Abstract
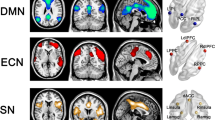
Alterations of the topological organization of abnormal regions or network-level structural aberrations are still poorly understood for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Herein, we investigated brain structural networks in recent-onset PTSD patients, all affected by the coalmine-flood disaster. Cortical networks were studied in recent onset PTSD patients (n = 15) and matched healthy controls (n = 25). Cortical networks were constructed by thresholding correlation matrices of 150 regions and quantified using graph theoretical approaches. Contributions of high-degree nodes, and regional and global network measures, including degree and betweenness, were studied. Compared with healthy controls, PTSD patients showed altered quantitative values in global network properties, characterized by shorter path length and higher clustering. Moreover, PTSD patients exhibited decreased connectivity in the right lingual gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, left supramarginal gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, bilateral superior and inferior frontal gyrus, superior frontal gyrus, and posterior cingulate gyrus. Nodal centrality decreased predominantly in the occipital regions (lingual gyrus) and default-mode regions, while increased correlations and centralities were observed in the medial temporal lobe and posterior cingulate cortex. PTSD-related networks exhibited a less efficient organization and regional connectivity. According to these findings, we conclude that regional connections involving fear-processing and re-experiential-processing cortex may play a role in maintaining or adapting to PTSD pathology.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bremner, J. D., Vermetten, E., Vythilingam, M., Afzal, N., Schmahl, C., Elzinga, B., & Charney, D. S. (2004). Neural correlates of the classic color and emotional stroop in women with abuse-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 55(6), 612–620. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2003.10.001.
Chen, S., Xia, W., Li, L., Liu, J., He, Z., Zhang, Z., Yan, L., Zhang, J., & Hu, D. (2006). Gray matter density reduction in the insula in fire survivors with posttraumatic stress disorder: A voxel-based morphometric study. Psychiatry Research, 146(1), 65–72. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2005.09.006.
Chen, Y., Fu, K., Feng, C., Tang, L., Zhang, J., Huan, Y., Cui, J., Mu, Y., Qi, S., Xiong, L., Ma, C., Wang, H., Tan, Q., & Yin, H. (2012). Different regional gray matter loss in recent onset PTSD and non PTSD after a single prolonged trauma exposure. PloS One, 7(11), e48298. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048298.
Chung, Y. A., Kim, S. H., Chung, S. K., Chae, J.-H., Yang, D. W., Sohn, H. S., & Jeong, J. (2006). Alterations in cerebral perfusion in posttraumatic stress disorder patients without re-exposure to accident-related stimuli. Clinical Neurophysiology, 117(3), 637–642. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2005.10.020.
Cloutman, L. L., & Lambon Ralph, M. A. (2012). Connectivity-based structural and functional parcellation of the human cortex using diffusion imaging and tractography. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 6(34). doi:10.3389/fnana.2012.00034.
Daniels, J. K., Lamke, J. P., Gaebler, M., Walter, H., & Scheel, M. (2013). White matter integrity and its relationship to PTSD and childhood trauma--a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depression and Anxiety, 30(3), 207–216. doi:10.1002/da.22044.
Davis, M., Walker, D. L., & Lee, Y. (1997). Roles of the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in fear and anxiety measured with the acoustic startle reflex. Possible relevance to PTSD. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 821, 305–331.
Dickie, E. W., Brunet, A., Akerib, V., & Armony, J. L. (2012). Anterior cingulate cortical thickness is a stable predictor of recovery from post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychological Medicine, 1–9. doi:10.1017/S0033291712001328.
Engdahl, B., Leuthold, A. C., Tan, H. R., Lewis, S. M., Winskowski, A. M., Dikel, T. N., & Georgopoulos, A. P. (2010). Post-traumatic stress disorder: A right temporal lobe syndrome? Journal of Neural Engineering, 7(6), 066005. doi:10.1088/1741-2560/7/6/066005.
Etkin, A., & Wager, T. D. (2007). Functional neuroimaging of anxiety: A meta-analysis of emotional processing in PTSD, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobia. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 164(10), 1476–1488. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07030504.
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11050–11055. doi:10.1073/pnas.200033797.
Greicius, M. D., Krasnow, B., Reiss, A. L., & Menon, V. (2003). Functional connectivity in the resting brain: A network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(1), 253–258. doi:10.1073/pnas.0135058100.
He, Y., Chen, Z. J., & Evans, A. C. (2007). Small-world anatomical networks in the human brain revealed by cortical thickness from MRI. Cerebral Cortex, 17(10), 2407–2419. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhl149.
He, Y., Chen, Z., & Evans, A. (2008). Structural insights into aberrant topological patterns of large-scale cortical networks in Alzheimer's disease. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(18), 4756–4766. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0141-08.2008.
Jelicic, M., & Merckelbach, H. (2004). Traumatic stress, brain changes, and memory deficits: A critical note. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 192(8), 548–553.
Jin, C., Qi, R., Yin, Y., Hu, X., Duan, L., Xu, Q., Zhang, Z., Zhong, Y., Feng, B., Xiang, H., Gong, Q., Liu, Y., Lu, G., & Li, L. (2014). Abnormalities in whole-brain functional connectivity observed in treatment-naive post-traumatic stress disorder patients following an earthquake. Psychological Medicine, 44(9), 1927–1936. doi:10.1017/S003329171300250X.
Landre, L., Destrieux, C., Baudry, M., Barantin, L., Cottier, J. P., Martineau, J., Hommet, C., Isingrini, M., Belzung, C., Gaillard, P., Camus, V., & El Hage, W. (2010). Preserved subcortical volumes and cortical thickness in women with sexual abuse-related PTSD. Psychiatry Research, 183(3), 181–186. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.01.015.
Lanius, R. A., Williamson, P. C., Hopper, J., Densmore, M., Boksman, K., Gupta, M. A., Neufeld, R. W., Gati, J. S., & Menon, R. S. (2003). Recall of emotional states in posttraumatic stress disorder: An fMRI investigation. Biological Psychiatry, 53(3), 204–210.
Liberzon, I., & Sripada, C. S. (2008). The functional neuroanatomy of PTSD: a critical review. Progress in Brain Research, 167, 151–169. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(07)67011-3.
Liu, Y., Li, Y. J., Luo, E. P., Lu, H. B., & Yin, H. (2012). Cortical thinning in patients with recent onset post-traumatic stress disorder after a single prolonged trauma exposure. PloS One, 7(6), e39025. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039025.
Long, Z., Duan, X., Xie, B., Du, H., Li, R., Xu, Q., Wei, L., Zhang, S. X., Wu, Y., Gao, Q., & Chen, H. (2013). Altered brain structural connectivity in post-traumatic stress disorder: A diffusion tensor imaging tractography study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 150(3), 798–806. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2013.03.004.
Lyoo, I. K., Kim, J. E., Yoon, S. J., Hwang, J., Bae, S., & Kim, D. J. (2011). The neurobiological role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in recovery from trauma. Longitudinal brain imaging study among survivors of the south Korean subway disaster. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68(7), 701–713. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.70.
Marrelec, G., Krainik, A., Duffau, H., Pelegrini-Issac, M., Lehericy, S., Doyon, J., & Benali, H. (2006). Partial correlation for functional brain interactivity investigation in functional MRI. NeuroImage, 32(1), 228–237. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.12.057.
Mcalonan, G. M., Cheung, V., Cheung, C., Suckling, J., Lam, G. Y., Tai, K. S., Yip, L., Murphy, D. G., & Chua, S. E. (2005). Mapping the brain in autism. A voxel-based MRI study of volumetric differences and intercorrelations in autism. Brain, 128(Pt 2), 268–276. doi:10.1093/brain/awh332.
Mitelman, S. A., Buchsbaum, M. S., Brickman, A. M., & Shihabuddin, L. (2005). Cortical intercorrelations of frontal area volumes in schizophrenia. NeuroImage, 27(4), 753–770. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.05.024.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D.G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339 b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535
Noppeney, U., Friston, K. J., Ashburner, J., Frackowiak, R., & Price, C. J. (2005). Early visual deprivation induces structural plasticity in gray and white matter. Current Biology, 15(13), R488–R490. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.06.053.
Qi, S., Mu, Y., Liu, K., Zhang, J., Huan, Y., Tan, Q., Shi, M., Wang, Q., Chen, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, N., Zhang, X., Xiong, L., & Yin, H. (2013). Cortical inhibition deficits in recent onset PTSD after a single prolonged trauma exposure. Neuroimage Clin, 3, 226–233. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2013.08.013.
Qin, L. D., Wang, Z., Sun, Y. W., Wan, J. Q., Su, S. S., Zhou, Y., & Xu, J. R. (2012). A preliminary study of alterations in default network connectivity in post-traumatic stress disorder patients following recent trauma. Brain Research, 1484, 50–56. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2012.09.029.
Rauch, S. L., Shin, L. M., Segal, E., Pitman, R. K., Carson, M. A., Mcmullin, K., Whalen, P. J., & Makris, N. (2003). Selectively reduced regional cortical volumes in post-traumatic stress disorder. Neuroreport, 14(7), 913–916. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000071767.24455.10.
Rogers, M. A., Yamasue, H., Abe, O., Yamada, H., Ohtani, T., Iwanami, A., Aoki, S., Kato, N., & Kasai, K. (2009). Smaller amygdala volume and reduced anterior cingulate gray matter density associated with history of post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Research, 174(3), 210–216. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.06.001.
Rossi, S., Cappa, S. F., Ulivelli, M., De Capua, A., Bartalini, S., & Rossini, P. M. (2006). rTMS for PTSD: Induced merciful oblivion or elimination of abnormal hypermnesia? Behavioural Neurology, 17(3–4), 195–199.
Rougemont-Bucking, A., Linnman, C., Zeffiro, T.A., Zeidan, M.A., Lebron-Milad, K., Rodriguez-Romaguera, J., Rauch, S.L., Pitman, R.K., & Milad, M.R. (2010). Altered processing of contextual information during fear extinction in PTSD: An fMRI Study. CNS Neurosci Ther. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00152.x.
Sanabria-Diaz, G., Melie-Garcia, L., Iturria-Medina, Y., Aleman-Gomez, Y., Hernandez-Gonzalez, G., Valdes-Urrutia, L., Galan, L., & Valdes-Sosa, P. (2010). Surface area and cortical thickness descriptors reveal different attributes of the structural human brain networks. NeuroImage, 50(4), 1497–1510. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.028.
Sanz-Arigita, E. J., Schoonheim, M. M., Damoiseaux, J. S., Rombouts, S. A., Maris, E., Barkhof, F., Scheltens, P., & Stam, C. J. (2010). Loss of 'small-world' networks in Alzheimer's disease: Graph analysis of FMRI resting-state functional connectivity. PloS One, 5(11), e13788. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013788.
Schuff, N., Zhang, Y., Zhan, W., Lenoci, M., Ching, C., Boreta, L., Mueller, S. G., Wang, Z., Marmar, C. R., Weiner, M. W., & Neylan, T. C. (2011). Patterns of altered cortical perfusion and diminished subcortical integrity in posttraumatic stress disorder: an MRI study. NeuroImage, 54(1), S62–S68. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.05.024.
Stam, C. J. (2004). Functional connectivity patterns of human magnetoencephalographic recordings: A 'small-world' network? Neuroscience Letters, 355(1–2), 25–28.
Stam, R. (2007). PTSD and stress sensitisation: A tale of brain and body part 2: Animal models. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 31(4), 558–584. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.01.001.
Van Den Heuvel, M. P., & Sporns, O. (2011). Rich-club organization of the human connectome. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(44), 15775–15786. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3539-11.2011.
Vincent, J. L., Patel, G. H., Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Baker, J. T., Van Essen, D. C., Zempel, J. M., Snyder, L. H., Corbetta, M., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Intrinsic functional architecture in the anaesthetized monkey brain. Nature, 447(7140), 83–86. doi:10.1038/nature05758.
Watts, D. J., & Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks. Nature, 393(6684), 440–442. doi:10.1038/30918.
Williams, L. M., Kemp, A. H., Felmingham, K., Barton, M., Olivieri, G., Peduto, A., Gordon, E., & Bryant, R. A. (2006). Trauma modulates amygdala and medial prefrontal responses to consciously attended fear. NeuroImage, 29(2), 347–357. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.03.047.
Woodward, S. H., Kaloupek, D. G., Grande, L. J., Stegman, W. K., Kutter, C. J., Leskin, L., Prestel, R., Schaer, M., Reiss, A. L., & Eliez, S. (2009a). Hippocampal volume and declarative memory function in combat-related PTSD. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 15(6), 830–839. doi:10.1017/S1355617709990476.
Woodward, S. H., Schaer, M., Kaloupek, D. G., Cediel, L., & Eliez, S. (2009b). Smaller global and regional cortical volume in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66(12), 1373–1382. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.160.
Yamasue, H., Kasai, K., Iwanami, A., Ohtani, T., Yamada, H., Abe, O., Kuroki, N., Fukuda, R., Tochigi, M., Furukawa, S., Sadamatsu, M., Sasaki, T., Aoki, S., Ohtomo, K., Asukai, N., & Kato, N. (2003). Voxel-based analysis of MRI reveals anterior cingulate gray-matter volume reduction in posttraumatic stress disorder due to terrorism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(15), 9039–9043. doi:10.1073/pnas.1530467100.
Yan, C., & He, Y. (2011). Driving and driven architectures of directed small-world human brain functional networks. PloS One, 6(8), e23460. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023460.
Zhang, J., Tan, Q., Yin, H., Zhang, X., Huan, Y., Tang, L., Wang, H., Xu, J., & Li, L. (2011a). Decreased gray matter volume in the left hippocampus and bilateral calcarine cortex in coal mine flood disaster survivors with recent onset PTSD. Psychiatry Research, 192(2), 84–90. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.09.001.
Zhang, J., Wang, J., Wu, Q., Kuang, W., Huang, X., He, Y., & Gong, Q. (2011b). Disrupted brain connectivity networks in drug-naive, first-episode major depressive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 70(4), 334–342. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.05.018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81171278) and National Key Technology R&D Program in the 11th Five-year Plan of China (2007BA117B02).
Conflict of interest
Shun Qi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yun-Feng Mu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Long-Biao Cui declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jian Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Fan Guo declares that she has no conflict of interest. Qing-Rong Tan declares that she has no conflict of interest. Mei Shi declares that she has no conflict of interest. Kang Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yi-Bin Xi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Nan-Yin Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xiao-Liang Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yong He declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jian Yang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hong Yin declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Shun Qi, Yun-Feng Mu, Long-Biao Cui and Jian Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 474 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, S., Mu, YF., Cui, LB. et al. Anomalous gray matter structural networks in recent onset post-traumatic stress disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior 12, 390–401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9693-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9693-z