Abstract
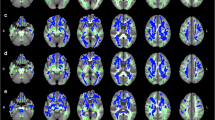
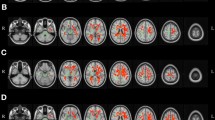
Aging is associated with microstructural changes in brain tissue that can be visualized using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). While previous studies have established age-related changes in white matter (WM) diffusion using DTI, the impact of age on gray matter (GM) diffusion remains unclear. The present study utilized DTI metrics of mean diffusivity (MD) to identify age differences in GM/WM microstructure in a sample of healthy older adults (N = 60). A secondary aim was to determine the functional significance of whole-brain GM/WM MD on global cognitive function using the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS). Participants were divided into three age brackets (ages 50–59, 60–69, and 70+) to examine differences in MD and cognition by decade. MD was examined bilaterally in the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes for the primary analyses and an aggregate measure of whole-brain MD was used to test relationships with cognition. Significantly higher MD was observed in bilateral GM of the temporal and parietal lobes, and in right hemisphere WM of the frontal and temporal lobes of older individuals. The most robust differences in MD were between the 50–59 and 70+ age groups. Higher whole-brain GM MD was associated with poorer RBANS performance in the 60–69 age group. Results suggest that aging has a significant and differential impact on GM/WM diffusion in healthy older adults, which may explain a modest degree of cognitive variability at specific time points during older adulthood.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M., & Field, A. S. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics, 4(3), 316–329.
Barnes, J., Foster, J., & Fox, N. C. (2007). Structural magnetic resonance imaging-derived biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomarkers in Medicine, 1, 79–92.
Baron, J. C., Chetelat, G., Desgranges, B., Perchey, G., Landeau, B., de la Sayette, V., & Eustache, F. (2001). In vivo mapping of gray matter loss with voxel-based morphometry in mild Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 14(2), 298–309.
Bartrés-Faz, D., & Arenaza-Urquijo, E. M. (2011). Structural and functional imaging correlates of cognitive and brain reserve hypotheses in healthy and pathological aging. Brain Topography, 24(3-4), 340–357.
Bartzokis, G., Tishler, T. A., Lu, P. H., Villablanca, P., Altshuler, L. L., Carter, M., & Mintz, J. (2007). Brain ferritin iron may influence age-and gender-related risks of neurodegeneration. Neurobiology of Aging, 28(3), 414–423.
Basser, P. J., & Pierpaoli, C. (1996). Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Series B, 111(3), 209–219.
Bhagat, Y. A., & Beaulieu, C. (2004). Diffusion anisotropy in subcortical white matter and cortical gray matter: changes with aging and the role of CSF-suppression. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 20(2), 216–227. doi:10.1002/jmri.20102.
Bilgic, B., Pfefferbaum, A., Rohlfing, T., Sullivan, E. V., & Adalsteinsson, E. (2012). MRI estimates of brain iron concentration in normal aging using quantitative susceptibility mapping. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2625–2635.
Bosch, B., Bartrés-Faz, D., Arenaza-Urquijo, E. M., Rami, L., Sala-Llonch, R., Junqué, C., & Solé-Padullés, C. (2012). Multiple DTI index analysis in normal aging, amnestic MCI and AD. Relationship with neuropsychological performance. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(1), 61–74.
Chetelat, G., Desgranges, B., de la Sayette, V., Viader, F., Eustache, F., & Baron, J. C. (2003). Mild cognitive impairment Can FDG-PET predict who is to rapidly convert to Alzheimer’s disease? Neurology, 60(8), 1374–1377.
Conturo, T. E., McKinstry, R. C., Akbudak, E., & Robinson, B. H. (1996). Encoding of anisotropic diffusion with tetrahedral gradients: a general mathematical diffusion formalism and experimental results. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 35(3), 399–412.
de Jong, G. I., Vos, R. D., Steur, E. J., & Luiten, P. G. M. (1997). Cerebrovascular hypoperfusion: a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 826(1), 56–74.
de Jong, G. I., Farkas, E., Stienstra, C. M., Plass, J. R. M., Keijser, J. C., de la Torre, J. C., & Luiten, P. G. M. (1999). Cerebral hypoperfusion yields capillary damage in the hippocampal CA1 area that correlates with spatial memory impairment. Neuroscience, 91(1), 203–210.
de la Torre, J. C. (2000). Critically attained threshold of cerebral hypoperfusion: the CATCH hypothesis of Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. Neurobiology of Aging, 21(2), 331–342.
de Toledo Ferraz Alves, T. C., Scazufca, M., Squarzoni, P., de Souza Duran, F. L., Tamashiro-Duran, J. H., Vallada, H. P., & Busatto, G. F. (2011). Subtle gray matter changes in temporo-parietal cortex associated with cardiovascular risk factors. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 27(3), 575–589.
Dolcos, F., Rice, H. J., & Cabeza, R. (2002). Hemispheric asymmetry and aging: right hemisphere decline or asymmetry reduction. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 26(7), 819–825.
Duff, K., Patton, D. E., Schoenberg, M. R., Mold, J., Scott, J. G., & Adams, R. A. (2003). Age- and education-corrected independent normative data for the RBANS in a community dwelling elderly sample. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 17, 351–366.
Dukart, J., Mueller, K., Villringer, A., Kherif, F., Draganski, B., Frackowiak, R., & Schroeder, M. L. (2013). Relationship between imaging biomarkers, age, progression and symptom severity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage Clin, 3, 84–94.
Eriksson, S. H., Rugg-Gunn, F. J., Symms, M. R., Barker, G. J., & Duncan, J. S. (2001). Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with epilepsy and malformations of cortical development. Brain, 124, 617–626.
Freeman, S. H., Kandel, R., Cruz, L., Rozkalne, A., Newell, K., Frosch, M. P., & Hedley-Whyte, E. T. (2008). Preservation of neuronal number despite age-related cortical brain atrophy in elderly subjects without Alzheimer disease. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology, 67(12), 1205–1212.
Ge, Y., Grossman, R. I., Babb, J. S., Rabin, M. L., Mannon, L. J., & Kolson, D. L. (2002). Age-related total gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: volumetric MR imaging analysis. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23(8), 1327–1333.
Gontkovsky, S. T., Beatty, W. W., & Mold, J. W. (2004). Repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status in a normal, geriatric sample. Clinical Gerontologist, 27(3), 79–86. doi:10.1300/J018v27n03_07.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Fristen, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2001). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage, 14, 21–26.
Hajnal, J. V., Bryant, D. J., Kasuboski, L., Pattany, P. M., de Coene, B., Lewis, P. D., & Bydder, G. M. (1992). Use of fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) pulse sequences in MRI of the brain. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 16(6), 841–844.
Jacobs, H. I., van Boxtel, M. P., Gronenschild, E. H., Uylings, H. B., Jolles, J., & Verhey, F. R. (2013). Decreased gray matter diffusivity: a potential early Alzheimer’s disease biomarker? Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 9(1), 93–97.
Jahng, G., Xu, S., Weiner, M. W., Meyerhoff, D. J., Park, S., & Schuff, N. (2011). DTI studies in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, or normal cognition with evaluation of the intrinsic background gradients. Neuroradiology, 53(10), 749–762. doi:10.1007/s00234-011-0845-3.
Jenkinson, M., & Smith, S. (2001). A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Medical Image Analysis, 5(2), 143–156.
Jespersen, S. N., Kroenke, C. D., Østergaard, L., Ackerman, J. J., & Yablonskiy, D. A. (2007). Modeling dendrite density from magnetic resonance diffusion measurements. NeuroImage, 34(4), 1473–1486.
Kim, H. J., Kim, S. J., Kim, H. S., Choi, C. G., Kim, N., Han, S., & Lee, C. S. (2013). Alterations of mean diffusivity in brain white matter and deep gray matter in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience Letters, 550, 64–68.
Koo, B. B., Hua, N., Choi, C. H., Ronen, I., Lee, J. M., & Kim, D. (2009). A framework to analyze partial volume effect on gray matter mean diffusivity measurements. NeuroImage, 44(1), 136–144.
Lawton, M. P., & Brody, E. (1969). Assessment of older people: Self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontology, 9, 179–186.
Li, Z., Moore, A. B., Tyner, C., & Hu, X. (2009). Asymmetric connectivity reduction and its relationship to “HAROLD” in aging brain. Brain Research, 1295, 149–158.
Ma, X., Kadah, Y. M., LaConte, S. M., & Hu, X. (2004). Enhancing measured diffusion anisotropy in gray matter by eliminating CSF contamination with FLAIR. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 51(2), 423–427.
Madden, D. J., Bennett, I. J., & Song, A. W. (2009). Cerebral white matter integrity and cognitive aging: contributions from diffusion tensor imaging. Neuropsychology Review, 19(4), 415–435. doi:10.1007/s11065-009-9113-2.
McNab, J. A., Polimeni, J. R., Wang, R., Augustinack, J. C., Fujimoto, K., Player, A., & Wald, L. L. (2013). Surface based analysis of diffusion orientation for identifying architectonic domains in the in vivo human cortex. NeuroImage, 69, 87–100.
Mielke, M. M., Kozauer, N. A., Chan, K. C. G., George, M., Toroney, J., Zerrate, M., & Albert, M. (2009). Regionally-specific diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 46(1), 47–55.
Molko, N., Pappata, S., Mangin, J. F., Poupon, C., Vahedi, K., Jobert, A., & Chabriat, H. (2001). Diffusion tensor imaging study of subcortical gray matter in CADASIL. Stroke, 32(9), 2049–2054.
Mortamet, B., Zeng, D., Gerig, G., Prastawa, M., & Bullitt, E. (2005). Effects of healthy aging measured by intracranial compartment volumes using a designed MR brain database. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2005 (pp. 383–391). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Mugler, J. P., & Brookeman, J. R. (1990). Three-dimensional magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo imaging (3D MP RAGE). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 15(1), 152–157.
Mugler, J. P., & Brookeman, J. R. (1991). Rapid three‐dimensional T1‐weighted MR imaging with the MP-RAGE sequence. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 1(5), 561–567.
Naganawa, S., Sato, K., Katagiri, T., Mimura, T., & Ishigaki, T. (2003). Regional ADC values of the normal brain: differences due to age, gender, and laterality. European Radiology, 13(1), 6–11.
Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., Bédirian, V., Charbonneau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., & Chertkow, H. (2005). The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 53(4), 695–699.
Ni, J. M., Chen, S., Liu, J. J., Huang, G., Shen, T. Z., & Chen, X. R. (2010). Regional diffusion changes of cerebral grey matter during normal aging—A fluid-inversion prepared diffusion imaging study. European Journal of Radiology, 75(2), 134–138.
Pal, D., Trivedi, R., Saksena, S., Yadav, A., Kumar, M., Pandey, C. M., & Gupta, R. K. (2011). Quantification of age- and gender-related changes in diffusion tensor imaging indices in deep grey matter of the normal human brain. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 18(2), 193–196. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2010.05.033.
Paul, R. H., Haque, O., Gunstad, J., Tate, D. F., Grieve, S. M., Hoth, K., & Gordon, E. (2005). Subcortical hyperintensities impact cognitive function among a select subset of healthy elderly. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 20(6), 697–704.
Paul, R., Lane, E. M., Tate, D. F., Heaps, J., Romo, D. M., Akbudak, E., & Conturo, T. E. (2011). Neuroimaging signatures and cognitive correlates of the Montreal cognitive assessment screen in a nonclinical elderly sample. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 26(5), 454–460.
Pfefferbaum, A., Adalsteinsson, E., Rohlfing, T., & Sullivan, E. V. (2009). MRI estimates of brain iron concentration in normal aging: comparison of field-dependent (FDRI) and phase (SWI) methods. NeuroImage, 47(2), 493–500.
Pfefferbaum, A., Adalsteinsson, E., Rohlfing, T., & Sullivan, E. V. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging of deep gray matter brain structures: effects of age and iron concentration. Neurobiology of Aging, 31(3), 482–493.
Plumet, J., Gil, R., & Gaonac’h, D. (2005). Neuropsychological assessment of executive functions in women: effects of age and education. Neuropsychology, 19(5), 566–577.
Randolph, C. C., Tireney, M. C., Mohr, E. E., & Chase, T. N. (1998). The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS): preliminary clinical validity. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 20(3), 310–320. doi:10.1076/jcen.20.3.310.823.
Rathi, Y., Pasternak, O., Savadjiev, P., Michailovich, O., Bouix, S., Kubicki, M., & Shenton, M. E. (2013). Gray matter alterations in early aging: a diffusion magnetic resonance imaging study. Human Brain Mapping, 35(8), 3841–3856. doi:10.1002/hbm.22441.
Ray, K. M., Wang, H., Chu, Y., Chen, Y. F., Bert, A., Hasso, A. N., & Su, M. Y. (2006). Mild cognitive impairment: apparent diffusion coefficient in regional gray matter and white matter structures 1. Radiology, 241(1), 197–205.
Resnick, S. M., Pham, D. L., Kraut, M. A., Zonderman, A. B., & Davatzikos, C. (2003). Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging studies of older adults: a shrinking brain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 3295–3301.
Rossini, P. M., Rossi, S., Babiloni, C., & Polich, J. (2007). Clinical neurophysiology of aging brain: from normal aging to neurodegeneration. Progress in Neurobiology, 83(6), 375–400.
Salminen, L. E., Schofield, P. R., Pierce, K. D., Conturo, T. E., Tate, D. F., Lane, E. M., & Paul, R. H. (2014). Impact of the AGTR1 A1166C polymorphism on subcortical hyperintensities and cognition in healthy older adults. Age, 36(4), 1–8. doi:10.1007/s11357-014-9664-x.
Sexton, C. E., Kalu, U. G., Filippini, N., Mackay, C. E., & Ebmeier, K. P. (2011). A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 32(12), 2322.e5–2322.e18. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.019.
Shaw, T. G., Mortel, K. F., Meyer, J. S., Rogers, R. L., Hardenberg, J., & Cutaia, M. M. (1984). Cerebral blood flow changes in benign aging and cerebrovascular disease. Neurology, 34(7), 855.
Sullivan, E. V., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2006). Diffusion tensor imaging and aging. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 30(6), 749–761.
Sundgren, P. C., Dong, Q., Gomez-Hassan, D., Mukherji, S. K., Maly, P., & Welsh, R. (2004). Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain: review of clinical applications. Neuroradiology, 46(5), 339–350.
Tamnes, C. K., Walhovd, K. B., Dale, A. M., Østby, Y., Grydeland, H., Richardson, G., & Fjell, A. M. (2013). Brain development and aging: overlapping and unique patterns of change. NeuroImage, 68, 63–74.
Trenkle, D. L., Shankle, W. R., & Azen, S. P. (2007). Detecting cognitive impairment in primary care: performance assessment of three screening instruments. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 11(3), 323–335.
Wald, L. L. (2012). The future of acquisition speed, coverage, sensitivity, and resolution. NeuroImage, 62(2), 1221–1229.
Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Haldar, J. P., Yeh, F. C., Xie, M., Sun, P., & Song, S. K. (2011). Quantification of increased cellularity during inflammatory demyelination. Brain, 134(12), 3590–3601.
Westlye, L. T., Walhovd, K. B., Dale, A. M., Bjørnerud, A., Due-Tønnessen, P., Engvig, A., & Fjell, A. M. (2010). Life-span changes of the human brain white matter: diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and volumetry. Cerebral Cortex, 20(9), 2055–2068.
Yoshiura, T., Noguchi, T., Hiwatashi, A., Togao, O., Yamashita, K., Nagao, E., & Honda, H. (2010). Intra- and interhemispheric variations of diffusivity in subcortical white matter in normal human brain. European Radiology, 20(1), 227–233. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1534-z.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke [grant numbers R01NS052470, R01NS039538]; the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Mental Health [grant number R21MH090494]; and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council [grant number 1037196]. Recruitment database searches were supported in part by the National Institutes of Health/National Center for Research Resources [grant number UL1 TR000448].
Conflict of interest
L. Salminen, T. Conturo, D. Laidlaw, R. Cabeen, E. Akbudak, E. Lane, J. Heaps, J. Bolzenius, L. Baker, S. Cooley, S. Scott, L. Cagle, S. Phillips, and R. Paul declare no conflicts of interest.
Informed Consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salminen, L.E., Conturo, T.E., Laidlaw, D.H. et al. Regional age differences in gray matter diffusivity among healthy older adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 203–211 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9383-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9383-7