Abstract
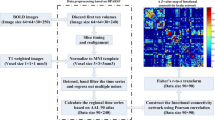
The basal ganglia (BG) are composed of several nuclei involved in neural processing associated with integration of sensory and motor information. Recent neuroimaging studies implicated its key role in control of voluntary motor function. As the sensorimotor abnormality is common among the end-stage renal disease (ESRD) population, in the current study, we aimed to investigate the abnormal structure and functional connectivity patterns of BG in ESRD patients. Twenty-nine ESRD and twenty-nine age and gender-matched healthy controls (HC) were enrolled to compare the volume of the subsets in the BG (e.g., caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus) by using the VBM analysis; resting-state functional connectivity was analyzed by a seed-based method. Compared with the HC group, ESRD patients had a smaller volume in the right putamen. Taking the right putamen as a seed region, we further found reduced functional connectivity in patients mainly between the putamen and supplementary motor area (SMA), insula, posterior mid-cingulate gyrus, and primary motor cortex. In ESRD group, the severity score of restless legs syndrome was negatively correlated with putamen-SMA functional connectivity, while the hemoglobin level was positively correlated with functional connectivity degree between the putamen and SMA. Our results revealed an abnormal volume of the putamen and its decreased functional connectivity patterns during resting state in ESRD with sensorimotor abnormalities. These preliminary results indicated that the decreased functional connectivity in putamen-SMA was associated with sensorimotor abnormalities, and anemia was correlated with this abnormal functional pattern in ESRD patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu, M., & Bara-Jimenez, W. (2002). State dependent excitability changes of spinal flexor reflex in patients with restless legs syndrome secondary to chronic renal failure. Sleep Medicine, 3(5), 427–430.
Allen, R. (2004). Dopamine and iron in the pathophysiology of restless legs syndrome (RLS). Sleep Medicine, 5(4), 385–391.
Beard, J., Erikson, K. M., & Jones, B. C. (2003). Neonatal iron deficiency results in irreversible changes in dopamine function in rats. Journal of Nutrition, 133(4), 1174–1179.
Bugnicourt, J. M., Godefroy, O., Chillon, J. M., Choukroun, G., & Massy, Z. A. (2013). Cognitive disorders and dementia in CKD: the neglected kidney-brain axis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 24(3), 353–363.
Chai, C., Zhang, M., Long, M., Chu, Z., Wang, T., Wang, L.et al (2015). Increased brain iron deposition is a risk factor for brain atrophy in patients with haemodialysis: a combined study of quantitative susceptibility mapping and whole brain volume analysis. Metabolic Brain Disease, 30(4), 1009–1016.
De Stefano, N., Filippi, M., Miller, D., Pouwels, P. J., Rovira, A., Gass, A.et al (2007). Guidelines for using proton MR spectroscopy in multicenter clinical MS studies. Neurology, 69(20), 1942–1952.
Di Martino, A., Scheres, A., Margulies, D. S., Kelly, A. M., Uddin, L. Q., Shehzad, Z.et al (2008). Functional connectivity of human striatum: a resting state FMRI study. Cerebral Cortex, 18(12), 2735–2747.
Earley, C. J., Allen, R. P., Connor, J. R., Ferrucci, L., & Troncoso, J. (2009). The dopaminergic neurons of the A11 system in RLS autopsy brains appear normal. Sleep Medicine, 10(10), 1155–1157.
Earley, C. J., Uhl, G. R., Clemens, S., & Ferre, S. (2016). Connectome and molecular pharmacological differences in the dopaminergic system in restless legs syndrome (RLS): plastic changes and neuroadaptations that may contribute to augmentation. Sleep Medicine.
Geng, D. Y., Li, Y. X., & Zee, C. S. (2006). Magnetic resonance imaging-based volumetric analysis of basal ganglia nuclei and substantia nigra in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgery, 58(2), 256–262; discussion 256–262.
Ghaemi, M., Hilker, R., Rudolf, J., Sobesky, J., & Heiss, W. D. (2002). Differentiating multiple system atrophy from Parkinson’s disease: contribution of striatal and midbrain MRI volumetry and multi-tracer PET imaging. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry, 73(5), 517–523.
Giannaki, C. D., Hadjigeorgiou, G. M., Karatzaferi, C., Pantzaris, M. C., Stefanidis, I., & Sakkas, G. K. (2014). Epidemiology, impact, and treatment options of restless legs syndrome in end-stage renal disease patients: an evidence-based review. Kidney International, 85(6), 1275–1282.
Giannaki, C. D., Sakkas, G. K., Karatzaferi, C., Hadjigeorgiou, G. M., Lavdas, E., Liakopoulos, V.et al (2011). Evidence of increased muscle atrophy and impaired quality of life parameters in patients with uremic restless legs syndrome. PLoS One, 6(10), e25180.
Gorges, M., Rosskopf, J., Muller, H. P., Lindemann, K., Hornyak, M., & Kassubek, J. (2016). Patterns of increased intrinsic functional connectivity in patients with restless legs syndrome are associated with attentional control of sensory inputs. Neuroscience Letters, 617264–269.
Hagemeier, J., Weinstock-Guttman, B., Bergsland, N., Heininen-Brown, M., Carl, E., Kennedy, C.et al (2012). Iron deposition on SWI-filtered phase in the subcortical deep gray matter of patients with clinically isolated syndrome may precede structure-specific atrophy. AJNR American Journal Neuroradiology, 33(8), 1596–1601.
Honey, C. J., Sporns, O., Cammoun, L., Gigandet, X., Thiran, J. P., Meuli, R.et al (2009). Predicting human resting-state functional connectivity from structural connectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(6), 2035–2040.
Joshua, M., Adler, A., & Bergman, H. (2009). The dynamics of dopamine in control of motor behavior. Current Opinion Neurobiology, 19(6), 615–620.
Jung, W. H., Jang, J. H., Park, J. W., Kim, E., Goo, E. H., Im, O. S.et al (2014). Unravelling the intrinsic functional organization of the human striatum: a parcellation and connectivity study based on resting-state FMRI. PLoS One, 9(9), e106768.
Kawauchi, A., Inoue, Y., Hashimoto, T., Tachibana, N., Shirakawa, S., Mizutani, Y.et al (2006). Restless legs syndrome in hemodialysis patients: health-related quality of life and laboratory data analysis. Clinical Nephrology, 66(6), 440–446.
Kong, X., Wen, J. Q., Qi, R. F., Luo, S., Zhong, J. H., Chen, H. J.et al (2014). Diffuse interstitial brain edema in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis: a tract-based spatial statistics study. Medicine (Baltimore), 93(28), e313.
Kumakura, Y., Gjedde, A., Danielsen, E. H., Christensen, S., & Cumming, P. (2006). Dopamine storage capacity in caudate and putamen of patients with early Parkinson’s disease: correlation with asymmetry of motor symptoms. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow Metabolism, 26(3), 358–370.
Lee, J. H., Han, Y. H., Kang, B. M., Mun, C. W., Lee, S. J., & Baik, S. K. (2013). Quantitative assessment of subcortical atrophy and iron content in progressive supranuclear palsy and parkinsonian variant of multiple system atrophy. Journal of Neurology, 260(8), 2094–2101.
Lehericy, S., Ducros, M., Krainik, A., Francois, C., Van de Moortele, P. F., Ugurbil, K.et al (2004). 3-D diffusion tensor axonal tracking shows distinct SMA and pre-SMA projections to the human striatum. Cerebral Cortex, 14(12), 1302–1309.
Luo, C., Li, Q., Xia, Y., Lei, X., Xue, K., Yao, Z.et al (2012). Resting state basal ganglia network in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Human Brain Mapping, 33(6), 1279–1294.
Ma, X., Jiang, G., Li, S., Wang, J., Zhan, W., Zeng, S.et al (2015). Aberrant functional connectome in neurologically asymptomatic patients with end-stage renal disease. PLoS One, 10(3), e0121085.
Mattson, M. P., & Shea, T. B. (2003). Folate and homocysteine metabolism in neural plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosciences, 26(3), 137–146.
Murtagh, F. E., Addington-Hall, J., & Higginson, I. J. (2007). The prevalence of symptoms in end-stage renal disease: a systematic review. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease, 14(1), 82–99.
Neuschmelting, V., Lucas, W., Stoffels, C., Oros-Peusquens, G., Lockau, A. M., Shah, H., N. J.et al (2016). Multimodal Imaging in Malignant Brain Tumors: Enhancing the Preoperative Risk Evaluation for Motor Deficits with a Combined Hybrid MRI-PET and Navigated Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Approach. AJNR American Journal of Neuroradiology, 37(2), 266–273.
Park, H. J., Kim, C. H., Park, E. S., Park, B., Oh, S. R., Oh, M. K.et al (2013). Increased GABA-A receptor binding and reduced connectivity at the motor cortex in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy: a multimodal investigation using 18F-fluoroflumazenil PET, immunohistochemistry, and MR imaging. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 54(8), 1263–1269.
Paulus, W., Dowling, P., Rijsman, R., Stiasny-Kolster, K., Trenkwalder, C., & de Weerd, A. (2007). Pathophysiological concepts of restless legs syndrome. Movement Disorders, 22(10), 1451–1456.
Power, J. D., Barnes, K. A., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2012). Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage, 59(3), 2142–2154.
Power, J. D., Mitra, A., Laumann, T. O., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2014). Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. Neuroimage, 84320–341.
Rieckmann, A., Gomperts, S. N., Johnson, K. A., Growdon, J. H., & Van Dijk, K. R. (2015). Putamen-midbrain functional connectivity is related to striatal dopamine transporter availability in patients with Lewy body diseases. Neuroimage Clinical, 8554 – 559.
Rijsman, R. M., de Weerd, A. W., Stam, C. J., Kerkhof, G. A., & Rosman, J. B. (2004). Periodic limb movement disorder and restless legs syndrome in dialysis patients. Nephrology (Carlton), 9(6), 353–361.
Rizzo, G., Tonon, C., Manners, D., Testa, C., & Lodi, R. (2013). Imaging brain functional and metabolic changes in restless legs syndrome. Current Neurology Neuroscience Reports, 13(9), 372.
Rossini, P. M., Treviso, M., Di Stefano, E., & Di Paolo, B. (1983). Nervous impulse propagation along peripheral and central fibres in patients with chronic renal failure. Electroencephalography Clinical Neurophysiology, 56(4), 293–303.
Sasson, E., Doniger, G. M., Pasternak, O., Tarrasch, R., & Assaf, Y. (2012). Structural correlates of cognitive domains in normal aging with diffusion tensor imaging. Brain Structure and Function, 217(2), 503–515.
Schormair, B., Plag, J., Kaffe, M., Gross, N., Czamara, D., Samtleben, W.et al (2011). MEIS1 and BTBD9: genetic association with restless leg syndrome in end stage renal disease. Journal of Medical Genetics, 48(7), 462–466.
Seifter, J., & Samuels, M. (2011). Uremic Encephalopathy and Other Brain Disorders Associated with Renal Failure. Seminars in Neurology, 31(02), 139–143.
Sharman, M., Valabregue, R., Perlbarg, V., Marrakchi-Kacem, L., Vidailhet, M., Benali, H.et al (2013). Parkinson’s disease patients show reduced cortical-subcortical sensorimotor connectivity. Movement Disorders, 28(4), 447–454.
Sloand, J. A., Shelly, M. A., Feigin, A., Bernstein, P., & Monk, R. D. (2004). A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of intravenous iron dextran therapy in patients with ESRD and restless legs syndrome. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 43(4), 663–670.
Smith, S. M. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17(3), 143–155.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H.et al (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage, 23Suppl 1S. 208–219.
Stocco, A., Lebiere, C., & Anderson, J. R. (2010). Conditional routing of information to the cortex: a model of the basal ganglia’s role in cognitive coordination. Psychological Review, 117(2), 541–574.
Stolic, R. V., Trajkovic, G. Z., Jekic, D., Sovtic, S. R., Jovanovic, A. N., Stolic, D. Z.et al (2014). Predictive parameters of survival in hemodialysis patients with restless leg syndrome. Saudi Journal Kidney Diseases and Transplantation, 25(5), 974–980.
Takaki, J., Nishi, T., Nangaku, M., Shimoyama, H., Inada, T., Matsuyama, N.et al (2003). Clinical and psychological aspects of restless legs syndrome in uremic patients on hemodialysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 41(4), 833–839.
Taniwaki, T., Okayama, A., Yoshiura, T., Nakamura, Y., Goto, Y., Kira, J.et al (2003). Reappraisal of the motor role of basal ganglia: a functional magnetic resonance image study. Journal of Neuroscience, 23(8), 3432–3438.
Tryc, A. B., Alwan, G., Bokemeyer, M., Goldbecker, A., Hecker, H., Haubitz, M.et al (2011). Cerebral metabolic alterations and cognitive dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantations, 26(8), 2635–2641.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N.et al (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage, 15(1), 273–289.
Walther, B. W. (2002). Treating restless legs syndrome: current pathophysiological concepts and clinical trials. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs, 11(4), 501–514.
Wang, Y., Isoda, M., Matsuzaka, Y., Shima, K., & Tanji, J. (2005). Prefrontal cortical cells projecting to the supplementary eye field and presupplementary motor area in the monkey. Neuroscience Research, 53(1), 1–7.
Watanabe, K., Watanabe, T., & Nakayama, M. (2014). Cerebro-renal interactions: impact of uremic toxins on cognitive function. Neurotoxicology, 44184–193.
Whishaw, I. Q., O’Connor, W. T., & Dunnett, S. B. (1986). The contributions of motor cortex, nigrostriatal dopamine and caudate-putamen to skilled forelimb use in the rat. Brain, 109 (Pt 5)805–843.
Winkelman, J. W., Gagnon, A., & Clair, A. G. (2013). Sensory symptoms in restless legs syndrome: the enigma of pain. Sleep Medicine, 14(10), 934–942.
Wu, T., Wang, L., Hallett, M., Chen, Y., Li, K., & Chan, P. (2011). Effective connectivity of brain networks during self-initiated movement in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage, 55(1), 204–215.
Yin, H. H., & Knowlton, B. J. (2006). The role of the basal ganglia in habit formation. Nature Reviews Neurosciences, 7(6), 464–476.
Yu, R., Liu, B., Wang, L., Chen, J., & Liu, X. (2013). Enhanced functional connectivity between putamen and supplementary motor area in Parkinson’s disease patients. PLoS One, 8(3), e59717.
Zhang, R., Liu, K., Yang, L., Zhou, T., Qian, S., Li, B.et al (2015). Reduced white matter integrity and cognitive deficits in maintenance hemodialysis ESRD patients: a diffusion-tensor study. European Radiology, 25(3), 661–668.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81371530) and the Research Funds of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, College of Medicine (Grant No. 2014YK3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dun Ding, Peng Li, Xueying Ma, Wanghuan Dun, Shifeng Yang, Shao-hui Ma, and Ming Zhang declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethical statements
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants for being included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, D., Li, P., Ma, Xy. et al. The relationship between putamen-SMA functional connectivity and sensorimotor abnormality in ESRD patients. Brain Imaging and Behavior 12, 1346–1354 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9808-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9808-6