Abstract
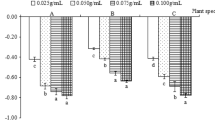
An experiment was conducted to observe the inhibitory effects of the leaf extracts derived from Albizia lebbeck (L.) Benth. on germination and growth behavior of some popular agricultural crops (receptor) of Bangladesh. Experiments were set on sterilized petridishes with a photoperiod of 24 h at room temperature of 27–30°C. The effects of the different concentrations of aqueous extracts were compared to distil water (control.). The aqueous extracts of leaf caused significant inhibitory effect on germination, root and shoot elongation and development of lateral roots of receptor plants. Bioassays indicated that the inhibitory effect was proportional to the concentrations of the extracts and higher concentration (50%–100%) had the stronger inhibitory effect whereas the lower concentration (10%–25%) showed stimulatory effect in some cases. The study also revealed that, inhibitory effect was much pronounced in root and lateral root development rather than germination and shoot growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benthal, A.P. 1933. The trees of Calcutta and its neighborhood. London: Thacker-Spink and Co. Ltd.. pp140–225.
Chaturvedi, O.P., and Jha, A.N. 1992. Studies on allelopathic potential of an important agroforestry species. Forest Ecology and Management, 53: 91–98.
Chou, C.H. 1992. Allelopathy in relation to agricultural productivity in Taiwan: Problems and Prospects. In: Rizvi, S.J.H. and Rizvi, V. (eds.), Allelopathy: Basic and Applied Aspects. London: Chapman and Hall, pp179–204.
Chou, C.H. and Kuo, Y.L. 1984. Allelopathic exclusion of understory by Leucaena leucocephala (Lam) de Wit. J. Chem. Ecol., 12: 1431–1448.
Chou, C.H., and Waller, G.R. 1980. Possible allelopathic constituents of Coffea Arabica. J. Chem. Ecol., 6: 643–654.
Daniel, W.G. 1999. Historical review and current models of forest succession and interference. Florida: CRC Press, pp237–251.
Das, D.K. and Alam, M.K. 2001. Trees of Bangladesh. Bangladesh: Bangladesh Forest Research Institute (BFRI), Chittagong, pp25–26.
Einhellig, F.A. and Rusmussen, J.A. 1978. Synergistic inhibitory effects of vanilic and p-hydroxybenzoic acids on radish and grain sorghum. J. Chem. Ecol., 4: 425–436.
Gaba, R.K. 1987. Role of allelopathy in social forestry. In: Khosla, P.K. and Kohli, R.K.(eds.), Social forestry for rural development. Solan,: ISTS, pp 228–234.
Jadhav, B.B. and Gaynar, D.G. 1992. Allelopathic effects of Acacia auriculiformis on germination of rice and cowpea. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 35: 86–89.
Joshi, P.C. and Prakash, O. 1992. Allelopathic effects of litter extract of some tree species on germination and seedling growth of agricultural crops. In: Tauro, P., Narwal, S.S. (eds.), Proceedings of the First National Symposium on Allelopathy in Agroecosystem, Hisar, India: Indian Society of Alleolopathy, pp127–128.
Khan, M.S. and Alam, M.K. 1996. Homestead Flora of Bangladesh. Bangladesh: BARC, IDRC, SDC, Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp 37–38.
King, K.F.S. 1979. Agroforestry and the utilization of fragile ecosystems. Forest Ecology Management, 2: 161–168.
Koul, V.K., Raina, A., Khanna, Y.P. Tickoo, M.L. and Singh, H. 1991. Evaluation of allelopathic influence of certain farm grown tree species on rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. PC-19). Indian Journal of Forestry, 14: 54–57.
NAS. 1979. Tropical legumes: Resources for the future. Washington D.C: National Academy of Science, Washington D.C., 331p.
Prinsen, J.H. 1986. Potential of Albizia Lebbeck (Mimosaceae) as a tropical fodder tree — a review of literature. Trop. Grasslands, 20(2): 78–83.
Prinsen, J.H. 1988. Albizia Lebbeck — A promising fodder tree for semi-arid regions. Nirtogen fixation tree highlights series 11. Hawai: Nitrogen Fixation Tree Association (NFTA), pp 88–93.
Rho, B.J. and Kil, B.S. 1986. Influence of phytotoxin from Pinus rigida on the selected plants. Journal of Natural Science, 5: 19–27.
Rice, E.L. 1984. Allelopathy (second edition). Orlando, Florida: Academic Press, 422p.
Rizvi, S.J. Sinha, H.R.C. and Rizvi, V. 1990. Implication of mimosine allelopathy in agroforestry In Proc. 19 th World Congress on Forestry, 2: 22–27.
Singh, R.P., and Nadal, D.P.S. 1993. Allelopathic effects of aqueous leaf extract of important agroforestry tree species on some fodder crops. Forage Research, 19: 59–61.
Streets, R.J. 1962. Exotic Forest Trees in the British Commonwealth. Oxford: Clarendon Press, pp169–170.
Surendra, M.P. and Pota, K.B. 1978. The allelopathic potentials of root exudates from different ages of Celosia argenta Linn. Nat. Acad. Sci. Lett., 1(2): 56–58.
Swaminathan, C., Rai, R.S.V., and Suresh, K.K. 1989. Allelopathic potentialities of Acacia nilotica (L.) wills ex Del. Journal of Tropical Forest Science, 2: 56–60.
Swami-Rao, N. and Reddy, P.C. 1984. Studies on the inhibitory effect of Eucalyptus (hybrid) leaf extracts on the germination of certain food crops. Indian Forester, 110 (2): 218–222.
Uddin, M.B., Ahmed, R. and Hossain, M.K. 2000. Allelopathic potential of water extracts of Leocaena leococephala leaf on some agricultural crops in Bangladesh. The Chittagong University Journal of Science, 24(1): 121–127.
Waller, G.R. (ed.). 1987. Allelochemicals: Role in Agriculture and Forestry. Washington, D.C.: American Chemical Society, ACS Symposium Series-330, 606p.
Williamson, G.B. 1990. Allelopathy, Koch’s postulates and the neck riddle. In: Grace, J.B. and Tilman, D. (eds.), Perspective on plant competition. New York: Academic Press, New York, pp143–162.
Zackrisson, O. and Nilsson, M.C. 1992. Allelopathic effects by Empetrum hermaphroditum on seed germination of two boreal tree species. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 22: 44–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic supplementary material is available in the online version of this article at http://dxdoi.org/10.1007/s11676-007-0025-9
Biography: Mohammad Belal Uddin (1976–), male, Assistant Professor in Department of Forestry, School of Agriculture and Mineral Sciences, Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, Sylhet 3114, Bangladesh.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uddin, M.B., Ahmed, R., Mukul, S.A. et al. Inhibitory effects of Albizia lebbeck leaf extracts on germination and growth behavior of some popular agricultural crops. J. of For. Res. 18, 128–132 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-007-0025-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-007-0025-9