue: the Discrepancy Between Tissue Ratio-Derived Binding Parameters and Kinetic Modeling-Derived Parameters After a Bolus of the Serotonin Transporter Radioligand 123I- ADAM. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 49(2), 176–178.
Smith, R., Puschmann, A., Scholl, M., Ohlsson, T., van Swieten, J., Honer, M., et al. (2016). 18F-AV-1451 tau PET imaging correlates strongly with tau neuropathology in MAPT mutation carriers. Brain, 139(9), 2372–2379.
Sperling, R., Mormino, E., & Johnson, K. (2014). The evolution of pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease: implications for prevention trials. Neuron, 84(3), 608–622.
Stepanov, V., Svedberg, M., Jia, Z., Krasikova, R., Lemoine, L., Okamura, N., et al. (2017). Development of [11C]/[3H]THK-5351 – a potential novel carbon-11 tau imaging PET radioligand. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 46, 50–53.
Sur, C., Struyk, A., Bennacef, I., Lohith, T., Salinas, C. A., Telan-Choing, F., et al. (2017). [18F]MK-6240, a novel neurofibrillary tangles PET tracer: evaluation in healthy subjects and Alzheimer’s disease patients. Human Amyloid Imaging, Conference abstract.
Vermeiren, C., Mercier, J., Viot, D., Mairet-Coello, G., Hannestad, J., Courade, J.-P., et al. (2015). T807 a reported selective tau tracer, binds with nanomolar affinity to monoamine oxidase A. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 11(7), P283.
Villemagne, V., Rowe, C., Tamagnan, G., Fodero-Tavoletti, M., Okamura, N., Furumoto, S., et al. (2014). In vivo tau imaging with 18F- THK5105 and 18F-THK5117. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 10(4), P241.
Villemagne, V. L., Fodero-Tavoletti, M. T., Masters, C. L., & Rowe, C. C. (2015). Tau imaging: early progress and future directions. The Lancet Neurology, 14(1), 114–124.
Villemagne, V. L., Furumoto, S., Fodero-Tavoletti, M., Harada, R., Mulligan, R. S., Kudo, Y., et al. (2012). The challenges of tau imaging. Future Neurology, 7(4), 409–421.
Walji, A. M., Hostetler, E. D., Selnick, H., Zeng, Z., Miller, P., Bennacef, I., et al. (2016). Discovery of 6-(Fluoro-18F)-3-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin- 1-yl)isoquinolin-5-amine ([18F]-MK-6240): A Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging agent for quantification of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 59(10), 4778–4789.
Wong, D. F., Borroni, E., Kuwabara, H., George, N., Rosenberg, P., Lyketsos, C., et al. (2015). First in-human PET study of 3 novel tau radiopharmaceuticals: [11C]RO6924963 [11C]RO6931643, and [18F]RO6958948. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 11(7), P850–P851.
Wood, H. (2013). Alzheimer disease: [11C]PBB3— a new PET ligand that identifies tau pathology in the brains of patients with AD. Nature Reviews Neurology, 9(11), 599–599.
Wooten, D., Guehl, N. J., Verwer, E. E., Shoup, T. M., Yokell, D. L., Zubcevik, N., et al. (2016). Pharmacokinetic evaluation of the tau PET radiotracer [18F]T807 ([18F]AV-1451) in human subjects. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(3): 484–491.
Xia, C.-F., Areteaga, J., Chen, G., Gangagharmath, U., Gomez, L. F., Kasi, D., et al. (2013). [18F]T807, a novel tau positron emission tomography imaging agent for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 9(6), 666–676.
Yanai, K., Harada, R., & Okamura, N. (2016). Advances in the development of tau PET radiotracers and their clinical applications. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 19(Suppl 1), 9.
Funding
This work was supported by NIH grants (R01AG046396, R01AG027435, R01DC014296 and P01AG036694).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
CL and IG declare no conflict of interest. KAJ reports grants from NIH, Fidelity Biosciences, Harvard Neurodiscovery Center, and from the Alzheimer’s Association; and consulting for Lilly/Avid, Piramal, Abbvie, Biogen, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Genentech and GEHC. JCP reports NIH grant R01 AG050436; speaker honoraria from Yale University, Mount Sinai Hospital and Georgetown University; and is a member of NIH Center for Scientific Review Advisory Council.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lois, C., Gonzalez, I., Johnson, K.A. et al. PET imaging of tau protein targets: a methodology perspective. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 333–344 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9847-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9847-7