Abstract
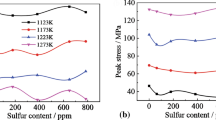
The hot tensile test was applied to study the influence of sulfur content on the high-temperature mechanical properties of C71500 Cu-Ni alloy. The hot processing map of C71500 alloy was established according to the test results. It is found that the increase of sulfur content has no visible effect on the tensile strength of C71500 alloy at high temperature, but has a great effect on the elongation and reduction area of fracture. Through optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy analysis of fracture samples, it can be qualitatively determined that the composition of sulfur inclusions is (Mn,Fe,Ni)S, which is plastically deformable in the process of hot deformation. However, due to the difference of plasticity between the inclusions and the matrix, stress concentration is easy to occur, thus reducing the overall plasticity of C71500 alloy. Based on the proposed dynamic material model theory, the processing maps with different sulfur contents were established, which could show the destruction effect of sulfur on the high-temperature plastic deformation of C71500 alloy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Ladan and S. John, Effect of Elemental Sulfur and Sulfide on the Corrosion Behavior of Cr-Mo Low Alloy Steel for Tubing and Tubular Components in Oil and Gas Industry, Materials, 2017, 10(4), p 430
F. Qayyum, S. Guk, R. Kawalla, and U. Prahl, Experimental Investigations and Multiscale Modeling to Study the Effect of Sulfur Content on Formability of 16MnCr5 Alloy Steel, Steel Res. Int., 2018, 90, p 1800369
Z. Feng, G. Ming, T. Ganfeng, L. Kui, and P. Kewu, Effect of Sulfur on Hot Ductility of Ni-Cr-W-Al Superalloy, Hot Work. Technol., 2013, 042(006), p 10–12
H. Sawada, First-Principles Study of Grain Boundary Embrittlement in Fe-Ni-S Alloy, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2012, 55, p 17–22
X.B. Li, Y.Q. Xie, and Y.X. Zhu, An Ultra-sulfur Hastelloy Alloy C-4, Mater. Corros., 2005, 56(9), p 636–638
H. Song, S. Guo, and Z. Hu, Effect of Sulfur on Creep Behavior of IN718 Alloy, J. Aeronaut. Mater., 1999, 19(1), p 15–16
H. Song, S. Guo, D. Lu, and Z. Hu, Influences of Sulfur Doping on Superalloy IN718, Acta Metall. Sin., 1999, 3, p 281–284
D.J. Xin, X.B. Liu, T. Bin, Y.H. Hu, X.Z. Chao, and X.X. Shan, Effect of Sulfur on Microstructure and Properties of Inconel 718 Superalloy, Acta Metall. Sin., 1996, 3, p 241–244
B. Lv, F.C. Zhang, M. Li, R.J. Hou, L.H. Qian, and T.S. Wang, Effects of Phosphorus and Sulfur on the Thermoplasticity of High Manganese Austenitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2010, 527(21–22), p 5648–5653
J.H. Hong, S.W. Nam, and S.P. Choi, The Influences of Sulphur and Phosphorus Additions on the Creep Cavitation Characteristics in Type 304 Stainless Steels, J. Mater. Sci., 1986, 21(11), p 3966–3976
M. Liu and J. Li, In-Situ Raman Characterization of Initial Corrosion Behavior of Copper in Neutral 3.5% (wt.) NaCl Solution, Materials, 2019, 12(13), p 2164
X. Gao, H.B. Wu, M. Liu, Y.X. Zhang, and X.D. Zhou, Dynamic Recovery and Recrystallization Behaviors of C71500 Copper-Nickel Alloy under Hot Deformation, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29, p 7678–7692
X. Gao, H.B. Wu, M. Liu, and X.D. Zhou, Effect of Annealing Time on Grain Boundary Characteristics of C71500 Cupronickel Alloy Tubes with Different Deformation, Mater. Charact., 2020, 169, p 110603
H.L. Gegel, J.C. Malas, J.S. Gunasekera, J.T. Morgan, S.M. Doraivelu, M. Whitaker, and H.L. Henrich, Computer-Aided Design of Extrusion Dies by Metal-Flow Simulation, Agard Process Modeling Appl. to Metal Forming & Thermomech process, Vol 1, 1984
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, H.L. Gegel, S.M. Doraivelu, J.C. Malas, J.T. Morgan, K.A. Lark, and D.R. Barker, Modeling of Dynamic Material Behavior in Hot Deformation: Forging of Ti-6242, Metall. Trans. A, 1984, 15(10), p 1883–1892
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Author’s Reply: Dynamic Materials Model: Basis and Principles, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, 27(1), p 235–236
Z. Yi, C. Zhe, A.A. Volinsky, B. Tian, H. Sun, L. Ping, and L. Yong, Processing Maps for the Cu-Cr-Zr-Y Alloy Hot Deformation Behavior, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, 662, p 320–329
Y. Zhang, H.L. Sun, A.A. Volinsky, B.H. Tian, Z. Chai, P. Liu, and Y. Liu, Characterization of the Hot Deformation Behavior of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy by Processing Maps, Acta Metall. Sin., 2016, 29(5), p 1–9
J. Gao, M.-Q. Li, S.-F. Liu, and G.-J. Liu, Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps during Isothermal Compression of TC21 Alloy, Rare Met., 2017, 36(2), p 1–9
Z. Zhou, Q. Fan, Z. Xia, A. Hao, W. Yang, J. Wei, and H. Cao, Constitutive Relationship and Hot Processing Maps of Mg-Gd-Y-Nb-Zr Alloy, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33(7), p 637–644
Q. Liang, Q. Hao, H. Zhao, and Y. Zhang, Constitutive Equation and Processing Map of CuNi10Fe1Mn Alloy Based on High-Temperature Deformation Behavior, Mater. Res. Express, 2018, 5(5), p 1–10
J. Deng, Y.C. Lin, S.-S. Li, J. Chen, and Y. Ding, Hot Tensile Deformation and Fracture Behaviors of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Des., 2013, 49, p 209–219
Y.C. Lin, J. Deng, Y.-Q. Jiang, D.-X. Wen, and G. Liu, Effects of Initial δ Phase on Hot Tensile Deformation Behaviors and Fracture Characteristics of a Typical Ni-Based Superalloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 55, p 949–957
M. Zhou, Y.C. Lin, J. Deng, and Y.-Q. Jiang, Hot Tensile Deformation Behaviors and Constitutive Model of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 59, p 141–150
B. Chen, W.M. Zhou, S. Li, X.L. Li, and C. Lu, Hot Compression Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(9), p 2458–2466
W. Prager, On Ideal Locking Materials, Trans. Soc. Rheol. (1957-1977), 1957, 1(1), p 169–175
Z. Wen, X. Gao, J. Cheng, Z. Hu, L. Li, B. Zhao, and P. Zhang, Processing Map and Hot Deformation Behavior of Mo-Nb Single Crystals, Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2018, 47(2), p 485–490
T. Zhong, P.K. Rao, V.R.K.Y. Prasad, and M. Gupta, Processing Maps, Microstructure Evolution and Deformation Mechanisms of Extruded AZ31-DMD during Hot Uniaxial Compression, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, 559, p 773–781
K.P. Rao, T. Zhong, Y.V.R.K. Prasad, K. Suresh, and M. Gupta, Hot Working Mechanisms in DMD-Processed Versus Cast AZ31-1 wt% CA Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2015, 644(8), p 184–193
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China (TC170A2KN-8), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51801149), the Industrialization Project of Scientific and Technological Achievements in Wuxi City (CYE22C1706), and the Wuxi Enterprise Academician Workstation (CYR1701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Wu, H., Liu, M. et al. Analysis of the Influence of Sulfur on the Hot Tensile Fracture of C71500 Cu-Ni Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 312–319 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05381-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05381-w