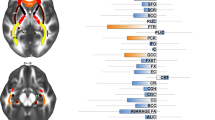
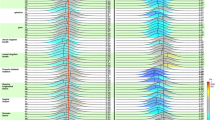
Abstract
Schizophrenia (SCZ) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) are psychiatric disorders with abnormalities in white matter structure. These disorders share high comorbidity and family history of OCD is a risk factor for SCZ which suggests some shared neurobiology. White matter was examined using diffusion tensor imaging in relativity large samples of SCZ (N = 48), OCD (N = 38) and non-psychiatric controls (N = 45). Fractional anisotropy (FA) was calculated and tract based spatial statistics were used to compare groups. In a whole brain analysis, SCZ and OCD both showed small FA reductions relative to controls in the corpus callosum. Both SCZ and OCD showed accelerated reductions in FA with age; specifically in the left superior longitudinal fasciculus in OCD, while the SCZ group demonstrated a more widespread pattern of FA reduction. Patient groups did not differ from each other in total FA or age effects in any regions. A general linear model using 13 a-priori regions of interest showed marginal group, group*gender, and group*age interactions. When OCD and SCZ groups were analyzed together, these marginal effects became significant (p < 0.05), suggesting commonalities exist between these patient groups. Overall, our results demonstrate a similar pattern of accelerated white matter decline with age and greater white matter deficit in females in OCD and SCZ, with overlap in the spatial pattern of deficits. There was no evidence for statistical differences in overall white matter between OCD and SCZ. Taken together, the results support the notion of shared neurobiology in SCZ and OCD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba-Ferrara, L. M., & de Erausquin, G. A. (2013). What does anisotropy measure? Insights from increased and decreased anisotropy in selective fiber tracts in schizophrenia. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 7, 9. doi:10.3389/fnint.2013.00009.
Alvarado-Alanis, P., Leon-Ortiz, P., Reyes-Madrigal, F., Favila, R., Rodriguez-Mayoral, O., Nicolini, H., et al. (2015). Abnormal white matter integrity in antipsychotic-naive first-episode psychosis patients assessed by a DTI principal component analysis. Schizophrenia Research, 162(1–3), 14–21. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2015.01.019.
Aoyama, F., Iida, J., Inoue, M., Iwasaka, H., Sakiyama, S., Hata, K., et al. (2000). Brain imaging in childhood- and adolescence-onset schizophrenia associated with obsessive-compulsive symptoms. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 102(1), 32–37.
Attademo, L., De Giorgio, G., Quartesan, R., & Moretti, P. (2012). Schizophrenia and obsessive-compulsive disorder: from comorbidity to schizo-obsessive disorder. Rivista di Psichiatria, 47(2), 106–115. doi:10.1708/1069.11715.
Bartzokis, G., Lu, P. H., Heydari, P., Couvrette, A., Lee, G. J., Kalashyan, G., et al. (2012). Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging assessment of white matter aging trajectories over the lifespan of healthy individuals. Biological Psychiatry, 72(12), 1026–1034. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.07.010.
Beaulieu, C. (2002). The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(7–8), 435–455. doi:10.1002/nbm.782.
Benedetti, F., Giacosa, C., Radaelli, D., Poletti, S., Pozzi, E., Dallaspezia, S., et al. (2013). Widespread changes of white matter microstructure in obsessive-compulsive disorder: effect of drug status. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 23(7), 581–593. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.07.002.
Billiet, T., Vandenbulcke, M., Madler, B., Peeters, R., Dhollander, T., Zhang, H., et al. (2015). Agerelated microstructural differences quantified using myelin water imaging and advanced diffusion MRI. Neurobiol Aging, 36(6), 2107–2121. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.029.
Bleich-Cohen, M., Jamshy, S., Sharon, H., Weizman, R., Intrator, N., Poyurovsky, M., et al. (2014a). Machine learning fMRI classifier delineates subgroups of schizophrenia patients. Schizophrenia Research, 160(1–3), 196–200. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2014.10.033.
Bleich-Cohen, M., Poyurovsky, M., Hendler, T., Weizman, R., & Sharon, H. (2014b). Does co-morbid obsessive-compulsive disorder modify the abnormal language processing in schizophrenia patients? An FMRI study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 560. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00560.
Bogetto, F., Venturello, S., Albert, U., Maina, G., & Ravizza, L. (1999). Gender-related clinical differences in obsessive-compulsive disorder. European Psychiatry, 14(8), 434–441.
Bottas, A., Cooke, R. G., & Richter, M. A. (2005). Comorbidity and pathophysiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in schizophrenia: is there evidence for a schizo-obsessive subtype of schizophrenia? Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 30(3), 187–193.
Brickman, A. M., Meier, I. B., Korgaonkar, M. S., Provenzano, F. A., Grieve, S. M., Siedlecki, K. L., et al. (2012). Testing the white matter retrogenesis hypothesis of cognitive aging. Neurobiol Aging, 33(8), 1699–1715. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.06.001.
Castle, D. J., Deale, A., & Marks, I. M. (1995). Gender differences in obsessive compulsive disorder. The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 29(1), 114–117.
Catani, M., Craig, M. C., Forkel, S. J., Kanaan, R., Picchioni, M., Toulopoulou, T., et al. (2011). Altered integrity of perisylvian language pathways in schizophrenia: relationship to auditory hallucinations. Biological Psychiatry, 70(12), 1143–1150. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.06.013.
Crow, T. J., Paez, P., & Chance, S. A. (2007). Callosal misconnectivity and the sex difference in psychosis. International Review of Psychiatry, 19(4), 449–457. doi:10.1080/09540260701486282.
de Haan, L., Sterk, B., Wouters, L., & Linszen, D. H. (2013). The 5-year course of obsessive-compulsive symptoms and obsessive-compulsive disorder in first-episode schizophrenia and related disorders. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 39(1), 151–160. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbr077.
Devi, S., Rao, N. P., Badamath, S., Chandrashekhar, C. R., & Janardhan Reddy, Y. C. (2015). Prevalence and clinical correlates of obsessive-compulsive disorder in schizophrenia. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 56, 141–148. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.09.015.
Ehrlich, S., Geisler, D., Yendiki, A., Panneck, P., Roessner, V., Calhoun, V. D., et al. (2014). Associations of white matter integrity and cortical thickness in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 40(3), 665–674. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbt056.
Fan, Q., Yan, X., Wang, J., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Li, C., et al. (2012). Abnormalities of white matter microstructure in unmedicated obsessive-compulsive disorder and changes after medication. PloS One, 7(4), e35889. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035889.
Filippi, M., Canu, E., Gasparotti, R., Agosta, F., Valsecchi, P., Lodoli, G., et al. (2014). Patterns of brain structural changes in first-contact, antipsychotic drug-naive patients with schizophrenia. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 35(1), 30–37. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3583.
Frias, A., Palma, C., Farriols, N., Becerra, C., Alvarez, A., & Canete, J. (2014a). Neuropsychological profile and treatment-related features among patients with comorbidity between schizophrenia spectrum disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder: is there evidence for a "schizo-obsessive" subtype? Psychiatry Research, 220(3), 846–854. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2014.10.003.
Frias, A., Palma, C., Farriols, N., Salvador, A., Bonet, J., & Bernaldez, I. (2014b). Psychopathology and quality of life among patients with comorbidity between schizophrenia spectrum disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder: no evidence for a "schizo-obsessive" subtype. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55(5), 1165–1173. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.03.016.
Friedman, J. I., Tang, C., Carpenter, D., Buchsbaum, M., Schmeidler, J., Flanagan, L., et al. (2008). Diffusion tensor imaging findings in first-episode and chronic schizophrenia patients. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 165(8), 1024–1032. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.07101640.
Goodman, W. K., Price, L. H., Rasmussen, S. A., Mazure, C., Fleischmann, R. L., Hill, C. L., et al. (1989). The Yale-Brown obsessive compulsive scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Archives of General Psychiatry, 46(11), 1006–1011.
Guo, W., Liu, F., Liu, Z., Gao, K., Xiao, C., Chen, H., et al. (2012). Right lateralized white matter abnormalities in first-episode, drug-naive paranoid schizophrenia. Neuroscience Letters, 531(1), 5–9. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.09.033.
Ha, T. H., Yoon, U., Lee, K. J., Shin, Y. W., Lee, J. M., Kim, I. Y., et al. (2005). Fractal dimension of cerebral cortical surface in schizophrenia and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuroscience Letters, 384(1–2), 172–176. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.04.078.
Highley, J. R., Esiri, M. M., McDonald, B., Cortina-Borja, M., Herron, B. M., & Crow, T. J. (1999). The size and fibre composition of the corpus callosum with respect to gender and schizophrenia: a post-mortem study. Brain, 122(Pt 1), 99–110.
Hoeft, F., Barnea-Goraly, N., Haas, B. W., Golarai, G., Ng, D., Mills, D., et al. (2007). More is not always better: increased fractional anisotropy of superior longitudinal fasciculus associated with poor visuospatial abilities in Williams syndrome. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(44), 11960–11965. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3591-07.2007.
Hoptman, M. J., Nierenberg, J., Bertisch, H. C., Catalano, D., Ardekani, B. A., Branch, C. A., et al. (2008). A DTI study of white matter microstructure in individuals at high genetic risk for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 106(2–3), 115–124. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2008.07.023.
Huster, R. J., Westerhausen, R., Kreuder, F., Schweiger, E., & Wittling, W. (2009). Hemispheric and gender related differences in the midcingulum bundle: a DTI study. Human Brain Mapping, 30(2), 383–391. doi:10.1002/hbm.20509.
Inano, S., Takao, H., Hayashi, N., Abe, O., & Ohtomo, K. (2011). Effects of age and gender on white matter integrity. AJNR American Journal of Neuroradiology, 32(11), 2103–2109. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2785.
Jayarajan, R. N., Venkatasubramanian, G., Viswanath, B., Janardhan Reddy, Y. C., Srinath, S., Vasudev, M. K., et al. (2012). White matter abnormalities in children and adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Depression and Anxiety, 29(9), 780–788. doi:10.1002/da.21890.
Jones, D. K. (2004). The effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 51(4), 807–815. doi:10.1002/mrm.20033.
Jones, D. K., & Leemans, A. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging. Methods in Molecular Biology, 711, 127–144. doi:10.1007/978-1-61737-992-5_6.
Jones, D. K., Knosche, T. R., & Turner, R. (2013). White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: the do's and don'ts of diffusion MRI. NeuroImage, 73, 239–254. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.081.
Kim, J. J., Youn, T., Lee, J. M., Kim, I. Y., Kim, S. I., & Kwon, J. S. (2003). Morphometric abnormality of the insula in schizophrenia: a comparison with obsessive-compulsive disorder and normal control using MRI. Schizophrenia Research, 60(2–3), 191–198.
King, J. B., Yurgelun-Todd, D., Stoeckel, A., DiMuzio, J. M., & Lopez-Larson, M. P. (2015). Sex differences in white matter integrity in youths with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a pilot study. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 9, 232. doi:10.3389/fnins.2015.00232.
Kirkpatrick, B., Messias, E., Harvey, P. D., Fernandez-Egea, E., & Bowie, C. R. (2008). Is schizophrenia a syndrome of accelerated aging? Schizophrenia Bulletin, 34(6), 1024–1032. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbm140.
Koch, K., Wagner, G., Dahnke, R., Schachtzabel, C., Schultz, C., Roebel, M., et al. (2010). Disrupted white matter integrity of corticopontine-cerebellar circuitry in schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 260(5), 419–426. doi:10.1007/s00406-009-0087-0.
Koch, K., Reess, T. J., Rus, O. G., Zimmer, C., & Zaudig, M. (2014). Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): a review. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 54, 26–35. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.03.006.
Kochunov, P., Jahanshad, N., Marcus, D., Winkler, A., Sprooten, E., Nichols, T. E., et al. (2015). Heritability of fractional anisotropy in human white matter: a comparison of human connectome project and ENIGMA-DTI data. NeuroImage, 111, 300–311. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.050.
Kopelowicz, A., Ventura, J., Liberman, R. P., & Mintz, J. (2008). Consistency of brief psychiatric rating scale factor structure across a broad spectrum of schizophrenia patients. Psychopathology, 41(2), 77–84. doi:10.1159/000111551.
Lebel, C., & Beaulieu, C. (2011). Longitudinal development of human brain wiring continues from childhood into adulthood. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(30), 10937–10947. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5302-10.2011.
Lebel, C., Walker, L., Leemans, A., Phillips, L., & Beaulieu, C. (2008). Microstructural maturation of the human brain from childhood to adulthood. NeuroImage, 40(3), 1044–1055. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.12.053.
Lebel, C., Gee, M., Camicioli, R., Wieler, M., Martin, W., & Beaulieu, C. (2012). Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter tract evolution over the lifespan. NeuroImage, 60(1), 340–352. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.094.
Li, F., Huang, X., Yang, Y., Li, B., Wu, Q., Zhang, T., et al. (2011). Microstructural brain abnormalities in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: diffusion-tensor MR imaging study at 3.0 T. Radiology, 260(1), 216–223. doi:10.1148/radiol.11101971.
Li, F., Huang, X., Tang, W., Yang, Y., Li, B., Kemp, G. J., et al. (2014). Multivariate pattern analysis of DTI reveals differential white matter in individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Human Brain Mapping, 35(6), 2643–2651. doi:10.1002/hbm.22357.
Malla, A. K., Bodnar, M., Joober, R., & Lepage, M. (2011). Duration of untreated psychosis is associated with orbital-frontal grey matter volume reductions in first episode psychosis. Schizophrenia Research, 125(1), 13–20. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2010.09.021.
Mathis, M. A., Alvarenga, P., Funaro, G., Torresan, R. C., Moraes, I., Torres, A. R., et al. (2011). Gender differences in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a literature review. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria, 33(4), 390–399.
Meier, S. M., Petersen, L., Pedersen, M. G., Arendt, M. C., Nielsen, P. R., Mattheisen, M., et al. (2014). Obsessive-compulsive disorder as a risk factor for schizophrenia: a nationwide study. JAMA Psychiatry, 71(11), 1215–1221. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1011.
Melicher, T., Horacek, J., Hlinka, J., Spaniel, F., Tintera, J., Ibrahim, I., et al. (2015). White matter changes in first episode psychosis and their relation to the size of sample studied: a DTI study. Schizophrenia Research, 162(1–3), 22–28. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2015.01.029.
Menzler, K., Belke, M., Wehrmann, E., Krakow, K., Lengler, U., Jansen, A., et al. (2011). Men and women are different: diffusion tensor imaging reveals sexual dimorphism in the microstructure of the thalamus, corpus callosum and cingulum. NeuroImage, 54(4), 2557–2562. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.029.
Mitelman, S. A., Torosjan, Y., Newmark, R. E., Schneiderman, J. S., Chu, K. W., Brickman, A. M., et al. (2007). Internal capsule, corpus callosum and long associative fibers in good and poor outcome schizophrenia: a diffusion tensor imaging survey. Schizophrenia Research, 92(1–3), 211–224. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2006.12.029.
Mori, T., Ohnishi, T., Hashimoto, R., Nemoto, K., Moriguchi, Y., Noguchi, H., et al. (2007). Progressive changes of white matter integrity in schizophrenia revealed by diffusion tensor imaging. Psychiatry Research, 154(2), 133–145. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2006.09.004.
Nakamae, T., Narumoto, J., Sakai, Y., Nishida, S., Yamada, K., Nishimura, T., et al. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging and tract-based spatial statistics in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 45(5), 687–690. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.09.016.
Nazeri, A., Chakravarty, M. M., Rajji, T. K., Felsky, D., Rotenberg, D. J., Mason, M., et al. (2015). Superficial white matter as a novel substrate of age-related cognitive decline. Neurobiol Aging, 36(6), 2094–2106. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.022.
Oh, J. S., Song, I. C., Lee, J. S., Kang, H., Park, K. S., Kang, E., et al. (2007). Tractography-guided statistics (TGIS) in diffusion tensor imaging for the detection of gender difference of fiber integrity in the midsagittal and parasagittal corpora callosa. NeuroImage, 36(3), 606–616. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.03.020.
Overall, J. E., & Gorham, D. R. (1980). The brief psychiatric rating scale. Journal Operational Psychiatry, 11, 46–64.
Penrose, L. S. (1991). Survey of cases of familial mental illness. L. S. Penrose, July 1945. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 240(6), 315–324 discussion 314-315.
Perez-Iglesias, R., Tordesillas-Gutierrez, D., McGuire, P. K., Barker, G. J., Roiz-Santianez, R., Mata, I., et al. (2010). White matter integrity and cognitive impairment in first-episode psychosis. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 167(4), 451–458. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09050716.
Peters, B. D., Blaas, J., & de Haan, L. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging in the early phase of schizophrenia: what have we learned? Journal of Psychiatric Research, 44(15), 993–1004. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.05.003.
Poletti, S., Mazza, E., Bollettini, I., Locatelli, C., Cavallaro, R., Smeraldi, E., et al. (2015). Adverse childhood experiences influence white matter microstructure in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 234(1), 35–43. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.08.003.
Poyurovsky, M., Kriss, V., Weisman, G., Faragian, S., Schneidman, M., Fuchs, C., et al. (2005). Familial aggregation of schizophrenia-spectrum disorders and obsessive-compulsive associated disorders in schizophrenia probands with and without OCD. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 133B(1), 31–36. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30148.
Prasad, K. M., Upton, C. H., Schirda, C. S., Nimgaonkar, V. L., & Keshavan, M. S. (2015). White matter diffusivity and microarchitecture among schizophrenia subjects and first-degree relatives. Schizophrenia Research, 161(1), 70–75. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2014.09.045.
Price, G., Bagary, M. S., Cercignani, M., Altmann, D. R., & Ron, M. A. (2005). The corpus callosum in first episode schizophrenia: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 76(4), 585–587. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.042952.
Price, G., Cercignani, M., Parker, G. J., Altmann, D. R., Barnes, T. R., Barker, G. J., et al. (2007). Abnormal brain connectivity in first-episode psychosis: a diffusion MRI tractography study of the corpus callosum. NeuroImage, 35(2), 458–466. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.12.019.
Prokscha, T., Guo, J., Hirsch, S., Braun, J., Sack, I., Meyer, T., et al. (2014). Diffusion tensor imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis--increased sensitivity with optimized region-of-interest delineation. Clinical Neuroradiology, 24(1), 37–42. doi:10.1007/s00062-013-0221-2.
Radhu, N., Garcia Dominguez, L., Farzan, F., Richter, M. A., Semeralul, M. O., Chen, R., et al. (2015). Evidence for inhibitory deficits in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Brain, 138(Pt 2), 483–497. doi:10.1093/brain/awu360.
Reis Marques, T., Taylor, H., Chaddock, C., Dell'acqua, F., Handley, R., Reinders, A. A., et al. (2014). White matter integrity as a predictor of response to treatment in first episode psychosis. Brain, 137(Pt 1), 172–182. doi:10.1093/brain/awt310.
Riffkin, J., Yucel, M., Maruff, P., Wood, S. J., Soulsby, B., Olver, J., et al. (2005). A manual and automated MRI study of anterior cingulate and orbito-frontal cortices, and caudate nucleus in obsessive-compulsive disorder: comparison with healthy controls and patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 138(2), 99–113. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2004.11.007.
Rojkova, K., Volle, E., Urbanski, M., Humbert, F., Dell'Acqua, F., & Thiebaut de Schotten, M. (2016). Atlasing the frontal lobe connections and their variability due to age and education: a spherical deconvolution tractography study. Brain Structure & Function, 221(3), 1751–1766. doi:10.1007/s00429-015-1001-3.
Salat, D. H., Tuch, D. S., Greve, D. N., van der Kouwe, A. J., Hevelone, N. D., Zaleta, A. K., et al. (2005). Age-related alterations in white matter microstructure measured by diffusion tensor imaging. Neurobiol Aging, 26(8), 1215–1227. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.09.017.
Savadjiev, P., Whitford, T. J., Hough, M. E., Clemm von Hohenberg, C., Bouix, S., Westin, C. F., et al. (2014). Sexually dimorphic white matter geometry abnormalities in adolescent onset schizophrenia. Cerebral Cortex, 24(5), 1389–1396. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs422.
Smith, S. M., & Nichols, T. E. (2009). Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage, 44(1), 83–98. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.061.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23(Suppl 1), S208–S219. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E., et al. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage, 31(4), 1487–1505. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024.
Swets, M., Dekker, J., van Emmerik-van Oortmerssen, K., Smid, G. E., Smit, F., de Haan, L., et al. (2014). The obsessive compulsive spectrum in schizophrenia, a meta-analysis and meta-regression exploring prevalence rates. Schizophrenia Research, 152(2–3), 458–468. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.10.033.
Szeszko, P. R., Vogel, J., Ashtari, M., Malhotra, A. K., Bates, J., Kane, J. M., et al. (2003). Sex differences in frontal lobe white matter microstructure: a DTI study. Neuroreport, 14(18), 2469–2473. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000099475.09597.23.
Szeszko, P. R., Ardekani, B. A., Ashtari, M., Kumra, S., Robinson, D. G., Sevy, S., et al. (2005). White matter abnormalities in first-episode schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(3), 602–605. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.3.602.
Szeszko, P. R., Robinson, D. G., Ashtari, M., Vogel, J., Betensky, J., Sevy, S., et al. (2008). Clinical and neuropsychological correlates of white matter abnormalities in recent onset schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology, 33(5), 976–984. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301480.
Vasavada, M. M., Leaver, A. M., Espinoza, R. T., Joshi, S. H., Njau, S. N., Woods, R. P., et al. (2016). Structural connectivity and response to ketamine therapy in major depression: a preliminary study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 190, 836–841. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2015.11.018.
Ventura, J., Nuechterlein, K. H., Subotnik, K. L., Gutkind, D., & Gilbert, E. A. (2000). Symptom dimensions in recent-onset schizophrenia and mania: a principal components analysis of the 24-item brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychiatry Research, 97(2–3), 129–135.
Voineskos, A. N., Lobaugh, N. J., Bouix, S., Rajji, T. K., Miranda, D., Kennedy, J. L., et al. (2010). Diffusion tensor tractography findings in schizophrenia across the adult lifespan. Brain, 133(Pt 5), 1494–1504. doi:10.1093/brain/awq040.
Voineskos, A. N., Felsky, D., Kovacevic, N., Tiwari, A. K., Zai, C., Chakravarty, M. M., et al. (2013a). Oligodendrocyte genes, white matter tract integrity, and cognition in schizophrenia. Cerebral Cortex, 23(9), 2044–2057. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs188.
Voineskos, A. N., Foussias, G., Lerch, J., Felsky, D., Remington, G., Rajji, T. K., et al. (2013b). Neuroimaging evidence for the deficit subtype of schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry, 70(5), 472–480. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.786.
Wang, Q., Cheung, C., Deng, W., Li, M., Huang, C., Ma, X., et al. (2013). White-matter microstructure in previously drug-naive patients with schizophrenia after 6 weeks of treatment. Psychological Medicine, 43(11), 2301–2309. doi:10.1017/S0033291713000238.
Wen, H., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Rekik, I., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2016). Combining tract- and atlas-based analysis reveals microstructural abnormalities in early Tourette syndrome children. Human Brain Mapping, 37(5), 1903–1919. doi:10.1002/hbm.23146.
Witthaus, H., Brune, M., Kaufmann, C., Bohner, G., Ozgurdal, S., Gudlowski, Y., et al. (2008). White matter abnormalities in subjects at ultra high-risk for schizophrenia and first-episode schizophrenic patients. Schizophrenia Research, 102(1–3), 141–149. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2008.03.022.
Wright, S. N., Kochunov, P., Chiappelli, J., McMahon, R. P., Muellerklein, F., Wijtenburg, S. A., et al. (2014). Accelerated white matter aging in schizophrenia: role of white matter blood perfusion. Neurobiology of Aging, 35(10), 2411–2418. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.02.016.
Yoo, S. Y., Jang, J. H., Shin, Y. W., Kim, D. J., Park, H. J., Moon, W. J., et al. (2007). White matter abnormalities in drug-naive patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a diffusion tensor study before and after citalopram treatment. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 116(3), 211–219. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2007.01046.x.
Zarei, M., Mataix-Cols, D., Heyman, I., Hough, M., Doherty, J., Burge, L., et al. (2011). Changes in gray matter volume and white matter microstructure in adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 70(11), 1083–1090. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.06.032.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported primarily by donations from the Grant Family and Temerty Family through the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) Foundation and the Campbell Institute. CH was supported by a Banting Post-Doctoral Fellowship from CIHR, and NR was supported by a doctoral award from OMHF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health and the University of Toronto, as well as the Canadian Institute of health Research and in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflicts of interest
Z.J.D. received research and equipment inkind support for an investigator-initiated study through Brainsway Inc. and a travel allowance through Merck. Z.J.D. has also received speaker funding through Sepracor Inc., AstraZeneca and served on the advisory board for Hoffmann-La Roche Limited and Merck and received speaker support from Eli Lilly.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hawco, C., Voineskos, A.N., Radhu, N. et al. Age and gender interactions in white matter of schizophrenia and obsessive compulsive disorder compared to non-psychiatric controls: commonalities across disorders. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1836–1848 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9657-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9657-8