Abstract
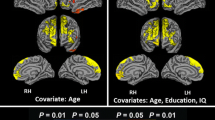
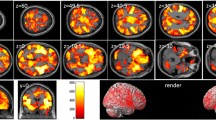
Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) was used to examine the relationship between gray matter (GM) volume and performance on two commonly used clinical neuropsychological measures of frontal lobe or executive function, the Trail Making Test part B (TrailsB) and the Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT) in 221 cognitively healthy adults between the ages of 18 and 84. We hypothesized that these measures would be associated with GM volume in the dorsolateral frontal lobes. Voxel-based multiple regression was used to correlate cognitive function with modulated GM probability maps while controlling for age, education, gender, and total intracranial volume. A relationship with TrailsB was found in bilateral lateral inferior frontal gyri and left basal ganglia. A relationship with COWAT was found in the left lateral inferior and middle frontal gyri. Lesion studies have long implicated the importance of these regions for executive function. The present results confirm and extend those prior findings to healthy adults.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C. V., Bigler, E. D., & Blatter, D. D. (1995). Frontal lobe lesions, diffuse damage, and neuropsychological functioning in traumatic brain-injured patients. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 17, 900–908.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2000). Voxel-based morphometry—The methods. Neuroimage, 11(6 Pt 1), 805–821.
Baker, S. C., Rogers, R. D., Owen, A. M., Frith, C. D., Dolan, R. J., Frackowiak, R. S., et al. (1996). Neural systems engaged by planning: A PET study of the tower of London task. Neuropsychologia, 34(6), 515–526.
Benton, L. A., Hamsher, K., & Sivan, A. B. (1994). Controlled oral word association test. Multilingual aphasia examination (3rd ed.). Iowa City: AJA.
Blatter, D. D., Bigler, E. D., Gale, S. D., Johnson, S. C., Anderson, C., Burnett, B. M., et al. (1995). Quantitative volumetric analysis of brain MR: Normative database spanning 5 decades of life. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 16, 241–251.
Buckner, R. L. (2004). Memory and executive function in aging and AD: Multiple factors that cause decline and reserve factors that compensate. Neuron, 44(1), 195–208.
Coffey, C. E., Ratcliff, G., Saxton, J. A., Bryan, R. N., Fried, L. P., & Lucke, J. F. (2001). Cognitive correlates of human brain aging: A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging investigation. Journal Neuropsychiatry Clinical Neuroscience, 13(4), 471–485.
Costafreda, S. G., Fu, C. H., Lee, L., Everitt, B., Brammer, M. J., & David, A. S. (2006). A systematic review and quantitative appraisal of fMRI studies of verbal fluency: Role of the left inferior frontal gyrus. Human Brain Mapping, 27(10), 799–810.
Dagher, A., Owen, A. M., Boecker, H., & Brooks, D. J. (1999). Mapping the network for planning: A correlational PET activation study with the tower of London task. Brain, 122(Pt 10), 1973–1987.
Dickerson, B. C., Salat, D. H., Greve, D. N., Chua, E. F., Rand-Giovannetti, E., Rentz, D. M., et al. (2005). Increased hippocampal activation in mild cognitive impairment compared to normal aging and AD. Neurology, 65(3), 404–411.
Friston, K. J., Frith, C. D., Liddle, P. F., & Frackowiak, R. S. (1991). Investigating a network model of word generation with positron emission tomography. Proceedings of the Biological Society, 244(1310), 101–106.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Friston, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2001). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage, 14(1 Pt 1), 21–36.
Lemaitre, H., Crivello, F., Grassiot, B., Alperovitch, A., Tzourio, C., & Mazoyer, B. (2005). Age- and sex-related effects on the neuroanatomy of healthy elderly. Neuroimage, 26(3), 900–911.
Lezak, M. D. (1995). Neuropsychological assessment (3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Maldjian, J. A., Laurienti, P. J., Kraft, R. A., & Burdette, J. H. (2003). An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. Neuroimage, 19(3), 1233–1239.
Moll, J., de Oliveira-Souza, R., Moll, F. T., Bramati, I. E., & Andreiuolo, P. A. (2002). The cerebral correlates of set-shifting: An fMRI study of the trail making test. Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria, 60(4), 900–905.
Monchi, O., Petrides, M., Mejia-Constain, B., & Strafella, A. P. (2007). Cortical activity in Parkinson’s disease during executive processing depends on striatal involvement. Brain, 130(Pt 1), 233–244.
Monchi, O., Petrides, M., Petre, V., Worsley, K., & Dagher, A. (2001). Wisconsin card sorting revisited: Distinct neural circuits participating in different stages of the task identified by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Neuroscience, 21(19), 7733–7741.
Moritz, C. H., Johnson, S. C., McMillan, K. M., Haughton, V. M., & Meyerand, M. E. (2004). Functional MRI neuroanatomic correlates of the hooper visual organization test. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 10(7), 939–947.
Murphy, D. G., DeCarli, C., Schapiro, M. B., Rapoport, S. I., & Horwitz, B. (1992). Age-related differences in volumes of subcortical nuclei, brain matter, and cerebrospinal fluid in healthy men as measured with magnetic resonance imaging. Archives of Neurology, 49(8), 839–845.
Owen, A. M., Doyon, J., Petrides, M., & Evans, A. C. (1996). Planning and spatial working memory: A positron emission tomography study in humans. European Journal of Neuroscience, 8(2), 353–364.
Pardo, J. V., Fox, P. T., & Raichle, M. E. (1991). Localization of a human system for sustained attention by positron emission tomography. Nature, 349(6304), 61–64.
Pfefferbaum, A., Sullivan, E. V., Jernigan, T. L., Zipursky, R. B., Rosenbloom, M. J., Yesavage, J. A., et al. (1990). A quantitative analysis of CT and cognitive measures in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatry Research, 35(2), 115–136.
Raz, N., Gunning, F. M., Head, D., Dupuis, J. H., McQuain, J., Briggs, S. D., et al. (1997). Selective aging of the human cerebral cortex observed in vivo: Differential vulnerability of the prefrontal gray matter. Cerebral Cortex, 7(3), 268–282.
Reitan, R. (1971). Trail making test results for normal and brain-damaged children. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 33(2), 575–581.
Reitan, R., & Wolfson, D. (1993). The Halstead–Reitan neuropsychological test battery: Theory and clinical interpretation (2nd ed.). Tucson: Neuropsychology Press.
Reitan, R., & Wolfson, D. (1995). Category test and trail making test as measures of frontal lobe functions. Clinical Neuropsychologist, 9, 50–56.
Rosen, W. G., Terry, R. D., Fuld, P. A., Katzman, R., & Peck, A. (1980). Pathological verification of ischemic score in differentiation of dementias. Annals of Neurology, 7(5), 486–488.
Roth, R., Randolph, J., Koven, N., & Isquith, P. (2006). Neural substrates of executive functions: Insights from functional neuroimaging. In J. Dupri (Ed.), Focus on neuropsychological research. New York: Nova.
Royall, D. R., Lauterbach, E. C., Cummings, J. L., Reeve, A., Rummans, T. A., Kaufer, D. I., et al. (2002). Executive control function: A review of its promise and challenges for clinical research. A report from the Committee on Research of the American Neuropsychiatric Association. Journal Neuropsychiatry Clinical Neuroscience, 14(4), 377–405.
Salat, D. H., Kaye, J. A., & Janowsky, J. S. (1999). Prefrontal gray and white matter volumes in healthy aging and Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology, 56(3), 338–344.
Salthouse, T. A. (1996). The processing-speed theory of adult age differences in cognition. Psychological Review, 103(3), 403–428.
Sandstrom, C. K., Krishnan, S., Slavin, M. J., Tran, T. T., Doraiswamy, P. M., & Petrella, J. R. (2006). Hippocampal atrophy confounds template-based functional MR imaging measures of hippocampal activation in patients with mild cognitive impairment. AJNR American Journal of Neuroradiology, 27(8), 1622–1627.
Schlosser, R., Hutchinson, M., Joseffer, S., Rusinek, H., Saarimaki, A., Stevenson, J., et al. (1998). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity in a verbal fluency task. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 64(4), 492–498.
Shafritz, K. M., Kartheiser, P., & Belger, A. (2005). Dissociation of neural systems mediating shifts in behavioral response and cognitive set. Neuroimage, 25(2), 600–606.
Smith, S. M., Zhang, Y., Jenkinson, M., Chen, J., Matthews, P. M., Federico, A., et al. (2002). Accurate, robust, and automated longitudinal and cross-sectional brain change analysis. Neuroimage, 17(1), 479–489.
Spreen, O., & Strauss, E. (1998). A compendium of neuropsychological tests (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Stuss, D. T., Alexander, M. P., Hamer, L., Palumbo, C., Dempster, R., Binns, M., et al. (1998). The effects of focal anterior and posterior brain lesions on verbal fluency. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 4(3), 265–278.
Stuss, D. T., Bisschop, S. M., Alexander, M. P., Levine, B., Katz, D., & Izukawa, D. (2001). The trail making test: A study in focal lesion patients. Psychological Assessment, 13(2), 230–239.
Tekin, S., & Cummings, J. L. (2002). Frontal-subcortical neuronal circuits and clinical neuropsychiatry: An update. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 53(2), 647–654.
Thompson, P. M., Hayashi, K. M., de Zubicaray, G., Janke, A. L., Rose, S. E., Semple, J., et al. (2003). Dynamics of gray matter loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 23(3), 994–1005.
Zakzanis, K. K., Mraz, R., & Graham, S. J. (2005). An fMRI study of the trail making test. Neuropsychologia, 43(13), 1878–1886.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by NIH grants AG021155, MH65723 and a Merit Review grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs. The assistance of Shelly Fitzgerald, Britta Jabbar, Taylor Schmitz, Allie Wichmann, Michael Ward, Gemma Gliori, and Howard Rowley is greatly appreciated. We especially thank the participants of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newman, L.M., Trivedi, M.A., Bendlin, B.B. et al. The Relationship Between Gray Matter Morphometry and Neuropsychological Performance in a Large Sample of Cognitively Healthy Adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior 1, 3–10 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-007-9000-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-007-9000-5