Abstract
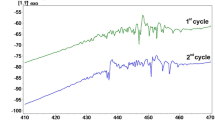
In situ optical microscope examinations were carried out on the thermally induced thermoelastic martensitic transformation in an untrained CuAlNi alloy and on the bainitic reaction in a CuAlNiMnFe alloy. It was found that a different martensite variant structure formed after every thermal cycle and the transformation was not accompanied with observable plastic deformation in the CuAlNi alloy. Elastic deformations were observed as the martensite plates reached grain boundaries. The growth of new martensite plates was initiated at these locations. The result are discussed and compared to results of other alloys found in the literature. The bainitic reaction was found to occur under isothermal conditions in the CuAlNiMnFe alloys. The reaction was accompanied with a relief formation much finer than that of the thermoelastic martensitic transformation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Funakabo, Shape Memory Alloys, Gordon and Breach, Amsterdam, 1987
K. Otsuka and C.M. Waymann, Shape Memory Materials, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998
K. Otsuka and X. Ren, Recent Developments in the Research of Shape Memory Alloys, Intermetallics, 1999, 7, p 511–528
V. Brailovski, S. Prokoshkin, P. Terriault and F. Trochou, Shape Memory Alloys: Fundamentals, Modeling and Applications, École de technologie supérieure, 2003
L.C. Brinson, I. Schmidt, and R. Lammering, Stress-Induced Transformation Behavior of a Polycrystalline NiTi Shape Memory Alloy: Micro and Macromechanical Investigations Via In Situ Optical Microscopy, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2004, 52, p 1549–1571
X. Jiang, M. Hida, Y. Takemoto, A. Sakakibara, H. Yasuda, and H. Mori, In Situ Observation of Stress-Induced Martensitic Transformation and Plastic Deformation in TiNi Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1997, A238, p 303–308
H.C. Tong and C.M. Wayman, Characteristic Temperatures and Other Properties of Thermoelastic Martensites, Acta Metall., 1974, 22, p 687–696
K. Takezawa and S. Sato, Composition Dependence of Bainite Morphology in Cu-Zn-Al Alloys, Mater. Trans. JIM, 1992, 33, p 102–109
W. Zou, H.Y. Peng, R. Wang, J. Gui, and D.Z. Yang, Heating Effects on Fine Structure of a Cu-Al-Ni-Mn-Ti Shape Memory Alloy, Acta. Mater., 1995, 43, p 3009–3016
W. Zou, J. Gui, R. Wang, C. Tang, M. Xiang, and D. Zhang, Bainitic Precipitation and its Effect on the Martensitic Transformation in the Cu-Al-Ni-Mn-Ti Shape Memory alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 1997, 32, p 5279–5286
M. Benke, V. Mertinger, and P. Pekker, Investigation of the Bainitic Reaction in a CuAlNiMnFe Shape Memory Alloy, J. Min. Metall. Sect. B, 2013, 49(1), p 43–47
V. Novak, P. Sittner, S. Ignacova, and T. Cernoch, Transformation Behavior of Prism Shaped Shape Memory Alloy Single Crystals, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 438-440, p 755–762
V. Novak and P. Sittner, Intergranular and Interphase Boundaries in Materials, Mater. Sci. Forum, 1999, 294-2, p 497–500
M. Benke, V. Mertinger, and F. Tranta, In Situ Optical Microscope Examinations of the ε ↔ γ Transformations in FeMn(Cr) Austenitic Steels During Thermal Cycling, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2013, 738-739, p 257–261
E. Hornbogen, V. Mertinger, and J. Spielfeld, Ausaging and Ausaging of a Copper Based Shape Memory Alloy with High Transformation Temperatures, Z. Metallkd., 1999, 90, p 318–322
Acknowledgments
The research work was based on the results achieved within the TÁMOP-4.2.1.B-10/2/KONV-2010-0001 project and carried out as part of the OTKA K 84065 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the International Conference on Shape Memory and Superelastic Technologies 2013, held May 20-24, 2013, in Prague, Czech Republic, and has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benke, M., Mertinger, V. In Situ Optical Microscope Study of the Thermally Induced Displacive Transformations in Cualni-Based Shape-Memory Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 2333–2338 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1078-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1078-5