Abstract
Previous studies have suggested that neurological factors partly explain the reduced motor competence found in many children with obesity. Accordingly, the aim of this study was to compare motor competence and white matter organization of important pathways for motor control (cerebellar peduncles) in children with and without obesity. Nineteen children with obesity and 25 children with a healthy weight, aged 7–11 years old, were included. Anthropometric measurements were taken and the level of motor competence was assessed using the Movement Assessment Battery for Children (2nd Edition). Children’s brain was scanned using diffusion weighted imaging preceded by a standard anatomical scan. Fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity were extracted from the cerebellar peduncles. Obese children’s level of motor competence was significantly lower than that in healthy weight peers (p < 0.05). Additionally, significant group differences (p < 0.05) were found for values of fractional anisotropy, but not for mean diffusivity. Further analyses revealed that lower values of fractional anisotropy in the inferior (p = 0.040) and superior (p = 0.007) cerebellar peduncles were present in children with obesity compared to children with a healthy weight. After controlling for multiple comparisons (p < 0.0167), only significant differences in the superior cerebellar peduncle remained significant. Our results showed that childhood obesity is accompanied by reduced motor competence and alterations in white matter organization. This suggests that the motor difficulties of children with obesity are not solely due to carrying excess weight, which may have implications for prevention and intervention programs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
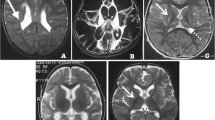
FA is a measure that captures the directionality of water diffusion along WM tracts and, hence, it is regarded as a proxy marker of WM microstructural organization.
MD refers to the magnitude of water diffusion along WM tracts. Lower values are considered to indicate more restricted water diffusion, which would be due to better myelination.
In Flanders, special schools are schools for children with special needs due to behavioral or developmental difficulties (e.g., autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, mental retardation).
Abbreviations
- OB:
-
Obesity
- HW:
-
Healthy weight
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- MD:
-
Mean diffusivity
- SCP:
-
Superior cerebellar peduncle
- ICP:
-
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
- MCP:
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
- WM:
-
White matter
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- MABC-2:
-
Movement assessment battery for children, second edition
References
Ahrens, W., Pigeot, I., Pohlabeln, H., De Henauw, S., Lissner, L., Molnár, D., Moreno, L. A., Tornaritis, M., Veidebaum, T., & Siani, A. (2014). Prevalence of overweight and obesity in European children below the age of 10. International Journal of Obesity, 38, S99–S107.
Alosco, M. L., Stanek, K. M., Galioto, R., Korgaonkar, M. S., Grieve, S. M., Brickman, A. M., Spitznagel, M. B., & Gunstad, J. (2014). Body mass index and brain structure in healthy children and adolescents. The International Journal of Neuroscience, 124(1), 49–55.
Broyles, S. T., Denstel, K. D., Church, T. S., Chaput, J. P., Fogelholm, M., Hu, G., Kuriyan, R., Kurpad, A., Lambert, E. V., Maher, C., Maia, J., Matsudo, V., Olds, T., Onywera, V., Sarmiento, O. L., Standage, M., Tremblay, M. S., Tudor-Locke, C., Zhao, P., & Katzmarzyk, P. T. (2015). The epidemiological transition and the global childhood obesity epidemic. International Journal of Obesity Supplements, 5, S3-8.
Byars, A. W., Holland, S. K., Strawsburg, R. H., Bommer, W., Dunn, R. S., Schmithorst, V. J., & Plante, E. (2002). Practical aspects of conducting large-scale functional magnetic resonance imaging studies in children. Journal of Child Neurology, 17(12), 885–890.
Caeyenberghs, K., Leemans, A., Geurts, M., Taymans, T., Vander Linden, C., Smits-Engelsman, B.C.M., Sunaert, S., & Swinnen, S. P. (2010). Brain-behavior relationships in young traumatic brain injury patients: DTI metrics are highly correlated with postural control. HBM, 31, 992–1002.
Castetbon, K., & Andreyeva, T. (2012). Obesity and motor skills among 4 to 6-year-old children in the united states: nationally-representative surveys. BMC Pediatric, 12(28), 1–9.
Cazettes, F., Cohen, J. I., Yau, P. L., Talbot, H., & Convit, A. (2011). Obesity-mediated inflammation may damage the brain circuit that regulates food intake. Brain Research, 1373, 101–109.
Cole, T. J., & Lobstein, T. (2012). Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatric Obesity, 7(4), 284–294.
D’Hondt, E., Deforche, B., De Bourdeaudhuij, I., & Lenoir, M. (2008). Childhood obesity affects fine motor skill performance under different postural constraints. Neuroscience Letters, 440, 72–75.
D’Hondt, E., Deforche, B., De Bourdeaudhuij, I., & Lenoir, M. (2009). Relationship between motor skill and body mass index in 5- to 10-year-old children. APAQ, 26(1), 21–37.
Davis, C. L., Tomporowski, P. D., Boyle, C. A., Waller, J. L., & Miller, P. H. (2007). Effects of aerobic exercise on overweight children’s cognitive functioning: a randomized controlled trial. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 78(5), 510–519.
Drijkoningen, D., Caeyenberghs, K., Leunissen, I., Vander Linden, C., Leemans, A., Sunaert, S., Duysens, J., & Swinnen, S. P. (2015). Training-induced improvements in postural control are accompanied by alterations in cerebellar white matter in brain injured patients. NeuroImage: Clinical, 7, 240–251.
Gentier, I., Augustijn, M., Deforche, B., Tanghe, A., De Bourdeaudhuij, I., Lenoir, M., & D’Hondt, E. (2013a). A comparative study of performance in simple and choice reaction time tasks between obese and healthy-weight children. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34, 2635–2641.
Gentier, I., D’Hondt, E., Shultz, S., Deforche, B., Augustijn, M., Hoorne, S., Verlaecke, K., De Bourdeaudhuij, I., & Lenoir, M. (2013b). Fine and gross motor skills differ between healthy-weight and obese children. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(11), 4043–4051.
Glickstein, M., & Doron, K. (2008). Cerebellum: connections and functions. Cerebellum, 7(4), 589–594.
Graf, C., Koch, B., Kretschmann-Kandel, E., Falkowski, G., Christ, H., Coburger, S., Lehmacher, W., Bjarnason-Wehrens, B., Platen, P., Tokarski, W., Predel, H. G., & Dordel, S. (2004). Correlation between BMI, leisure habits and motor abilities in childhood (CHILT-project). International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 28(1), 22–26.
Haga, M. (2008). The relationship between motor competence, physical fitness and self-perception in children. Child: Care, Health and Development, 34, 329–334.
Haltia, L. T., Viljanen, A., Parkkola, R., Kemppainen, N., Rinne, J. O., Nuutila, P., & Kaasinen, V. (2007). Brain white matter expansion in human obesity and the recovering effect of dieting. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 92(8), 3278–3284.
Hanaie, R., Mohri, I., Kagitani-Shimono, K., Tachibana, M., Azuma, J., Matsuzaki, J., Watanabe, Y., Fujita, N., & Taniike, M. (2013). Altered microstructural connectivity of the superior cerebellar peduncle is related to motor dysfunction in children with autistic spectrum disorders. Cerebellum, 12(5), 645–656.
Henderson, S. E., Sugden, D. A., & Barnett, A. L. (2007). Movement assessment battery for children – 2: Movement ABC-2: Examiner’s manual. London: Psychological Corporation.
Hermoye, L., Saint-Martin, C., Cosnard, G., Lee, S. K., Kim, J., Nassogne, M. C., Menten, R., Clapuyt, P., Donohue, P. K., Hua, K., Wakana, S., Jiang, H., van Zijl, P.C.M., & Mori, S. (2006). Pediatric diffusion tensor imaging: Normal database and observation of the white matter maturation in early childhood. NeuroImage, 29(2), 493–504.
Hue, O., Simoneau, M., Marcotte, J., Berrigan, F., Doré, J., Marceau, P., Marceau, S., Tremblay, A., & Teasdale, N. (2007). Body weight is a strong predictor of postural stability. Gait & Posture, 26(1), 32–38.
Jbabdi, S., Behrens, T.E.J., & Smith, S. M. (2010). Crossing fibres in tract-based spatial statistics. NeuroImage, 49(1), 249–256.
Jeurissen, B., Leemans, A., Tournier, J. D., Jones, D. K., & Sijbers, J. (2010). Estimating the number of fiber orientations in diffusion MRI voxels: a constrained spherical deconvolution study. Proceedings Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM), 573.
Jones, D. K., Knösche, T. R., & Turner, R. (2013). White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: the do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. NeuroImage, 73, 239–254.
Kamijo, K., Khan, N. A., Pontifex, M. B., Scudder, M. R., Drollette, E. S., Raine, L. B., Evans, E. M., Castelli, D. M., & Hillman, C. H. (2012). The relation of adiposity to cognitive control and scholastic achievement in preadolescent children. 20(12), 2406–2411.
Kravitz, A. V., O’Neal, T. J., & Friend, D. M. (2016). Do dopaminergic impairments underlie physical inactivity in people with obesity? Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 514.
Kullmann, S., Callaghan, M. F., Heni, M., Weiskopf, N., Scheffler, K., Häring, H. U., Fritsche, A., Veit, R., & Preissl, H. (2016). Specific white matter tissue microstructure changes associated with obesity. NeuroImage, 125, 36–44.
Kullmann, S., Schweizer, F., Veit, R., Fritsche, A., & Preissl, H. (2015). Compromised white matter integrity in obesity. Obesity Reviews, 16(4), 273–281.
Kumar, S., & Kelly, A. S. (2017). Review of childhood obesity: from epidemiology, etiology, and comorbidities to clinical assessment and treatment. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 1–15.
Leemans, A., Jeurissen, B., Sijbers, J., & Jones, D. K. (2009). ExploreDTI†¯: a graphical toolbox for processing, analyzing, and visualizing diffusion MR data. Proceedings of the International Society Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 245(2), 3300.
Lobstein, T., Baur, L., & Uauy, R. (2004). Obesity in children and young people†¯: a crisis in public health. Obesity Reviews, 5(1), 4–85.
Marqués-Iturria, I., Pueyo, R., Garolera, M., Segura, B., Junqué, C., García-García, I., Sender-Palacios, M. J., Vernet-Vernet, M., Narberhaus, A., Ariza, M., & Jurado, M. Á. (2013). Frontal cortical thinning and subcortical volume reductions in early adulthood obesity. Psychiatry Reseach Neuroimaging, 214(2), 109–115.
Metzler-Baddeley, C., Baddeley, R. J., Jones, D. K., Aggleton, J. P., & O’Sullivan, M. J. (2013). Individual differences in fornix microstructure and body mass index. PloS One, 8(3), 1–8.
Mori, S., Oishi, K., & Faria, A. V. (2009). White matter atlases based on diffusion tensor imaging. Current Opinion in Neurology, 22(4), 362–369.
Mori, S., Oishi, K., Jiang, H., Jiang, L., Li, X., Akhter, K., et al. (2008). Stereotaxic white matter atlas based on diffusion tensor imaging in an ICBM template. NeuroImage, 40(2), 570–582.
Ng, M., Fleming, T., Robinson, M., Thomson, B., Graetz, N., Margono, C., et al. (2014). Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet, 384(9945), 766–781.
Ou, X., Andres, A., Pivik, R. T., Cleves, M. A., & Badger, T. M. (2015). Brain gray and white matter differences in healthy normal weight and obese children. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: JMRI, 42(5), 1205–1213.
Piek, J. P., Baynam, G. B., & Barrett, N. C. (2006). The relationship between fine and gross motor ability, self-perceptions and self-worth in children and adolescents. Human Movement Science, 25(1), 65–75.
Raffelt, D., Tournier, J. D., Rose, S., Ridgway, G. R., Henderson, R., Crozier, S., Salvado, O., & Connelly, A. (2012). Apparent fibre density: a novel measure for the analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage, 59(4), 3976–3994.
Smits-Engelsman, B. C., Fiers, M. J., Henderson, S. E., & Henderson, L. (2008). Interrater reliability of the movement assessment battery for children. Physical Therapy, 88(2), 286–294.
Smits-Engelsman, B.C.M., Henderson, S. E., Sugden, D. A., & Barnett, A. L. (2010). Movement assessment battery for children-2: Manual. Amsterdam: Pearson, Incl. 208p
Sporns, O. (2011). The human connectome: a complex network. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1224(1), 109–125.
Stanek, K. M., Grieve, S. M., Brickman, A. M., Korgaonkar, M. S., Paul, R. H., Cohen, R. A., & Gunstad, J. J. (2011). Obesity is associated with reduced white matter integrity in otherwise healthy adults. Obesity Research, 19(3), 500–504.
Stoodley, C. J., Valera, E. M., & Schmahmann, J. D. (2012). Functional topography of the cerebellum for motor and cognitive tasks: an fMRI study. NeuroImage, 59(2), 1560–1570.
Thomas, A. R., Lacadie, C., Vohr, B., Ment, L. R., & Scheinost, D. (2017). Fine motor skill mediates visual memory ability with microstructural neuro-correlates in cerebellar peduncles in prematurely born adolescents. Cerebral Cortex, 172(Suppl 4), 81–87.e82.
Tuch, D. S., Reese, T. G., Wiegell, M. R., Makris, N., Belliveau, J. W., & Wedeen, V. J. (2002). High angular resolution diffusion imaging reveals intravoxel white matter fiber heterogeneity. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 48(4), 577–582.
Verstynen, T. D., Weinstein, A., Erickson, K. I., Sheu, L. K., Marsland, A. L., & Gianaros, P. J. (2013). Competing physiological pathways link individual differences in weight and abdominal adiposity to white matter microstructure. NeuroImage, 79, 129–137.
Verstynen, T. D., Weinstein, A. M., Schneider, W. W., Jakicic, J. M., Rofey, D. L., & Erickson, K. E. (2012). Increased body mass index is associated with a global and distributed decrease in white matter microstructural integrity. Psychosomatic Medicine, 74, 682–690.
Wang, F., Sun, Z., Du, X., Wang, X., Cong, Z., Zhang, H., Zhang, D., & Hong, N. (2003). A diffusion tensor imaging study of middle and superior cerebellar peduncle in male patients with schizophrenia. Neuroscience Letters, 348(3), 135–138.
Xu, J., Li, Y., Lin, H., Sinha, R., & Potenza, M. N. (2013). Body mass index correlates negatively with white matter integrity in the fornix and corpus callosum: a diffusion tensor imaging study. HBM, 34(5), 1044–1052.
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by the Ph.D. fellowship of the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO) awarded to Mireille Augustijn [3F000714]. The authors are very grateful to all participants and their parents, the staff from the rehabilitation centre “Zeepreventorium” (De Haan, Belgium) and the board of the participating schools. Finally, the authors would like to thank Kris Bakeland, Nele Bassier, Marieke Paredis, Hanne Lyskawa, Teresa Gobert and Helena Verhelst for their assistance in collecting the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of the experiment: MJCM Augustijn, FJA Deconinck, E D’Hondt, M. Lenoir, K. Caeyenberghs
Collection, processing of the data: MJCM Augustijn, L Van Acker.
Interpretation of the results: MJCM Augustijn, FJA Deconinck, E D’Hondt, M Lenoir, K Caeyenberghs
Drafting of the manuscript and critical revision: MJCM Augustijn, FJA Deconinck, E D’Hondt, M Lenoir, K Caeyenberghs, A De Guchtenaere.
All authors had final approval of the submitted and published version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest and declare to be responsible for the content.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augustijn, M.J.C.M., Deconinck, F.J.A., D’Hondt, E. et al. Reduced motor competence in children with obesity is associated with structural differences in the cerebellar peduncles. Brain Imaging and Behavior 12, 1000–1010 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9760-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9760-5