Abstract
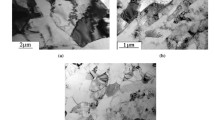
Grain structure and mechanical properties of steel A570 GR36 alloy subjected to four passes via combined “pressing–drawing” process at room temperature were investigated. In the “pressing–drawing” process, the structure of the wire is significantly reduced to ultrafine-grained state; so in the steel of grade A570 GR36, the average grain size of 12 microns after deformation was reduced up to 20 times (0.6 microns). The values of tensile strength and yield strength increased after four passes from 380 to 740 MPa and from 220 to 680 MPa, respectively. The contraction changed from 63 to 55%, but the change was not as significant as under the classic drawing. The four-pass combined “pressing–drawing” process is an effective way to form UFG structure and improved mechanical properties in steel A570 GR36 alloy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.V. Chukin, M.A.Poljakova, and D.G. Emaleeva, Деформационное наноструктурирование проволок (Strain nanostructuring wire) (Magnitogorsk, 2012), p. 57
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov, Bulk Nanostructured Materials from Severe Plastic Deformation, Prog. Mater Sci., 2000, 45, p 103–189
X. Zhao, N. Chen, and N. Zhao, Numerical Simulation of Equal Channel Angular Pressing for Multi-Pass in Different Routes, Appl. Mech. Mater., 2012, 268–270, p 373–377
I.E. Volokitina and G.G. Kurapov, Effect of Initial Structural State on Formation of Structure and Mechanical Properties of Steels Under ECAP, Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2018, 59, p 786–792
D. Orlov, G. Raab, T.T. Lamark, M. Popov, and Y. Estrin, Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Alloy ZK60 by Integrated Extrusion and Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 375–385
A.B. Naizabekov, S.N. Lezhnev, and I.E. Volokitina, Change in Copper Microstructure and Mechanical Properties with Deformation in an Equal Channel Stepped Die, Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2015, 57(5–6), p 254–260
S. Wang, W. Liang, Yu Wang, L. Bian, and K. Chen, A Modified Die for Equal Channel Angular Pressing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209, p 3182–3186
M. Jahedi, M. Knezevic, and M.H. Paydar, High-Pressure Doublem Torsion as Severe Plastic Deformation Process: Experimental Procedure and Finite Element Modeling, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(4), p 1471–1482
M. Kawasakia, Z. Horitab, and T.G. Langdona, Microstructural Evolution in High Purity Aluminum Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 524(1–2), p 143–150
M. Vaseghi, H.S. Kim, A.K. Taheri, and A. Momeni, Inhomogeneity Through Warm Equal Channel Angular Pressing, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(6), p 1666–1671
V.M. Segal, A.E. Reznikov, A.E. Drobyshevskiy, and V.I. Kopylov, Plastic Working of Metals by Simple Shear, Russ. Metall., 1981, 1, p 971–974
V.M. Segal, Engineering and Commercialization of Equal Channel Angular Extrusion (ECAE), Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, 386, p 269–276
S. Lezhnev, A. Naizabekov, and I. Volokitina, Features of Change of the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Steel at ECAP Depending on the Initial State, J. Chem. Technol. Metall., 2017, 52(4), p 626–635
G. Raab, R. Valiev, T. Lowe, and Y. Zhu, Continuous Processing of Ultrafine Grained A1 by ECAP-Conform, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2004, 382, p 30–34
G.I. Raab, E.I. Fakhretdinova, R.Z. Valiev, L.P. Trifonenkov, and V.F. Frolov, Computer Study of the Effect of Tooling Geometry on Deformation Parameters in the Plastic Shaping of Aluminum Wire Rod by Multi-ECAP-Conform, Metallurgist, 2016, 59(11–12), p 1007–1014
M.V. Chukin, M.A. Poljakova, E.M. Golubchik, V.P Rudako, S.E. Noskov, and A.E. Gulin, Method of Making Ultrafine Semis by Drawing with Twisting. Patent of RF, No. 2467816 (2012)
G.I. Raab and A.G.Raab, Device for Drawing and Production of Ultrafine-Grained Semi-Finished Products. Patent of RF No. 2347632 (2007)
Y.G. Jin, I.H. Son, S.H. Kang, and Y.T. Im, Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Multi-pass Equal-Channel Angular Extrusion of Aluminum AA1050 with Split Dies, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2009, 503, p 152–155
S. Lezhnev, A.B. Naizabekov, E. Panin, I. Volokitina, and T. Koinov, The Effect of Preliminary and Final Heat Treatment in Course of the Combined “Rolling-Pressing” Process Realization on Microstructure Evolution of Copper, J. Chem. Technol. Metall., 2016, 51, p 315–321
K. Muszka, M. Wielgus, K. Doniec, and M. Stefanska-Kadziela, Influence of Strain Changes on Microstructure Inhomogeneity and Mechanical Behavior of Wire Drawing Products, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, 654, p 314–317
M.V. Chukin, D.G. Emaleeva, M.P. Baryshnikov, and M.A. Poljakova, Method of Producing Long Round Billets with Ultrafine Granular Structure. Patent of RF No. 2446027 (2012)
I. Volokitina and A. Volokitin, Evolution of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Copper During the Pressing–Drawing Process, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2018, 119, p 917–921
S. Lezhnev, A. Naizabekov, A. Volokitin, and I. Volokitina, New Combined Process Pressing–Drawing and Impact on Properties of Deformable Aluminum Wire, Proc. Eng., 2014, 81, p 1505–1510
P. Basavaraj, U. Chakkingal, and T.S. Prasanna Kumar, Study of Channel Angle Influence on Material Flow and Strain Inhomogeneity in Equal Channel Angular Pressing Using 3D Finite Element Simulation, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209, p 89–95
User’s Manual, DEFORM™ Integrated 2D-3D Version 10.2.1. (Columbus, Ohio, 2012)
P.M. Dixit and U.S. Dixit, Modeling of Metal Forming and Machining Processes by Finite Element and Soft Computing Methods, Springer, London, 2008
H. Yada, N. Matsuzu, K. Nakajima, K. Watanabe, and H. Tokita, Strength and Structural-Changes Under High Strain-Rate Hot Deformation of C-Steels, Trans. ISIJ, 1983, 23, p 100–109
S. Kobayashi, S. Oh, and T. Altan, Metal Forming and the Finite-Element Method, Oxford University Press, New York, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naizabekov, A., Volokitina, I., Volokitin, A. et al. Structure and Mechanical Properties of Steel in the Process “Pressing–Drawing”. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 1762–1771 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-3880-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-3880-6